C++实现二叉树的基本操作:建立、遍历、计算深度、节点数、叶子数等
题意:
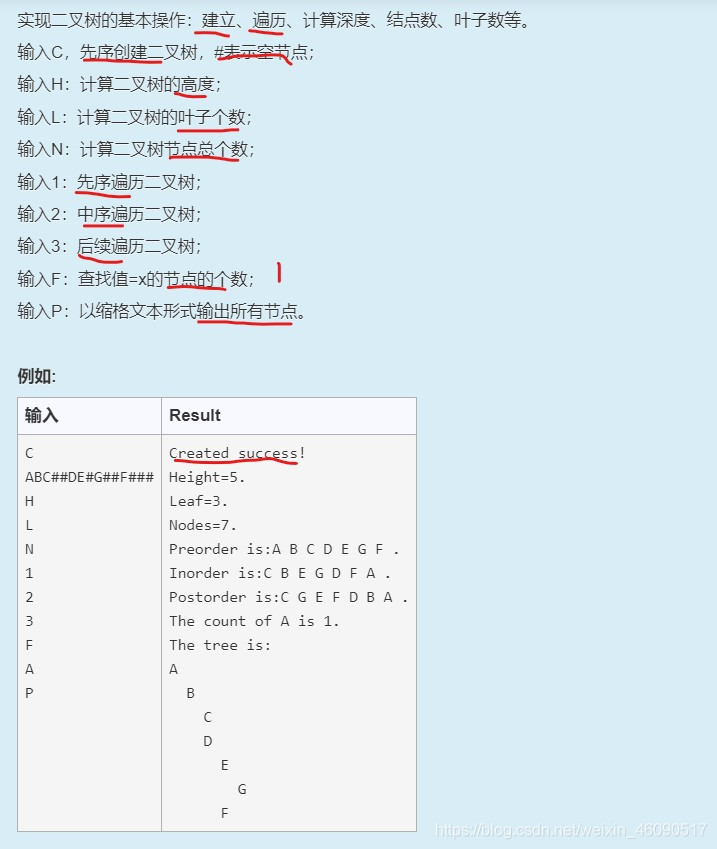
代码实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
//二叉树节点
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
char data;
BinaryTreeNode* leftChild;
BinaryTreeNode* rightChild;
};
//堆栈节点,用于深度遍历
struct stackNode
{
BinaryTreeNode* ptr;
char tag;//tag=0标志进入左子树,tag=1标志进入右子树
};
class BinaryTree //二叉树的类
{
public:
//根据完全前序遍历创建二叉树
void createBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
root=new BinaryTreeNode();
char newData;
cin>>newData;
if(newData=='#')
{
root=NULL;
}
else
{
root->data=newData;
createBinaryTree(root->leftChild);
createBinaryTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
//递归实现前序遍历
void preTraversal(BinaryTreeNode* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
cout<<root->data<<" ";
preTraversal(root->leftChild);
preTraversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
//递归实现后续遍历
void lastTraversal(BinaryTreeNode* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
lastTraversal(root->leftChild);
lastTraversal(root->rightChild);
cout<<root->data<<" ";
}
}
//非递归实现中序遍历
void mid(BinaryTreeNode* root)
{
stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S;
BinaryTreeNode* p=root;
do
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
S.push(p);
p=p->leftChild;
}
if(!S.empty())
{
p=S.top();
cout<<p->data<<" ";
S.pop();
p=p->rightChild;
}
}
while(p!=NULL||!S.empty());
}
//计算节点总数
int nodeCount(BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return nodeCount(root->leftChild)+nodeCount(root->rightChild)+1;
}
}
//计算二叉树的高度
int treeHight(BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
int LH=treeHight(root->leftChild);
int RH=treeHight(root->rightChild);
return LH > RH ? LH+1 : RH+1;
}
}
//计算二叉树的叶子个数
int getLeavesCount(BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else if (root->leftChild == NULL && root->rightChild == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
int leftLeavesCount = getLeavesCount(root->leftChild);
int rightLeavesCount = getLeavesCount(root->rightChild);
return leftLeavesCount + rightLeavesCount;
}
}
//查找值=x的节点个数
int findNode(BinaryTreeNode* &root,char x,int coun)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
if(root->data==x) coun++;
findNode(root->leftChild,x,coun);
findNode(root->rightChild,x,coun);
}
return coun;
}
//以缩格文本形式输出所有节点
void outputNode(BinaryTreeNode* &root,int x)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
for(int i=0;i<x;i++) cout<<" ";
cout<<root->data<<endl;
x=x+2;
outputNode(root->leftChild,x);
outputNode(root->rightChild,x);
}
}
};
int main()
{
BinaryTree tree;
BinaryTreeNode* treeRoot;
char func;
while(cin>>func){
if(func=='C')
{
tree.createBinaryTree(treeRoot);
cout<<"Created success!";
}
if(func=='1') {cout<<"Preorder is:";tree.preTraversal(treeRoot);cout<<".";}
if(func=='2') {cout<<"Inorder is:";tree.mid(treeRoot);cout<<".";}
if(func=='3') {cout<<"Postorder is:";tree.lastTraversal(treeRoot);cout<<".";}
if(func=='N') cout<<"Nodes="<<tree.nodeCount(treeRoot)<<".";
if(func=='H') cout<<"Height="<<tree.treeHight(treeRoot)<<".";
if(func=='L') cout<<"Leaf="<<tree.getLeavesCount(treeRoot)<<".";
if(func=='F')
{
char x;
cin>>x;
cout<<"The count of "<<x<<" is "<<tree.findNode(treeRoot,x,0)<<".";
}
if(func=='P')
{
cout<<"The tree is:"<<endl;
tree.outputNode(treeRoot,0);
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
PS:有时间再补充注意点吧
C++实现二叉树的基本操作:建立、遍历、计算深度、节点数、叶子数等的更多相关文章
- <二叉树的基本操作(有层次遍历)>
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #define num 100 #define OK ...
- C++编程练习(8)----“二叉树的建立以及二叉树的三种遍历方式“(前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历)
树 利用顺序存储和链式存储的特点,可以实现树的存储结构的表示,具体表示法有很多种. 1)双亲表示法:在每个结点中,附设一个指示器指示其双亲结点在数组中的位置. 2)孩子表示法:把每个结点的孩子排列起来 ...
- 数据结构实习 - problem K 用前序中序建立二叉树并以层序遍历和后序遍历输出
用前序中序建立二叉树并以层序遍历和后序遍历输出 writer:pprp 实现过程主要是通过递归,进行分解得到结果 代码如下: #include <iostream> #include &l ...
- c语言描述的二叉树的基本操作(层序遍历,递归,非递归遍历)
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define TRUE 1 #define ...
- Python --- 二叉树的层序建立与三种遍历
二叉树(Binary Tree)时数据结构中一个非常重要的结构,其具有....(此处省略好多字)....等的优良特点. 之前在刷LeetCode的时候把有关树的题目全部跳过了,(ORZ:我这种连数据结 ...
- 二叉树的基本操作(C语言版)
今天走进数据结构之二叉树 二叉树的基本操作(C 语言版) 1 二叉树的定义 二叉树的图长这样: 二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构,常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆.二叉树是链式存储结构,用的是二叉 ...
- 二叉树的基本操作(含Huffman树)
大二时候写的烂代码,翻出来复习复习(o(╯□╰)o). 代码: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define Max_Size ...
- <二叉树的基本操作>
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #define num 100 #define OK ...
- 数据结构《10》----二叉树 Morris 中序遍历
无论是二叉树的中序遍历还是用 stack 模拟递归, 都需要 O(n)的空间复杂度. Morris 遍历是一种 常数空间 的遍历方法,其本质是 线索二叉树(Threaded Binary Tree), ...
- SDUT 3344 数据结构实验之二叉树五:层序遍历
数据结构实验之二叉树五:层序遍历 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536KB Submit Statistic Problem Description 已知一个按 ...
随机推荐
- java中如何踢人下线?封禁某个账号后使其会话立即掉线!
需求场景 封禁账号是一个比较常见的业务需求,尤其是在论坛.社区类型的项目中,当出现了违规用户时我们需要将其账号立即封禁. 常规的设计思路是:在设计用户表时增加一个状态字段,例如:status,其值为1 ...
- kafka安装流程
本文是作者原创,版权归作者所有.若要转载,请注明出处. 安装前的环境准备 1.由于Kafka是用Scala语言开发的,运行在JVM上,在安装之前需要先安装JDK(省略) 2.kafka依赖zookee ...
- PHP设计模式之装饰器模式(Decorator)
PHP设计模式之装饰器模式(Decorator) 装饰器模式 装饰器模式允许我们给一个类添加新的功能,而不改变其原有的结构.这种类型的类属于结构类,它是作为现有的类的一个包装 装饰器模式的应用场景 当 ...
- Lambda架构正是这样一种用来处理不能够直接实时计算问题的通用架构
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BGHOw12iCASJy1pgkYZi3w 当数据处理做不到实时,应该怎么办?
- Python 代码的加密混淆
py 脚本编译成 c 文件(cython) 用 cython 将核心代码 py 模块文件转化成 .c 文件,再用 gcc 编译成 so(unix)文件,或者将其编译成 pyd(windows)文件. ...
- loj10001种树
好久不写博客了,发现不好找做过和题!还得接着写啊! ------------------------------------------------------------------ 题目描述 某条 ...
- LOJ10144宠物收养所
HNOI 2004 最近,阿 Q 开了一间宠物收养所.收养所提供两种服务:收养被主人遗弃的宠物和让新的主人领养这些宠物. 每个领养者都希望领养到自己满意的宠物,阿 Q 根据领养者的要求通过他自己发明的 ...
- SpringMVC听课笔记(一:SpringMVC概述)
地址 :https://www.bilibili.com/video/av14907450 版本:4.x 概述: 概要: 一:SpringMVC概述 二:SpringMVC的 HelloWorld 三 ...
- Java8种排序算法学习
冒泡排序 public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub ...
- SealClient
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import ja ...
