cocos2dx[3.2](8) 数学类Vec2/Size/Rect
数学类Vec2、Size、Rect,是cocos2dx中比较常用的类。
比如设置图片位置,设置图片大小,两图片的碰撞检测等等。
比起2.x版本,在3.x中本质上其实没有太大的变化,主要的变化就是将全局宏定义相关的操作封装到各自的类中而已。比如:Vec2的向量运算宏定义ccp***(),现在都已经封装到Vec2类里面去了。
在V2.x中,底层数学库使用的是:Kazmath数学库。
而在 V3.1 中,由于 Sprite3D 需要我们提供更多的API给开发者,这是Kazmath库所不能提供的,而cocos2d-x内部拥有多个数学库是没有意义的。
所以V3.1中,底层选择了新的数学库:GamePlay3D数学库。
【Vec2】
Vec2原名Point,它既可以表示一个二维坐标点,又可以表示一个二维向量。
同时Vec2对运算符进行了重载,可以很方便的完成Vec2的赋值、加减乘除等操作。另外还有与坐标向量相关的:距离、角度、点积、叉积、投影、标准化等操作。
此外在3.x中,还将2.x里的函数定义ccp***(如ccp,ccpAdd,ccpSub)相关的操作都封装到了这个Vec2的类中,这样就可以更加系统化地管理向量的运算操作了。
此外,除了Vec2。还有两个坐标类:Vec3、Vec4,分别代表了三维、四维坐标向量。
Vec2可以是一个二维坐标点,也可以是一个二维向量。
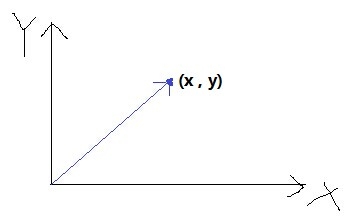
1、创建方式
//
/**
* Vec2只有两个成员变量x , y
*/
float x; //X坐标
float y; //Y坐标
/**
* 构造函数
*/
Vec2(); //(0 , 0)
Vec2(float xx, float yy); //(xx , yy)
Vec2(const float* array); //(array[0] , array[1])
Vec2(const Vec2& copy); //copy
Vec2(const Vec2& p1, const Vec2& p2); //p2 - p1
//2、设置向量坐标
使用set可以给向量重新设置新坐标值。
//
void set(float xx, float yy); //(xx , yy)
void set(const float* array); //(array[0] , array[1])
void set(const Vec2& v); //v
void set(const Vec2& p1, const Vec2& p2); //p2 - p1
//3、向量运算
其中包含了一些2.x中的ccp***()宏定义的函数,都全部封装到了Vec2类中。
//
/**
* 向量运算
* void : 自身运算 , 值会改变
* 有返回值 : 返回运算结果, 值不会改变
*/
void add(const Vec2& v); //相加( x+v.x , y+v.y )
void subtract(const Vec2& v); //相减( x-v.x , y-v.y )
void clamp(const Vec2& min, const Vec2& max); //将向量值限制在[min,max]区间内
void negate(); //向量取负( -x , -y )
void normalize(); //标准化向量. 若为零向量,忽略
void scale(float scalar); //x,y坐标同时放缩
void scale(const Vec2& scale); //x,y坐标分别放缩
void rotate(const Vec2& point, float angle); //绕point点, 旋转angle弧度
float dot(const Vec2& v) const; //点积: x*v.x + y*v.y
float cross(const Vec2& v) const; //叉积: x*v.y - y*v.x
Vec2 project(const Vec2& v) const; //投影: 向量在v上的投影向量
float distance(const Vec2& v) const; //与v的距离.
float distanceSquared(const Vec2& v) const; //与v的距离平方.
float length() const; //向量长度. 即与原点的距离
float lengthSquared() const; //向量长度平方. 即与原点的距离平方
Vec2 getNormalized() const; //获取向量的标准化形式. 若为零向量,返回(0,0)
inline Vec2 getPerp() const; //逆时针旋转90度. Vec2(-y, x);
inline Vec2 getRPerp() const //顺时针旋转90度. Vec2(y, -x);
inline float getAngle() const; //与X轴的夹角(弧度)
float getAngle(const Vec2& v) const; //与v向量的夹角(弧度)
inline Vec2 getMidpoint(const Vec2& v) const; //计算两点间的中点
//将向量值限制在[min,max]区间内,返回该点
inline Vec2 getClampPoint(const Vec2& min, const Vec2& max) const
{
return Vec2(clampf(x, min.x, max.x), clampf(y, min.y, max.y));
}
bool isZero() const; //是否为(0,0)
bool isOne() const; //是否为(1,1)
//判断target是否在坐标点模糊偏差为var的范围内.
//if( (x - var <= target.x && target.x <= x + var) &&
// (y - var <= target.y && target.y <= y + var) )
// return true;
bool fuzzyEquals(const Vec2& target, float variance) const;
//以pivot为轴, 逆时针旋转angle度(弧度)
Vec2 rotateByAngle(const Vec2& pivot, float angle) const;
//绕other向量旋转
//返回向量: 角度 this.getAngle() +other.getAngle();
// 长度 this.getLength()*other.getLength();
inline Vec2 rotate(const Vec2& other) const {
return Vec2(x*other.x - y*other.y, x*other.y + y*other.x);
};
//绕other向量旋转前的向量值
//返回向量: 角度 this.getAngle() -other.getAngle();
// 长度 this.getLength()*other.getLength();
//(这里是不是有点问题,难道不应该是this.getLength()/other.getLength()么?)
inline Vec2 unrotate(const Vec2& other) const {
return Vec2(x*other.x + y*other.y, y*other.x - x*other.y);
};
//两个点a和b之间的线性插值
//alpha ==0 ? a alpha ==1 ? b 否则为a和b之间的一个值
inline Vec2 lerp(const Vec2& other, float alpha) const {
return *this * (1.f - alpha) + other * alpha;
};
//平滑更新向量的当前位置,指向目标向量target.
//responseTime定义了平滑时间量,该值越大结果越平滑,相应的延迟时间越长。
//如果希望向量紧跟target向量,提供一个相对elapsedTime小很多的responseTime值即可。
//参数
//target 目标值
//elapsedTime 消逝时间
//responseTime 响应时间
void smooth(const Vec2& target, float elapsedTime, float responseTime);
/**
* 自定义运算
* compOp
*/
//对该点向量形式的各分量进行function参数来指定的运算,
//如absf,floorf,ceilf,roundf等,
//任何函数拥有如下形式:float func(float)均可。
//例如:我们对x,y进行floor运算,则调用方法为p.compOp(floorf);
//3.0
inline Vec2 compOp(std::function<float(float)> function) const
{
return Vec2(function(x), function(y));
}
/**
* 兼容代码
* 估计是要被抛弃了~(>_<)~
*/
void setPoint(float xx, float yy); //同set(float xx, float yy)
bool equals(const Vec2& target) const; //同==
float getLength() const; //同length()
float getLengthSq() const; //同lengthSquared()
float getDistance(const Vec2& other) const; //同distance(const Vec2& v)
float getDistanceSq(const Vec2& other) const; //同distanceSquared(const Vec2& v)
//4、运算符重载
//
inline const Vec2 operator+(const Vec2& v) const; //( x+v.x , y+v.y )
inline const Vec2 operator-(const Vec2& v) const; //( x-v.x , y-v.y )
inline const Vec2 operator*(float s) const; //( x*s , y*s )
inline const Vec2 operator/(float s) const; //( x/s , y/s )
inline const Vec2 operator-() const; //( -x , -y )
inline Vec2& operator+=(const Vec2& v); //(x,y) = ( x+v.x , y+v.y )
inline Vec2& operator-=(const Vec2& v); //(x,y) = ( x-v.x , y-v.y )
inline Vec2& operator*=(float s); //(x,y) = ( x*s , y*s )
inline bool operator<(const Vec2& v) const;
inline bool operator==(const Vec2& v) const;
inline bool operator!=(const Vec2& v) const;
//5、静态函数与常量
//
/**
* 静态方法
*/
static void add(const Vec2& v1, const Vec2& v2, Vec2* dst); //dst = v1 + v2
static void subtract(const Vec2& v1, const Vec2& v2, Vec2* dst); //dst = v1 - v2
static void clamp(const Vec2& v, const Vec2& min, const Vec2& max, Vec2* dst); //将向量v限制在[min,max]区间内,结果存入dst
static float angle(const Vec2& v1, const Vec2& v2); //两向量夹角(弧度)
static float dot(const Vec2& v1, const Vec2& v2); //两向量点积
static inline Vec2 forAngle(const float a); //返回向量坐标 x=cos(a) , y=sin(a)
/**
* 静态常量
*/
static const Vec2 ZERO; //Vec2(0, 0)
static const Vec2 ONE; //Vec2(1, 1)
static const Vec2 UNIT_X; //Vec2(1, 0)
static const Vec2 UNIT_Y; //Vec2(0, 1)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE; //Vec2(0.5, 0.5)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_BOTTOM_LEFT; //Vec2(0, 0)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_TOP_LEFT; //Vec2(0, 1)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_BOTTOM_RIGHT; //Vec2(1, 0)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_TOP_RIGHT; //Vec2(1, 1)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE_RIGHT; //Vec2(1, 0.5)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE_LEFT; //Vec2(0, 0.5)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE_TOP; //Vec2(0.5, 1)
static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE_BOTTOM; //Vec2(0.5, 0)
//6、线段相交检测
这些用于检测线段相交的函数,也都是静态的成员函数。
//
/**
线段相交检测 v3.0
参数:
A 为线段L1起点. L1 = (A - B)
B 为L1终点 . L1 = (A - B)
C 为线段L2起点. L2 = (C - D)
D 为L2终点 . L2 = (C - D)
S 为L1上计算各点的插值参数,计算方法为:p = A + S*(B - A)
T 为L2上计算各点的插值参数,计算方法为:p = C + T*(D - C)
*/
//直线AB与线段CD是否平行
static bool isLineParallel(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D);
//直线AB与线段CD是否重叠
static bool isLineOverlap(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D);
//直线AB与直线CD是否相交
static bool isLineIntersect(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D,
float *S = nullptr, float *T = nullptr);
//线段AB与线段CD是否重叠
static bool isSegmentOverlap(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D,
Vec2* S = nullptr, Vec2* E = nullptr);
//线段AB与线段CD是否相交
static bool isSegmentIntersect(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D);
//返回直线AB与直线CD的交点
static Vec2 getIntersectPoint(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D);
//【Size】
Size比较简单,只是一个用来表示尺寸大小的类。宽为width,高为height。
和Vec2一样,也对一些运算符进行了重载。
与2.x相比,没有太大的变化。
PS: 因为和Vec2一样,都只有两个成员变量,所以Size和Vec2之间可以相互转换。
1、主要函数如下
//
class CC_DLL Size
{
/**
* Size只有两个成员变量width , height
*/
float width; //宽
float height; //高
/**
* 构造函数
*/
Size(); //(0, 0)
Size(float width, float height); //(width, height)
Size(const Size& other); //other
explicit Size(const Vec2& point); //(显式)构造函数. 构造时Size size = Size(Vec2&), 而不能Size size = vec2;
/**
* 相关操作
* - setSize
* - equals
* - Vec2()
*/
void setSize(float width, float height); //设置尺寸
bool equals(const Size& target) const; //判断是否等于target
//Size::Vec2()
//返回类型为Vec2
operator Vec2() const { return Vec2(width, height); }
/**
* 静态常量
*/
static const Size ZERO; //(0, 0)
/**
* 运算符重载
*/
Size& operator= (const Size& other);
Size& operator= (const Vec2& point); //可以用Vec2赋值
Size operator+(const Size& right) const;
Size operator-(const Size& right) const;
Size operator*(float a) const;
Size operator/(float a) const;
};
//【Rect】
Rect是一个矩形类。包含两个成员属性:起始坐标(左下角)Vec2、矩阵尺寸大小Size。
Rect只对“=”运算符进行了重载。
与2.x相比,多了一个函数unionWithRect,用于合并两个矩形。
值得注意的是Rect类中:
intersectsRect函数,可以用作两个Rect矩形是否相交,即碰撞检测。
containsPoint 函数,可以用作判断点Vec2是否在Rect矩形中。
unionWithRect 函数,可以用做将两矩形进行合并操作。
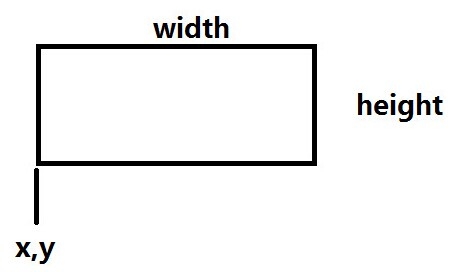
1、主要函数如下
//
class CC_DLL Rect
{
public:
Vec2 origin; //起始坐标: 矩形左下角坐标
Size size; //尺寸大小
/**
* 构造函数
*/
Rect();
Rect(float x, float y, float width, float height);
Rect(const Rect& other);
/**
* 运算符重载
* 只重载了 “=” 运算符
*/
Rect& operator= (const Rect& other);
/**
* 相关操作
* - setRect
* - getMinX , getMidX , getMaxX
* - getMinY , getMidY , getMaxY
* - equals , containsPoint , intersectsRect
* - unionWithRect
*/
//设置矩形
void setRect(float x, float y, float width, float height);
//获取矩形信息
float getMinX() const; //origin.x
float getMidX() const; //origin.x + size.width/2
float getMaxX() const; //origin.x + size.width
float getMinY() const; //origin.y
float getMidY() const; //origin.y + size.height/2
float getMaxY() const; //origin.y + size.height
//判断是否与rect相同. 原点相同,尺寸相同.
bool equals(const Rect& rect) const;
//判断point是否包含在矩形内或四条边上
bool containsPoint(const Vec2& point) const;
//判断矩形是否相交. 常常用作碰撞检测.
bool intersectsRect(const Rect& rect) const;
//与rect矩形合并. 并返回结果. v3.0
//不会改变原矩形的值
Rect unionWithRect(const Rect & rect) const;
/**
* 静态常量
* Rect::ZERO
*/
static const Rect ZERO;
};
//2、精灵创建中的一种方式
还记得Sprite的几种创建方式吗?里面有一种创建方式如下:
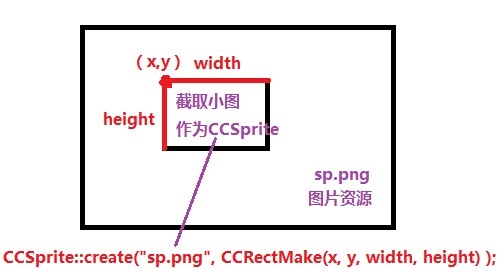
> Sprite::create(const std::string& filename, const Rect& rect)
若用Rect来作为创建Sprite精灵的参数,需要注意,从大图中截取某一区域的图片的Rect rect的构造应该是这样的:
> Rect("小图左上角坐标x", "小图左上角坐标y", 小图宽, 小图高);
使用的是UIKit坐标系,而不是cocos2dx的OpenGL坐标系是不一样的。
如下图所示:
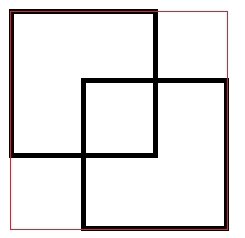
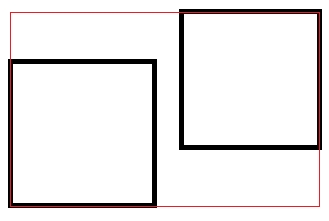
3、矩形合并函数unionWithRect
看几张图,你应该就会明白了。
两个黑色矩形区域,使用unionWithRect合并后,变成红色矩形区域。
cocos2dx[3.2](8) 数学类Vec2/Size/Rect的更多相关文章
- 【转】Cocos2d-x 3.x基础学习: 总结数学类Vec2/Size/Rect
转载:http://www.taikr.com/article/1847 在Cocos2d-x 3.x中,数学类Vec2.Size.Rect,是比较常用的类.比如设置图片位置,图片大小,两图片的碰撞检 ...
- Lua 数学类
数学类主要有Vec2(坐标向量).Size(尺寸).Rect(矩形). 创建 在Lua中创建的 Vec2.Size.Rect 都是一个table类型. 其中只有相应的成员变量,没有相关的函数运算. c ...
- Java:日历类、日期类、数学类、运行时类、随机类、系统类
一:Calendar类 java.util 抽象类Calendar 1.static Calendar getInstance()使用默认时区和语言环境获得一个日历. 2. int get(int ...
- cocos2d-x v3.2 FlappyBird 各个类对象详细代码分析(7)
今天我们介绍最后两个类 GameOverLayer类 GameLayer类 GameLayer类是整个游戏中最重要的类,由于是整个游戏的中央系统,控制着各个类(层)之间的交互,这个类中实现了猪脚小鸟和 ...
- [19/03/18-星期一] 常用类_Math(数学)类&Rondom(随机数)类
一.Math(数学)类(单独一个Java.Math 包中) java.lang.Math提供了一系列静态方法用于科学计算;其方法的参数和返回值类型一般为double型.如果需要更加强大的数学运算能力, ...
- 说说C#的数学类,Math,浮点数(上)
说说C#的数学类,Math,浮点数 C#语言支持下图所看到的的数值类型,各自是整数,浮点数和小数 可能不是非常清楚,可是细致看看还是能看清楚的. 在一个C#程序中,整数(没有小数点的数)被觉得是一个i ...
- Math 数学类
/* Math 数学类, 主要是提供了很多的数学公式. abs(double a) 获取绝对值 ceil(double a) 向上取整 floor(double a) 向下取整 round(float ...
- cocos2dx 3.17.1 导演类
进入导演类的头文件,首先看到的是一些头文件的引用:CCPlatformMacros(适配),CCRef(继承的父类),CCVector(3.0以后的新向量),CCScene(场景),CCMath(数学 ...
- cocos2d-x 的两大基类
cocos2d-x 有两个重要的基类,一个管理引用计数的 Ref,别一个则定义许多基本属性的 Node. 在 cocos2d-x 中的基本概念 说到 create 函数的时候提到 cocos2d-x ...
随机推荐
- requests结合xpath爬取豆瓣最新上映电影
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ 豆瓣最新上映电影爬取 # ul = etree.tostring(ul, encoding="utf-8 ...
- spark 三种数据集的关系(一)
Catalyst Optimizer: Dataset 数据集仅可用Scala或Java.但是,我们提供了以下上下文来更好地理解Spark 2.0的方向数据集是在2015年作为Apache Spark ...
- Release和Debug的区别
Debug与Release版本的区别 Debug 和 Release 并没有本质的区别,他们只是VC预定义提供的两组编译选项的集合,编译器只是按照预定的选项行动.如果我们愿意,我们完全可以把Debug ...
- C语言 - strcmp和strncmp的编程实现及总结
一.strcmp和strncmp的编程实现及总结 1.strcmp函数的实现 要求: 原型: int strcmp(char *dest,char * src,int n); 头文件:# ...
- CMS 与 框架
Framework:框架.是整合的工具集,基于编程语言.可以帮助我们快速开发网站.比较常见的是J2EE(基于Java),Symfony2(基于PHP),Django(基于Python),Ruby on ...
- CodeForces 557C Arthur and Table STL的使用
题意:一个桌子有n条腿,每条腿有一定的长度l,和砍下的花费w,现在规定,桌子稳的条件是长度最长的腿(可多个)的数量大于长度小于它的桌子腿数量,且不存在比他还长的桌子腿,求让桌子腿稳定的最小的花费 #i ...
- 【PKUSC2019】树染色【线段树合并】【树形DP】
Description 给出一棵n个点的树,现在有m种颜色,要给每个节点染色,相邻节点不能同色. 另外有k条限制,形如x号点不能为颜色y 同一节点有可能有多条限制. 求方案数对998244353取模的 ...
- CodeForces451E Devu and Flowers
题目链接 问题分析 没有想到母函数的做法-- 其实直接看题思路挺简单的.发现如果每种花都有无限多的话,问题变得十分简单,答案就是\(s+n-1\choose n - 1\).然后发现\(n\)只有\( ...
- JS框架_(Esign.js)仿信用卡电子签名特效
百度云盘 传送门 密码:l60w 电子签名特效效果: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <m ...
- Mac开发如何处理键盘事件
Mac上输入与手机输入的不同是,Mac需要处理更多的键盘交互,因为Mac上的键盘输入会有多种快捷键组合. 代理方法处理 NSTextField #pragma mark - NSTextFieldDe ...
