Fundmentals in Stream Computing
Spark programs are structured on RDDs: they invole reading data from stable storage into the RDD format, performing a number of computations and
data transformations on the RDD, and writing the result RDD to stable storage on collecting to the driver. Thus, most of the power of Spark comes from
its transformation: operations that are defined on RDDs and return RDDs.
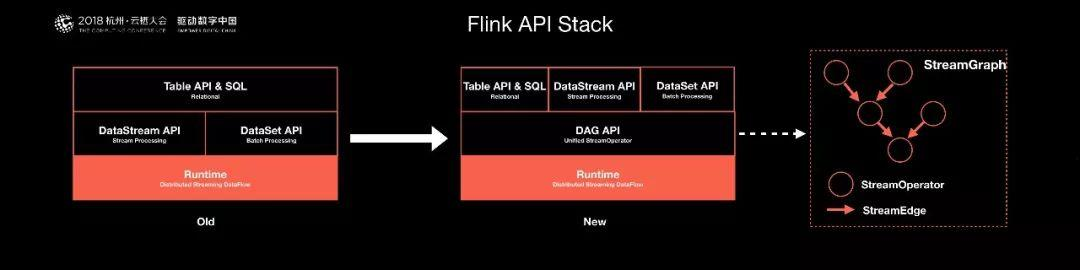
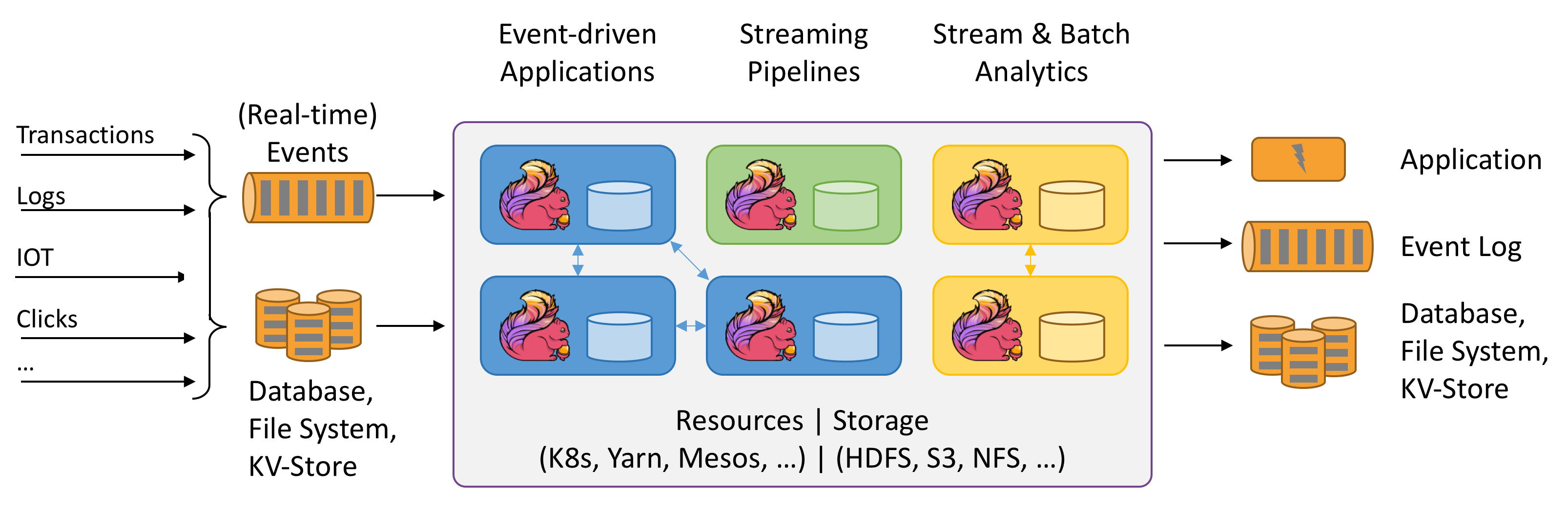
1. Need core underlying layer as basic fundmentals
2. Providing the API to high level
3. Stream computing = core underlying API + Distributed RPC + Computing Template + Cluster of executor
4.What will be computed, the Sequence of computed and definition of (K,V) are totally in hand of Users through the defined Computing Template.
5. We can say that Distributed Computing is a kind of platform to provide more Computing Template to operate the user data which is splited and distributed in cluster.
6. The ML/Bigdata SQL alike use these Stream API to do there jobs.
7. Remmeber that Stream Computing is a platform or runtime of operating distributed data with Computing Template (transformation API).
8. We can see a lot of common between StreamComputing and OS, which all provide the API to have operation on Data in Stream and on Hardeware in OS.
9.Stream Computing Runtime has API of Computing Template / Computing Generic; OS has API of Resource Operation on PC hardware.
Operators transform one or more DataStreams into a new DataStream. Programs can combine multiple transformations into sophisticated dataflow topologies.
| ransformation | Description |
|---|---|
| Map DataStream → DataStream |
Takes one element and produces one element. A map function that doubles the values of the input stream: |
| FlatMap DataStream → DataStream |
Takes one element and produces zero, one, or more elements. A flatmap function that splits sentences to words: |
| Filter DataStream → DataStream |
Evaluates a boolean function for each element and retains those for which the function returns true. A filter that filters out zero values: |
| KeyBy DataStream → KeyedStream |
Logically partitions a stream into disjoint partitions. All records with the same key are assigned to the same partition. Internally, keyBy() is implemented with hash partitioning. There are different ways to specify keys. This transformation returns a KeyedStream, which is, among other things, required to use keyed state. Attention A type cannot be a key if:
|
| Reduce KeyedStream → DataStream |
A "rolling" reduce on a keyed data stream. Combines the current element with the last reduced value and emits the new value. A reduce function that creates a stream of partial sums: |
| Fold KeyedStream → DataStream |
A "rolling" fold on a keyed data stream with an initial value. Combines the current element with the last folded value and emits the new value. A fold function that, when applied on the sequence (1,2,3,4,5), emits the sequence "start-1", "start-1-2", "start-1-2-3", ... |
| Aggregations KeyedStream → DataStream |
Rolling aggregations on a keyed data stream. The difference between min and minBy is that min returns the minimum value, whereas minBy returns the element that has the minimum value in this field (same for max and maxBy). |
| Window KeyedStream → WindowedStream |
Windows can be defined on already partitioned KeyedStreams. Windows group the data in each key according to some characteristic (e.g., the data that arrived within the last 5 seconds). See windows for a complete description of windows. |
| WindowAll DataStream → AllWindowedStream |
Windows can be defined on regular DataStreams. Windows group all the stream events according to some characteristic (e.g., the data that arrived within the last 5 seconds). See windows for a complete description of windows. WARNING: This is in many cases a non-parallel transformation. All records will be gathered in one task for the windowAll operator. |
| Window Apply WindowedStream → DataStream AllWindowedStream → DataStream |
Applies a general function to the window as a whole. Below is a function that manually sums the elements of a window. Note: If you are using a windowAll transformation, you need to use an AllWindowFunction instead. |
| Window Reduce WindowedStream → DataStream |
Applies a functional reduce function to the window and returns the reduced value. |
| Window Fold WindowedStream → DataStream |
Applies a functional fold function to the window and returns the folded value. The example function, when applied on the sequence (1,2,3,4,5), folds the sequence into the string "start-1-2-3-4-5": |
| Aggregations on windows WindowedStream → DataStream |
Aggregates the contents of a window. The difference between min and minBy is that min returns the minimum value, whereas minBy returns the element that has the minimum value in this field (same for max and maxBy). |
| Union DataStream* → DataStream |
Union of two or more data streams creating a new stream containing all the elements from all the streams. Note: If you union a data stream with itself you will get each element twice in the resulting stream. |
| Window Join DataStream,DataStream → DataStream |
Join two data streams on a given key and a common window. |
| Interval Join KeyedStream,KeyedStream → DataStream |
Join two elements e1 and e2 of two keyed streams with a common key over a given time interval, so that e1.timestamp + lowerBound <= e2.timestamp <= e1.timestamp + upperBound |
| Window CoGroup DataStream,DataStream → DataStream |
Cogroups two data streams on a given key and a common window. |
| Connect DataStream,DataStream → ConnectedStreams |
"Connects" two data streams retaining their types. Connect allowing for shared state between the two streams. |
| CoMap, CoFlatMap ConnectedStreams → DataStream |
Similar to map and flatMap on a connected data stream |
| Split DataStream → SplitStream |
Split the stream into two or more streams according to some criterion. |
| Select SplitStream → DataStream |
Select one or more streams from a split stream. |
| Iterate DataStream → IterativeStream → DataStream |
Creates a "feedback" loop in the flow, by redirecting the output of one operator to some previous operator. This is especially useful for defining algorithms that continuously update a model. The following code starts with a stream and applies the iteration body continuously. Elements that are greater than 0 are sent back to the feedback channel, and the rest of the elements are forwarded downstream. See iterations for a complete description. |
| Extract Timestamps DataStream → DataStream |
Extracts timestamps from records in order to work with windows that use event time semantics. See Event Time. |
Fundmentals in Stream Computing的更多相关文章
- [Note] Stream Computing
Stream Computing 概念对比 静态数据和流数据 静态数据,例如数据仓库中存放的大量历史数据,特点是不会发生更新,可以利用数据挖掘技术和 OLAP(On-Line Analytical P ...
- Stream computing
stream data 从广义上说,所有大数据的生成均可以看作是一连串发生的离散事件.这些离散的事件以时间轴为维度进行观看就形成了一条条事件流/数据流.不同于传统的离线数据,流数据是指由数千个数据源持 ...
- [Linux] 流 ( Stream )、管道 ( Pipeline ) 、Filter - 笔记
流 ( Stream ) 1. 流,是指可使用的数据元素一个序列. 2. 流,可以想象为是传送带上等待加工处理的物品,也可以想象为工厂流水线上的物品. 3. 流,可以是无限的数据. 4. 有一种功能, ...
- MapReduce的核心资料索引 [转]
转自http://prinx.blog.163.com/blog/static/190115275201211128513868/和http://www.cnblogs.com/jie46583173 ...
- 分布式系统(Distributed System)资料
这个资料关于分布式系统资料,作者写的太好了.拿过来以备用 网址:https://github.com/ty4z2008/Qix/blob/master/ds.md 希望转载的朋友,你可以不用联系我.但 ...
- 资源list:Github上关于大数据的开源项目、论文等合集
Awesome Big Data A curated list of awesome big data frameworks, resources and other awesomeness. Ins ...
- Mac OS X 背后的故事
Mac OS X 背后的故事 作者: 王越 来源: <程序员> 发布时间: 2013-01-22 10:55 阅读: 25840 次 推荐: 49 原文链接 [收藏] ...
- 想从事分布式系统,计算,hadoop等方面,需要哪些基础,推荐哪些书籍?--转自知乎
作者:廖君链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/19868791/answer/88873783来源:知乎 分布式系统(Distributed System)资料 < ...
- 【原】Kryo序列化篇
Kryo是一个快速有效的对象图序列化Java库.它的目标是快速.高效.易使用.该项目适用于对象持久化到文件或数据库中或通过网络传输.Kryo还可以自动实现深浅的拷贝/克隆. 就是直接复制一个对象对象到 ...
随机推荐
- 2019年华南理工大学程序设计竞赛(春季赛)A NB群友
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/625/A 题意:给出一个区间范围 , 求有多少个数的每一位的积是在这个区间里面的 分析:没错了 ,就是记忆化暴力搜索 ,不断的 ...
- 128th LeetCode Weekly Contest Pairs of Songs With Total Durations Divisible by 60
In a list of songs, the i-th song has a duration of time[i] seconds. Return the number of pairs of s ...
- sklearn的train_test_split
train_test_split函数用于将矩阵随机划分为训练子集和测试子集,并返回划分好的训练集测试集样本和训练集测试集标签. 格式: X_train,X_test, y_train, y_test ...
- Tomcat部署项目的三种方式
目录 1.下载 Tomcat 服务器 2.启动并部署 Tomcat 服务器 3.Tomcat 的目录结构 4.部署项目的第一种方法(项目直接放入 webapps 目录中) 5.部署项目的第二种方法(修 ...
- 正则基础之——NFA引擎匹配原理
记录一下一篇很好的博文:https://blog.csdn.net/lxcnn/article/details/4304651
- 换个角度看Salesforce之基础配置学习笔记(一)
1. Salesforce.com与force.com的关系: Salesforce.com is build on the force.com platform seamlessly.That is ...
- html5在手机熄屏后倒计时会出现延迟情况
今天开发了一个手机端的倒计时,然后同事说出现了Bug,怎么回事呢?Bug很简单,就是在手机返回主界面或者熄屏后倒计时会暂停在熄屏前的时间(注意时间是页面加载时获取的服务器的时间),问题很简单,知道问题 ...
- es第二篇:Document APIs
文档CRUD API分为单文档API和多文档API.这些API的索引名参数既可以是一个真正的索引的名称,也可以是某个索引的别名alias. 单文档API有:Index API.Get API.Dele ...
- Angular CLI
简介 ng 官方命令行 Angular CLI 自己的官方文档 https://github.com/angular/angular-cli/wiki/new 常用代码 临时代码 ng new ...
- 微信公共平台注册 bug: 验证码不应该输入后,就立即检查其有效性
本文链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/hchengmx/p/10793037.html 刚刚想注册个微信公众号,就发现了这个问题,在这里记录一下. 已经发到testhome了,链 ...
