k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(6)-Indexer源码分析
client-go之Indexer源码分析
1.Indexer概述
Indexer中有informer维护的指定资源对象的相对于etcd数据的一份本地内存缓存,可通过该缓存获取资源对象,以减少对apiserver、对etcd的请求压力。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type threadSafeMap struct {
items map[string]interface{}
indexers Indexers
indices Indices
...
}
informer所维护的缓存依赖于threadSafeMap结构体中的items属性,其本质上是一个用map构建的键值对,资源对象都存在items这个map中,key为资源对象的namespace/name组成,value为资源对象本身,这些构成了informer的本地缓存。
Indexer除了维护了一份本地内存缓存外,还有一个很重要的功能,便是索引功能了。索引的目的就是为了快速查找,比如我们需要查找某个node节点上的所有pod、查找某个命名空间下的所有pod等,利用到索引,可以实现快速查找。关于索引功能,则依赖于threadSafeMap结构体中的indexers与indices属性。
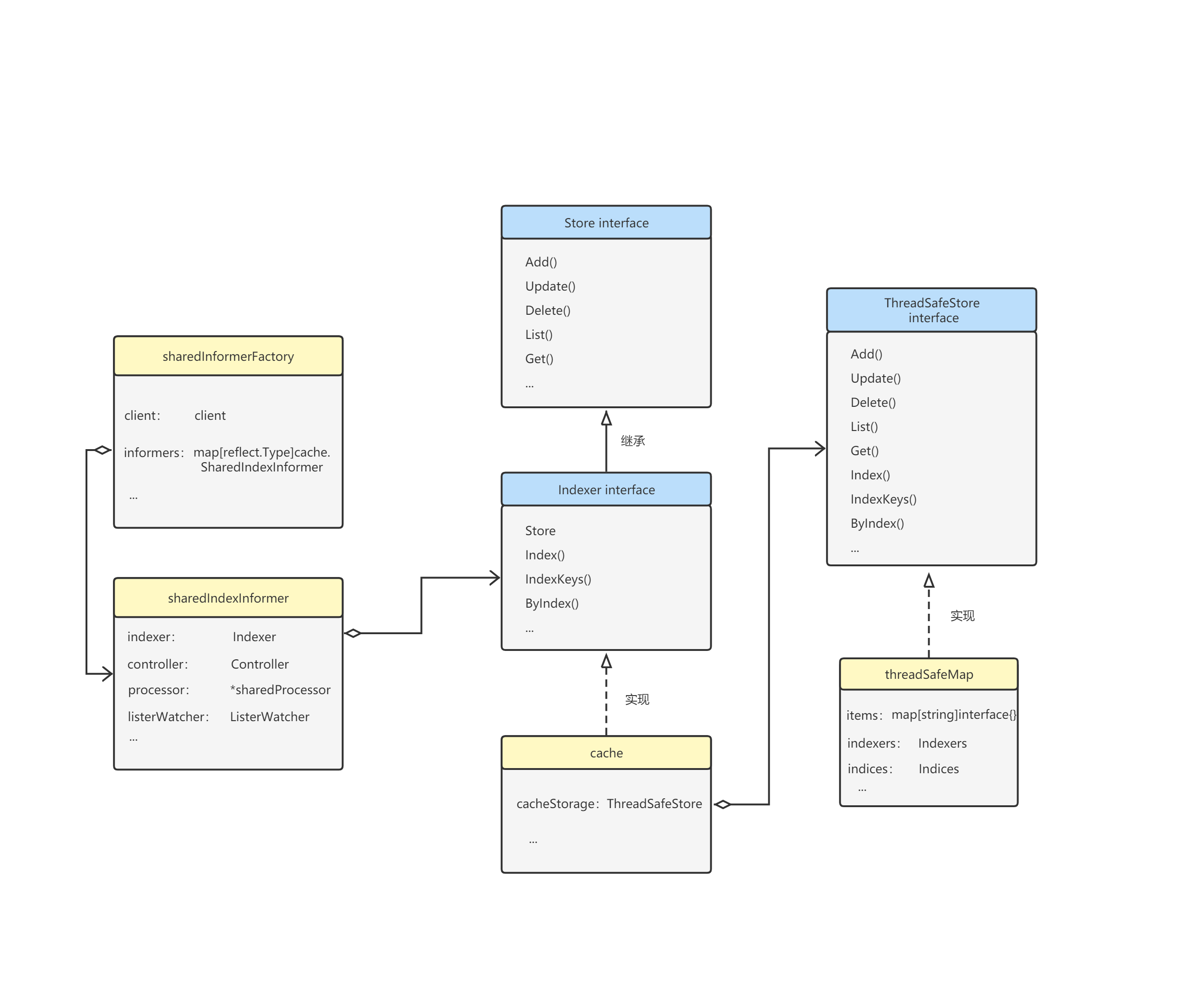
先通过一张informer概要架构图看一下Indexer所处位置与其概要功能。

2.Indexer的结构定义分析
2.1 Indexer interface
Indexer接口继承了一个Store接口(实现本地缓存),以及包含几个index索引相关的方法声明(实现索引功能)。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/index.go
type Indexer interface {
Store
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
2.2 Store interface
Store接口本身,定义了Add、Update、Delete、List、Get等一些对象增删改查的方法声明,用于操作informer的本地缓存。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
type Store interface {
Add(obj interface{}) error
Update(obj interface{}) error
Delete(obj interface{}) error
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
Replace([]interface{}, string) error
Resync() error
}
2.3 cache struct
结合代码,可以看到cache struct是Indexer接口的一个实现,所以自然也是Store接口的一个实现,cache struct包含一个ThreadSafeStore接口的实现,以及一个计算object key的函数KeyFunc。
cache struct会根据keyFunc生成某个obj对象对应的一个唯一key, 然后调用ThreadSafeStore接口中的方法来操作本地缓存中的对象。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
type cache struct {
cacheStorage ThreadSafeStore
keyFunc KeyFunc
}
2.4 ThreadSafeStore interface
ThreadSafeStore接口包含了操作本地缓存的增删改查方法以及索引功能的相关方法,其方法名称与Indexer接口的类似,最大区别是ThreadSafeStore接口的增删改查方法入参基本都有key,由cache struct中的KeyFunc函数计算得出object key。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type ThreadSafeStore interface {
Add(key string, obj interface{})
Update(key string, obj interface{})
Delete(key string)
Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool)
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Replace(map[string]interface{}, string)
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(name string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
Resync() error
}
2.5 threadSafeMap struct
threadSafeMap struct是ThreadSafeStore接口的一个实现,其最重要的一个属性便是items了,items是用map构建的键值对,资源对象都存在items这个map中,key根据资源对象来算出,value为资源对象本身,这里的items即为informer的本地缓存了,而indexers与indices属性则与索引功能有关。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
2.6 Indexer结构定义小结
下面对上面介绍的Indexer的相关struct与interface做个小结:
(1)Store interface: 定义了Add、Update、Delete、List、Get等一些对象增删改查的方法声明,用于操作informer的本地缓存;
(2)Indexer interface: 继承了一个Store接口(实现本地缓存),以及包含几个index索引相关的方法声明(实现索引功能);
(3)cache struct: Indexer接口的一个实现,所以自然也是Store接口的一个实现,cache struct包含一个ThreadSafeStore接口的实现,以及一个计算object key的函数KeyFunc;
(4)ThreadSafeStore interface: 包含了操作本地缓存的增删改查方法以及索引功能的相关方法,其方法名称与Indexer接口的类似,最大区别是ThreadSafeStore接口的增删改查方法入参基本都有key,由cache struct中的KeyFunc函数计算得出object key;
(5)threadSafeMap struct: ThreadSafeStore接口的一个实现,其最重要的一个属性便是items了,items是用map构建的键值对,资源对象都存在items这个map中,key根据资源对象来算出,value为资源对象本身,这里的items即为informer的本地缓存了,而indexers与indices属性则与索引功能有关;
3.Indexer的索引功能
在threadSafeMap struct中,与索引功能有关的是indexers与indices属性;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
type Indices map[string]Index
type Index map[string]sets.String
3.1 type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc / type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
Indexers包含了所有索引器(索引分类)及其索引器函数IndexFunc,IndexFunc为计算某个索引键下的所有对象键列表的方法;
Indexers: {
"索引器1": 索引函数1,
"索引器2": 索引函数2,
}
数据示例:
Indexers: {
"namespace": MetaNamespaceIndexFunc,
"nodeName": NodeNameIndexFunc,
}
func MetaNamespaceIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
meta, err := meta.Accessor(obj)
if err != nil {
return []string{""}, fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)
}
return []string{meta.GetNamespace()}, nil
}
func NodeNameIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
pod, ok := obj.(*v1.Pod)
if !ok {
return []string{""}, fmt.Errorf("object is not a pod)
}
return []string{pod.Spec.NodeName}, nil
}
3.2 type Indices map[string]Index / type Index map[string]sets.String
Indices包含了所有索引器(索引分类)及其所有的索引数据Index;而Index则包含了索引键以及索引键下的所有对象键的列表;
Indices: {
"索引器1": {
"索引键1": ["对象键1", "对象键2"],
"索引键2": ["对象键3"],
},
"索引器2": {
"索引键3": ["对象键1"],
"索引键4": ["对象键2", "对象键3"],
}
}
数据示例:
pod1 := &v1.Pod {
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta {
Name: "pod-1",
Namespace: "default",
},
Spec: v1.PodSpec{
NodeName: "node1",
}
}
pod2 := &v1.Pod {
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta {
Name: "pod-2",
Namespace: "default",
},
Spec: v1.PodSpec{
NodeName: "node2",
}
}
pod3 := &v1.Pod {
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta {
Name: "pod-3",
Namespace: "kube-system",
},
Spec: v1.PodSpec{
NodeName: "node2",
}
}
Indices: {
"namespace": {
"default": ["pod-1", "pod-2"],
"kube-system": ["pod-3"],
},
"nodeName": {
"node1": ["pod-1"],
"node2": ["pod-2", "pod-3"],
}
}
3.3 索引结构小结
Indexers: {
"索引器1": 索引函数1,
"索引器2": 索引函数2,
}
Indices: {
"索引器1": {
"索引键1": ["对象键1", "对象键2"],
"索引键2": ["对象键3"],
},
"索引器2": {
"索引键3": ["对象键1"],
"索引键4": ["对象键2", "对象键3"],
}
}
3.4 索引功能方法分析
看到Indexer interface,除了继承的Store外,其他的几个方法声明均与索引功能相关,下面对几个常用方法进行介绍。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/index.go
type Indexer interface {
Store
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
下面的方法介绍基于以下数据:
Indexers: {
"namespace": MetaNamespaceIndexFunc,
"nodeName": NodeNameIndexFunc,
}
Indices: {
"namespace": {
"default": ["pod-1", "pod-2"],
"kube-system": ["pod-3"],
},
"nodeName": {
"node1": ["pod-1"],
"node2": ["pod-2", "pod-3"],
}
}
3.4.1 ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
调用ByIndex方法,传入索引器名称indexName,以及索引键名称indexedValue,方法寻找该索引器下,索引键对应的对象键列表,然后根据对象键列表,到Indexer缓存(即threadSafeMap中的items属性)中获取出相应的对象列表。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
func (c *cache) ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error) {
return c.cacheStorage.ByIndex(indexName, indexKey)
}
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error) {
c.lock.RLock()
defer c.lock.RUnlock()
indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]
if indexFunc == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)
}
index := c.indices[indexName]
set := index[indexKey]
list := make([]interface{}, 0, set.Len())
for key := range set {
list = append(list, c.items[key])
}
return list, nil
}
使用示例:
pods, err := index.ByIndex("namespace", "default")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
for _, pod := range pods {
fmt.Println(pod.(*v1.Pod).Name)
}
fmt.Println("=====")
pods, err := index.ByIndex("nodename", "node1")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
for _, pod := range pods {
fmt.Println(pod.(*v1.Pod).Name)
}
输出:
pod-1
pod-2
=====
pod-1
3.4.2 IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
IndexKeys方法与ByIndex方法类似,只不过只返回对象键列表,不会根据对象键列表,到Indexer缓存(即threadSafeMap中的items属性)中获取出相应的对象列表。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
func (c *cache) IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error) {
return c.cacheStorage.IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey)
}
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error) {
c.lock.RLock()
defer c.lock.RUnlock()
indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]
if indexFunc == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)
}
index := c.indices[indexName]
set := index[indexKey]
return set.List(), nil
}
4.Indexer本地缓存
从前面的分析可以知道,informer中的本地缓存实际上指的是Indexer中的threadSafeMap,具体到属性,则是threadSafeMap中的items属性;
threadSafeMap struct
threadSafeMap struct中的items属性即为informer的本地缓存;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
接下来分析下threadSafeMap的几个核心方法,主要都是操作items属性的;
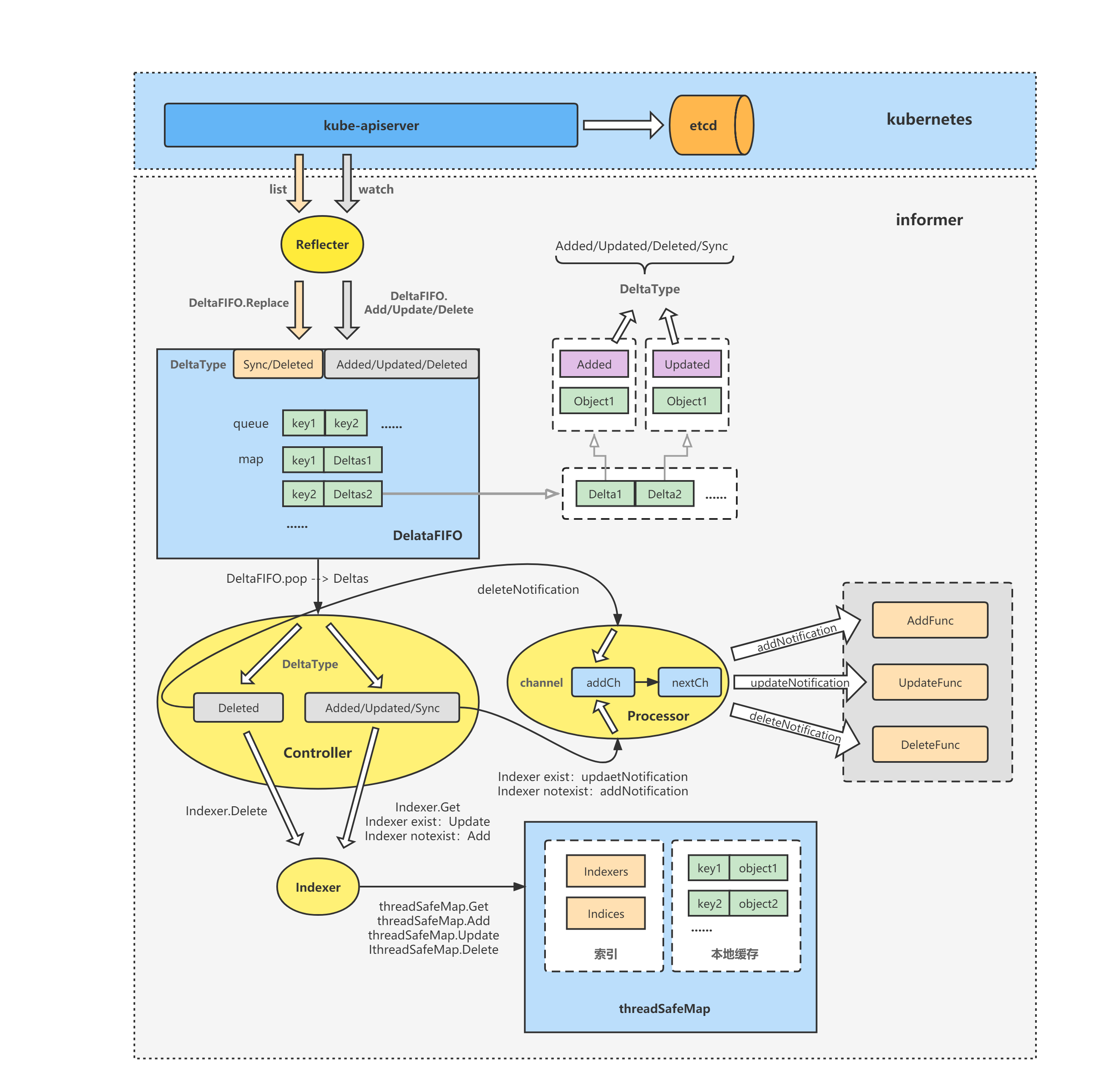
前面对informer-Controller的分析中(代码如下),提到的s.indexer.Add、s.indexer.Update、s.indexer.Delete、s.indexer.Get等方法其实最终就是调用的threadSafeMap.Add、threadSafeMap.Update、threadSafeMap.Delete、threadSafeMap.Get等;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/shared_informer.go
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HandleDeltas(obj interface{}) error {
s.blockDeltas.Lock()
defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()
// from oldest to newest
for _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Added, Updated:
isSync := d.Type == Sync
s.cacheMutationDetector.AddObject(d.Object)
if old, exists, err := s.indexer.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {
if err := s.indexer.Update(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(updateNotification{oldObj: old, newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
} else {
if err := s.indexer.Add(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
}
case Deleted:
if err := s.indexer.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(deleteNotification{oldObj: d.Object}, false)
}
}
return nil
}
4.1 threadSafeMap.Add
调用链:s.indexer.Add --> cache.Add --> threadSafeMap.Add
threadSafeMap.Add方法将key:object存入items中,并调用updateIndices方法更新索引(updateIndices方法这里不展开分析,可以自行查看源码);
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) Add(key string, obj interface{}) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
oldObject := c.items[key]
c.items[key] = obj
c.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key)
}
也可以看到对threadSafeMap进行操作的方法,基本都会先获取锁,然后方法执行完毕释放锁,所以是并发安全的。
4.2 threadSafeMap.Update
调用链:s.indexer.Update --> cache.Update --> threadSafeMap.Update
threadSafeMap.Update方法逻辑与threadSafeMap.Add方法相同;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) Update(key string, obj interface{}) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
oldObject := c.items[key]
c.items[key] = obj
c.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key)
}
4.3 threadSafeMap.Delete
调用链:s.indexer.Delete --> cache.Delete --> threadSafeMap.Delete
threadSafeMap.Delete方法中,先判断本地缓存items中是否存在该key,存在则调用deleteFromIndices删除相关索引,然后删除items中的key及其对应object;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) Delete(key string) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
if obj, exists := c.items[key]; exists {
c.deleteFromIndices(obj, key)
delete(c.items, key)
}
}
4.4 threadSafeMap.Get
调用链:s.indexer.Get --> cache.Get --> threadSafeMap.Get
threadSafeMap.Get方法逻辑相对简单,没有索引的相关操作,而是直接从items中通过key获取对应的object并返回;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool) {
c.lock.RLock()
defer c.lock.RUnlock()
item, exists = c.items[key]
return item, exists
}
总结
Indexer中有informer维护的指定资源对象的相对于etcd数据的一份本地内存缓存,可通过该缓存获取资源对象,以减少对apiserver、对etcd的请求压力。
informer所维护的缓存依赖于threadSafeMap结构体中的items属性,其本质上是一个用map构建的键值对,资源对象都存在items这个map中,key为资源对象的namespace/name组成,value为资源对象本身,这些构成了informer的本地缓存。
Indexer除了维护了一份本地内存缓存外,还有一个很重要的功能,便是索引功能了。索引的目的就是为了快速查找,比如我们需要查找某个node节点上的所有pod、查找某个命名空间下的所有pod等,利用到索引,可以实现快速查找。关于索引功能,则依赖于threadSafeMap结构体中的indexers与indices属性。
最后以一张图来回顾总结一下Indexer在informer中所处位置与其概要功能。
k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(6)-Indexer源码分析的更多相关文章
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(1)-概要分析
k8s informer概述 我们都知道可以使用k8s的Clientset来获取所有的原生资源对象,那么怎么能持续的获取集群的所有资源对象,或监听集群的资源对象数据的变化呢?这里不需要轮询去不断执行L ...
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(2)-初始化与启动分析
k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(2)-初始化与启动分析 前面一篇文章对k8s informer做了概要分析,本篇文章将对informer的初始化与启动进行分析. info ...
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(3)-Reflector源码分析
k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(3)-Reflector源码分析 1.Reflector概述 Reflector从kube-apiserver中list&watc ...
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(4)-DeltaFIFO源码分析
client-go之DeltaFIFO源码分析 1.DeltaFIFO概述 先从名字上来看,DeltaFIFO,首先它是一个FIFO,也就是一个先进先出的队列,而Delta代表变化的资源对象,其包含资 ...
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(5)-Controller&Processor源码分析
client-go之Controller&Processor源码分析 1.controller与Processor概述 Controller Controller从DeltaFIFO中pop ...
- external-provisioner源码分析(2)-main方法与Leader选举分析
更多ceph-csi其他源码分析,请查看下面这篇博文:kubernetes ceph-csi分析目录导航 external-provisioner源码分析(2)-main方法与Leader选举分析 本 ...
- dubbo源码解析五 --- 集群容错架构设计与原理分析
欢迎来我的 Star Followers 后期后继续更新Dubbo别的文章 Dubbo 源码分析系列之一环境搭建 博客园 Dubbo 入门之二 --- 项目结构解析 博客园 Dubbo 源码分析系列之 ...
- ceph-csi组件源码分析(1)-组件介绍与部署yaml分析
更多ceph-csi其他源码分析,请查看下面这篇博文:kubernetes ceph-csi分析目录导航 ceph-csi组件源码分析(1)-组件介绍与部署yaml分析 基于tag v3.0.0 ht ...
- Java并发包源码学习系列:阻塞队列BlockingQueue及实现原理分析
目录 本篇要点 什么是阻塞队列 阻塞队列提供的方法 阻塞队列的七种实现 TransferQueue和BlockingQueue的区别 1.ArrayBlockingQueue 2.LinkedBloc ...
随机推荐
- OllyDbg---call和ret指令
call和ret call指令 cal指令是转移到指定的子程序处,后面紧跟的操作数就是给定的地址. 例如,call 401362表示转移到地址401362处,调用401362处的子程序,当子程序调用完 ...
- numpy---(精简)
numpy get started 导入numpy库, 并查看版本 import numpy as np np.__version__ '1.14.3' # pyplot显示画图, 数据分析与可视化 ...
- Java实现单链表的反转
思路1:初始化一个新的头节点reverseHead,然后遍历旧链表,利用头插法向reverseHead进行插入 思路2: 1.反转相当于数据的更换(1和n,2和n-1,3和n-2)n为链表的长度 2. ...
- 【面试普通人VS高手系列】谈谈你对Seata的理解
很多面试官都喜欢问一些"谈谈你对xxx技术的理解". 大家遇到这种问题时,是不是完全不知道从何说起. 那么我们来看一下,普通人和高手是如何回答这个问题的? 普通人: Seata是用 ...
- 性能优化之html、css、js三者的加载顺序
前言 我们知道一个页面通常由,html,css,js三部分组成,一般我们会把css文件放在head头部加载,而js文件则放在页面的最底部加载,想要知道为什么大家都会不约而同的按照这个标准进行构建页面, ...
- Python Requests 速通爆肝、这么牛逼的库你还不会用吗?
上网原理 爬虫原理 Get.Post Requests 介绍 安装 常用方法 Http协议 开发者工具网络界面 Response对象 下载保存一张图片.一首音乐 添加Headers发送请求 判断HTT ...
- Java学习day26
进程.多任务 1.例如吃饭的时候玩手机,边上厕所边玩手机,看似是同时做多个事情,本质上我们的大脑在同一时间只做了一件事情,这就是多任务 2.道路窄的时候容易造成拥堵,可以拓宽道路,加多车道,同一个方向 ...
- vue3响应式模式设计原理
vue3响应式模式设计原理 为什么要关系vue3的设计原理?了解vue3构建原理,将有助于开发者更快速上手Vue3:同时可以提高Vue调试技能,可以快速定位错误 1.vue3对比vue2 vue2的原 ...
- golang内存对齐分析(转载)
问题 type Part1 struct { a bool b int32 c int8 d int64 e byte } 在开始之前,希望你计算一下 Part1 共占用的大小是多少呢? func m ...
- 爬虫篇-如何下载selenium及其适配谷歌浏览器插件chromedriver(含chrome各版本及下载地址)
最近换了电脑,练习爬虫时用到selenium,结果在重新安装chromedriver插件的时候发现原网址不能使用,找了好久终于找到了了新网址,顺便更一篇详细使用的文章,希望可以对屏幕前的你有所帮助.本 ...
