Linux设备驱动工程师之路——内核链表的使用【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/forever_key/article/details/6798685
Linux设备驱动工程师之路——内核链表的使用
K-Style
转载请注明来自于衡阳师范学院08电2 K-Style http://blog.csdn.net/ayangke,QQ:843308498 邮箱:yangkeemail@qq.com
一、重要知识点
1.内核链表和普通链表的区别
内核链表是一个双向链表,但是与普通的双向链表又有所区别。内核链表中的链表元素不与特定类型相关,具有通用性。
我们先来看一幅图
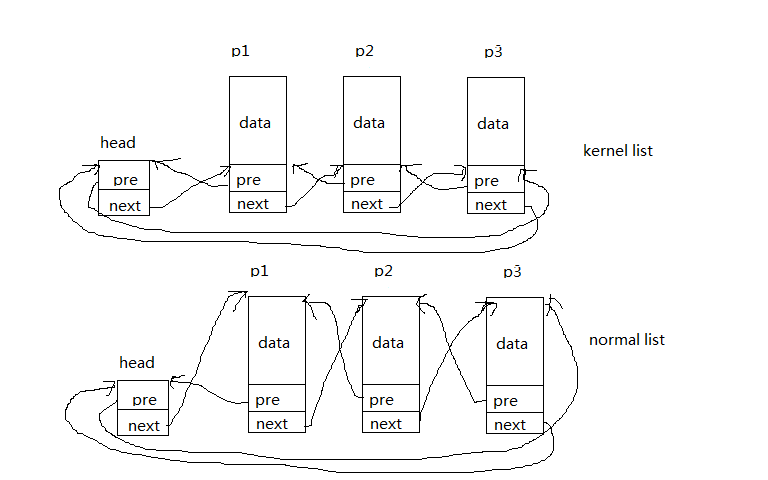
kernel list展示的是内核链表的结构,normallist展示的是普通链表的结构。head是链表头,p1,p2,p3是链表节点。从图中可以看出普通链表的p1的next指针是指向的结构体p2的地址,p2的pre指针指向p1结构体的地址。而内核链表的p1的next指向的是p2结构体中包含pre和next部分的地址,的p2的pre指向的是p1结构体中包含pre和next部分的地址。依此类推,这就是区别。内核结构元素不与特定类型结构相关,任何结构体都可通过内核的添加成为链表中的节点。
2.内核链表的具体操作
链表数据结构的定义
structlist_head
{
struct list_head *next, *prev;
}
初始化链表头
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list_head*head)
插入节点
list_add(structlist_head *new, struct list_head *head)
list_add_tail(structlist_head *new, sturct list_head *head)
第一个函数在head后面插入一个节点
第二个函数在链表尾部插入一个节点
删除节点:
list_del(structlist_head *entry)
提取数据结构:
list_entry(ptr,type, member)
ptr为已知节点指针ptr,type为节点结构体类型,member为节点指针的type结构体中的名字。返回type结构体的指针。
遍历:
list for each(structlist_head *ops, struct list_head *head)
从head开始遍历每个节点,节点指针保存在ops里面。
二、实例
- #include <linux/kernel.h>
- #include <linux/module.h>
- #include <linux/init.h>
- #include <linux/slab.h>
- #include <linux/list.h>
- MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- MODULE_AUTHOR("David Xie");
- MODULE_DESCRIPTION("ListModule");
- MODULE_ALIAS("List module");
- struct student
- {
- char name[100];
- int num;
- struct list_head list;
- };
- struct student *pstudent;
- struct student *tmp_student;
- struct list_head student_list;
- struct list_head *pos;
- int mylist_init()
- {
- inti = 0;
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&student_list);
- pstudent= kmalloc(sizeof(struct student)*5,GFP_KERNEL);
- memset(pstudent,0,sizeof(structstudent)*5);
- for(i=0;i<5;i++)
- {
- sprintf(pstudent[i].name,"Student%d",i+1);
- pstudent[i].num= i+1;
- list_add(&(pstudent[i].list), &student_list);
- }
- list_for_each(pos,&student_list)
- {
- tmp_student= list_entry(pos,struct student,list);
- printk("<0>student%d name: %s\n",tmp_student->num,tmp_student->name);
- }
- return0;
- }
- void mylist_exit()
- {
- inti ;
- for(i=0;i<5;i++)
- {
- list_del(&(pstudent[i].list));
- }
- kfree(pstudent);
- }
- module_init(mylist_init);
- module_exit(mylist_exit);
Linux设备驱动工程师之路——内核链表的使用【转】的更多相关文章
- linux设备驱动归纳总结(一)内核的相关基础概念【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25014876-id-59413.html linux设备驱动归纳总结(一):内核的相关基础概念 xxxxxxxxxxxxxx ...
- 转:Linux设备驱动开发(1):内核基础概念
一.linux设备驱动的作用 内核:用于管理软硬件资源,并提供运行环境.如分配4G虚拟空间等. linux设备驱动:是连接硬件和内核之间的桥梁. linux系统按个人理解可按下划分: 应用层:包括PO ...
- 【Linux开发】linux设备驱动归纳总结(一):内核的相关基础概念
linux设备驱动归纳总结(一):内核的相关基础概念 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx ...
- 《Linux设备驱动开发具体解释(第3版)》(即《Linux设备驱动开发具体解释:基于最新的Linux 4.0内核》)网购链接
<Linux设备驱动开发具体解释:基于最新的Linux 4.0内核> china-pub spm=a1z10.3-b.w4011-10017777404.30.kvceXB&i ...
- linux设备驱动归纳总结(七):1.时间管理与内核延时【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25014876-id-100005.html linux设备驱动归纳总结(七):1.时间管理与内核延时 xxxxxxxxxxx ...
- (转载)小白的linux设备驱动归纳总结(一):内核的相关基础概念---学习总结
1. 学习总结 小白的博客讲的linux内核驱动这一块的东西比较基础,因此想通过学习他的博客,搭配着看书的方式来学习linux内核和驱动.我会依次更新在学习小白的博客的过程的感悟和体会. 2.1 内核 ...
- 【Linux开发】linux设备驱动归纳总结(七):1.时间管理与内核延时
linux设备驱动归纳总结(七):1.时间管理与内核延时 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx ...
- 【Linux开发】linux设备驱动归纳总结(七):2.内核定时器
linux设备驱动归纳总结(七):2.内核定时器 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx ...
- linux 设备驱动概述
linux 设备驱动概述 目前,Linux软件工程师大致可分为两个层次: (1)Linux应用软件工程师(Application Software Engineer): 主要利用C库函数和 ...
随机推荐
- css中的盒子模型
css中的盒子模型 css中的盒子模型,有两种,一种是“标准 W3C 盒子模型”,另外一种是IE盒子模型. 1.w3c盒子模型 从图中可以看出:w3c盒子模型的范围包括了:margin,borde ...
- 微信公众平台开发(110) 微信连Wi-Fi
关键字:微信公众平台 微信连Wi-Fi 微信 WiFi 硬件鉴权作者:方倍工作室 原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/txw1958/p/weixin-wifi.html 微信连Wi- ...
- 深度实践KVM笔记
深度实践KVM笔记 libvirt(virt-install,API,服务,virsh)->qemu(qemu-kvm进程,qemu-img)->KVM虚拟机->kvm.ko 内核模 ...
- MySQL之数据类型与操作数据表
上节回顾 一.数据类型 什么是数据类型? 数据类型是指列.存储过程参数.表达式和局部变量的数据特征,它决定了数据的存储格式,代表了不同的信息类型. 所谓数据类型,最直接的理解就是我们有些是存储数字的, ...
- glusterFS安装维护文档
.规划: .依赖包 yum install libibverbs librdmacm xfsprogs nfs-utils rpcbind libaio liblvm2app lvm2-devel l ...
- cocos2dx 3.x(获取当前系统时间)
// // MainScene.cpp // helloworld // // Created by apple on 16/10/21. // // #include "MainScene ...
- ios-点击图片放大,背景变半透明
在view中点击一个图片,图片放大,背景变半透明,图片不会变透明的效果图如下 思路:图片框是一个按钮,监听点击事件. 当点击图片后:改变图片的frame,使图片放大,并且在controller.vie ...
- RadioButton 组,ComboBox用法:
RadioButton 组 final ToggleGroup group = new ToggleGroup(); final RadioButton rb1 = new RadioButton(& ...
- FTP规范
FTP协议命令+返回值+返回值解析 FTP message format:FTP commands are Telnet strings terminated by the Telnet end of ...
- Fixed 鸟粪一样的TreeView下的NodeMouseDoubleClick Bug
private void treeView1_NodeMouseDoubleClick(object sender, TreeNodeMouseClickEventArgs e) { Rectangl ...
