[Leetcode] Construct binary tree from inorder and postorder travesal 利用中序和后续遍历构造二叉树
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree.
Note:
You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree.
利用中序和后序遍历构造二叉树,要注意到后序遍历的最后一个元素是二叉树的根节点,而中序遍历中,根节点前面为左子树节点后面为右子树的节点。例如二叉树:{1,2,3,4,5,6,#}的后序遍历为4->5->2->6->3->1;中序遍历为:4->2->5->1->6->3。
故,递归的整体思路是,找到根节点,然后遍历左右子树。这里有一个很重要的条件是:树中没有重复元素。
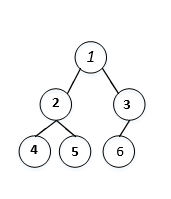
方法一:递归
值得注意的是:递归过程中,起始点的选取。Grandyang对下标的选取有较为详细的说明。至于这个递归过程,(个人愚见,欢迎大神给出更好递归过程)可以在脑海想,构造顺序为4->5->2构建好左子树,接上1,然后6->3构建好右子树,最后接上1,完成。
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &inorder, vector<int> &postorder)
{
int len=inorder.size();
return build(inorder,,len-,postorder,,len-);
}
TreeNode *build(vector<int> &inorder,int inBeg,int inEnd,vector<int> &postorder,int postBeg,int postEnd)
{
if(inBeg>inEnd||postBeg>postEnd) return NULL;
TreeNode *root=new TreeNode(postorder[postEnd]); for(int i=;i<inorder.size();++i)
{
if(inorder[i]==postorder[postEnd])
{
root->left=build(inorder,inBeg,i-,postorder,postBeg,postBeg+i--inBeg);
root->right=build(inorder,i+,inEnd,postorder,postBeg+i-inBeg,postEnd-);
}
}
return root;
}
};
方法二:
利用栈。这个方法是以前看到出处也尴尬的忘了,分析过程等我再次看懂了再补上。这种方法改变了数组。
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &inorder, vector<int> &postorder)
{
if(inorder.size()==) return NULL;
TreeNode* p;
TreeNode* root;
stack<TreeNode*> stn; root=new TreeNode(postorder.back());
stn.push(root);
postorder.pop_back(); while(true)
{
if(inorder.back()==stn.top()->val)
{
p=stn.top();
stn.pop();
inorder.pop_back(); if(inorder.size()==) break;
if(stn.size()&&inorder.back()==stn.top()->val)
continue; p->left=new TreeNode(postorder.back());
postorder.pop_back();
stn.push(p->left);
}
else
{
p=new TreeNode(postorder.back());
postorder.pop_back();
stn.top()->right=p;
stn.push(p);
}
}
return root;
}
};
[Leetcode] Construct binary tree from inorder and postorder travesal 利用中序和后续遍历构造二叉树的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal 由中序和后序遍历建立二叉树
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note: You may assume tha ...
- Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal(根据中序遍历和后序遍历构建二叉树)
根据中序和后续遍历构建二叉树. /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * Tree ...
- [LeetCode] 106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal 由中序和后序遍历建立二叉树
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note:You may assume that ...
- LeetCode 106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal 由中序和后序遍历建立二叉树 C++
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note:You may assume that ...
- Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal ——通过中序、后序遍历得到二叉树
题意:根据二叉树的中序遍历和后序遍历恢复二叉树. 解题思路:看到树首先想到要用递归来解题.以这道题为例:如果一颗二叉树为{1,2,3,4,5,6,7},则中序遍历为{4,2,5,1,6,3,7},后序 ...
- LeetCode: 106_Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal | 根据中序和后序遍历构建二叉树 | Medium
要求:根据中序和后序遍历序列构建一棵二叉树 代码如下: struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode *left; TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int ...
- LeetCode:Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal,Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
LeetCode:Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal Given inorder and postorder trav ...
- LeetCode: Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal 解题报告
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal Given inorder and postorder traversal of ...
- Leetcode Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note:You may assume that ...
随机推荐
- thinkphp5
分页: thinkphp5分页默认只带page参数 在使用form表单method='get'传递关键字来筛选: 保证每次刷新依旧带上筛选参数 但遇到分页时,下面的分页默认自带page,没有之前筛选的 ...
- 汽车后市场:数据入口在哪里?不看你就OUT啦!
当前中国汽车后服务市场基本可分七个大类:包括养护.维修.改装.二手车.汽车配件.相关电商及金融保险等,汽车后市场整个产业链对数据服务都有刚性需求. 数据能为行业服务提高效率,提升商家对于客户以及业务的 ...
- 怎样下载JDBC驱动
MySQL官网: https://www.mysql.com/ 请注意: 需要把mysql-connector-java-5.1.45-bin.jar放到C:\JMeter\apache-jmeter ...
- 关于java中“使用了未经检查或不安全的操作、有关详细信息,请使用 ——Xlint:unchecked重新编译”
今天看<算法 第4版>排序章节时,发现了一个了一个小问题.先贴一下代码: public class Selection{ public static void main(String[]a ...
- Trie 树——搜索关键词提示
当你在搜索引擎中输入想要搜索的一部分内容时,搜索引擎就会自动弹出下拉框,里面是各种关键词提示,这个功能是怎么实现的呢?其实底层最基本的就是 Trie 树这种数据结构. 1. 什么是 "Tri ...
- Python3 小工具-ARP扫描
from scapy.all import * import optparse import threading import os def scan(ipt): pkt=Ether(dst='ff: ...
- HADOOP (十一).安装hbase
下载安装包并解压设置hbase环境变量配置hbase-site.xml启动hbase检测hbase启动情况测试hbase shell 下载安装包并解压 https://mirrors.tuna.tsi ...
- CentOS6 安装VNCserver
1.下载vncserver yum install tigervnc tigervnc-server -y 2.配置 vncserver vi /etc/sysconfig/vncserver 在文件 ...
- Sum of Consecutive Prime Numbers(素数打表+尺取)
Description Some positive integers can be represented by a sum of one or more consecutive prime numb ...
- Python—字典(当索引不好用时)
一.定义与概念 1.字典是针对非序列集合而提供的一种数据类型 举例:检索学生信息. “<键><值>对”. 键(即身份证号码) 值(即学生信息). “键值对”例子 姓名和电话号码 ...
