最小二乘法多项式拟合的Java实现
背景
由项目中需要根据一些已有数据学习出一个y=ax+b的一元二项式,给定了x,y的一些样本数据,通过梯度下降或最小二乘法做多项式拟合得到a、b,解决该问题时,首先想到的是通过spark mllib去学习,可是结果并不理想:少量的文档,参数也很难调整。于是转变了解决问题的方式:采用了最小二乘法做多项式拟合。
最小二乘法多项式拟合描述下: (以下参考:https://blog.csdn.net/funnyrand/article/details/46742561)
假设给定的数据点和其对应的函数值为 (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ... (xm, ym),需要做的就是得到一个多项式函数f(x) = a0 * x + a1 * pow(x, 2) + .. + an * pow(x, n),使其对所有给定x所计算出的f(x)与实际对应的y值的差的平方和最小,也就是计算多项式的各项系数 a0, a1, ... an.
根据最小二乘法的原理,该问题可转换为求以下线性方程组的解:Ga = B,
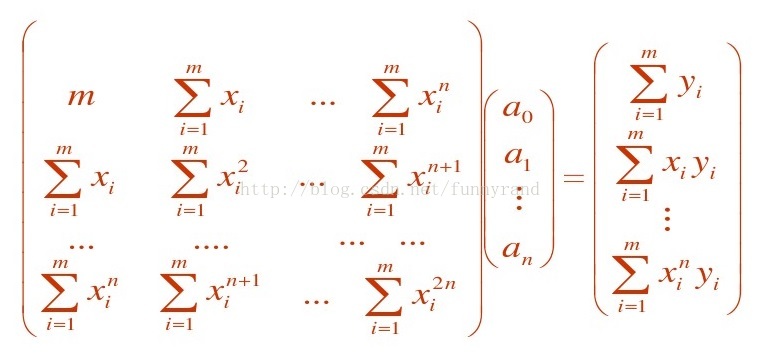
所以从编程的角度来说需要做两件事情:
1)确定线性方程组的各个系数:
确定系数比较简单,对给定的 (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ... (xm, ym) 做相应的计算即可,相关代码:
private void compute() {
...
}
2)解线性方程组:
解线性方程组稍微复杂,这里用到了高斯消元法,基本思想是通过递归做矩阵转换,逐渐减少求解的多项式系数的个数,相关代码:
private double[] calcLinearEquation(double[][] a, double[] b) {
...
}
Java代码
public class JavaLeastSquare {
private double[] x;
private double[] y;
private double[] weight;
private int n;
private double[] coefficient;
/**
* Constructor method.
* @param x Array of x
* @param y Array of y
* @param n The order of polynomial
*/
public JavaLeastSquare(double[] x, double[] y, int n) {
if (x == null || y == null || x.length < 2 || x.length != y.length
|| n < 2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"IllegalArgumentException occurred.");
}
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.n = n;
weight = new double[x.length];
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
weight[i] = 1;
}
compute();
}
/**
* Constructor method.
* @param x Array of x
* @param y Array of y
* @param weight Array of weight
* @param n The order of polynomial
*/
public JavaLeastSquare(double[] x, double[] y, double[] weight, int n) {
if (x == null || y == null || weight == null || x.length < 2
|| x.length != y.length || x.length != weight.length || n < 2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"IllegalArgumentException occurred.");
}
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.n = n;
this.weight = weight;
compute();
}
/**
* Get coefficient of polynomial.
* @return coefficient of polynomial
*/
public double[] getCoefficient() {
return coefficient;
}
/**
* Used to calculate value by given x.
* @param x x
* @return y
*/
public double fit(double x) {
if (coefficient == null) {
return 0;
}
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < coefficient.length; i++) {
sum += Math.pow(x, i) * coefficient[i];
}
return sum;
}
/**
* Use Newton's method to solve equation.
* @param y y
* @return x
*/
public double solve(double y) {
return solve(y, 1.0d);
}
/**
* Use Newton's method to solve equation.
* @param y y
* @param startX The start point of x
* @return x
*/
public double solve(double y, double startX) {
final double EPS = 0.0000001d;
if (coefficient == null) {
return 0;
}
double x1 = 0.0d;
double x2 = startX;
do {
x1 = x2;
x2 = x1 - (fit(x1) - y) / calcReciprocal(x1);
} while (Math.abs((x1 - x2)) > EPS);
return x2;
}
/*
* Calculate the reciprocal of x.
* @param x x
* @return the reciprocal of x
*/
private double calcReciprocal(double x) {
if (coefficient == null) {
return 0;
}
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < coefficient.length; i++) {
sum += i * Math.pow(x, i - 1) * coefficient[i];
}
return sum;
}
/*
* This method is used to calculate each elements of augmented matrix.
*/
private void compute() {
if (x == null || y == null || x.length <= 1 || x.length != y.length
|| x.length < n || n < 2) {
return;
}
double[] s = new double[(n - 1) * 2 + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < x.length; j++) {
s[i] += Math.pow(x[j], i) * weight[j];
}
}
double[] b = new double[n];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < x.length; j++) {
b[i] += Math.pow(x[j], i) * y[j] * weight[j];
}
}
double[][] a = new double[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
a[i][j] = s[i + j];
}
}
// Now we need to calculate each coefficients of augmented matrix
coefficient = calcLinearEquation(a, b);
}
/*
* Calculate linear equation.
* The matrix equation is like this: Ax=B
* @param a two-dimensional array
* @param b one-dimensional array
* @return x, one-dimensional array
*/
private double[] calcLinearEquation(double[][] a, double[] b) {
if (a == null || b == null || a.length == 0 || a.length != b.length) {
return null;
}
for (double[] x : a) {
if (x == null || x.length != a.length)
return null;
}
int len = a.length - 1;
double[] result = new double[a.length];
if (len == 0) {
result[0] = b[0] / a[0][0];
return result;
}
double[][] aa = new double[len][len];
double[] bb = new double[len];
int posx = -1, posy = -1;
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= len; j++)
if (a[i][j] != 0.0d) {
posy = j;
break;
}
if (posy != -1) {
posx = i;
break;
}
}
if (posx == -1) {
return null;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
if (i == posx) {
continue;
}
bb[count] = b[i] * a[posx][posy] - b[posx] * a[i][posy];
int count2 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= len; j++) {
if (j == posy) {
continue;
}
aa[count][count2] = a[i][j] * a[posx][posy] - a[posx][j] * a[i][posy];
count2++;
}
count++;
}
// Calculate sub linear equation
double[] result2 = calcLinearEquation(aa, bb);
// After sub linear calculation, calculate the current coefficient
double sum = b[posx];
count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
if (i == posy) {
continue;
}
sum -= a[posx][i] * result2[count];
result[i] = result2[count];
count++;
}
result[posy] = sum / a[posx][posy];
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JavaLeastSquare eastSquareMethod = new JavaLeastSquare(
new double[]{
2, 14, 20, 25, 26, 34,
47, 87, 165, 265, 365, 465,
565, 665
},
new double[]{
0.7 * 2 + 20 + 0.4,
0.7 * 14 + 20 + 0.5,
0.7 * 20 + 20 + 3.4,
0.7 * 25 + 20 + 5.8,
0.7 * 26 + 20 + 8.27,
0.7 * 34 + 20 + 0.4,
0.7 * 47 + 20 + 0.1,
0.7 * 87 + 20,
0.7 * 165 + 20,
0.7 * 265 + 20,
0.7 * 365 + 20,
0.7 * 465 + 20,
0.7 * 565 + 20,
0.7 * 665 + 20
},
2);
double[] coefficients = eastSquareMethod.getCoefficient();
for (double c : coefficients) {
System.out.println(c);
}
// 测试
System.out.println(eastSquareMethod.fit(4));
}
}
输出结果:
com.datangmobile.biz.leastsquare.JavaLeastSquare
22.27966881467629
0.6952475907448203
25.06065917765557
Process finished with exit code 0
使用开源库
也可使用Apache开源库commons math(http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-math/userguide/fitting.html),提供的功能更强大:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-math3</artifactId>
<version>3.5</version>
</dependency>
实现代码:
import org.apache.commons.math3.fitting.PolynomialCurveFitter;
import org.apache.commons.math3.fitting.WeightedObservedPoints; public class WeightedObservedPointsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final WeightedObservedPoints obs = new WeightedObservedPoints();
obs.add(2, 0.7 * 2 + 20 + 0.4);
obs.add(12, 0.7 * 12 + 20 + 0.3);
obs.add(32, 0.7 * 32 + 20 + 3.4);
obs.add(34 , 0.7 * 34 + 20 + 5.8);
obs.add(58 , 0.7 * 58 + 20 + 8.4);
obs.add(43 , 0.7 * 43 + 20 + 0.28);
obs.add(27 , 0.7 * 27 + 20 + 0.4); // Instantiate a two-degree polynomial fitter.
final PolynomialCurveFitter fitter = PolynomialCurveFitter.create(2); // Retrieve fitted parameters (coefficients of the polynomial function).
final double[] coeff = fitter.fit(obs.toList());
for (double c : coeff) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
}
测试输出结果:
20.47425047847121
0.6749744063035112
0.002523043547711147
Process finished with exit code 0
使用org.ujmp(矩阵)实现最小二乘法:
pom.xml中需要引入org.ujmp
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.dtgroup</groupId>
<artifactId>dtgroup</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <repositories>
<repository>
<id>limaven</id>
<name>aliyun maven</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
<layout>default</layout>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ujmp</groupId>
<artifactId>ujmp-core</artifactId>
<version>0.3.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
java代码:
/**
* 采用最小二乘法多项式拟合方式,获取多项式的系数。
* @param sampleCount 采样点个数
* @param fetureCount 多项式的系数
* @param samples 采样点集合
* **/
private static void leastsequare(int sampleCount, int fetureCout, List<Sample> samples) {
// 构件 2*2矩阵 存储X,元素值都为1.0000的矩阵
Matrix matrixX = DenseMatrix.Factory.ones(sampleCount, fetureCout); for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) {
matrixX.setAsDouble(samples.get(i).getX(), i, 1);
} // System.out.println(matrixX);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
// 构件 2*2矩阵 存储X
Matrix matrixY = DenseMatrix.Factory.ones(sampleCount, 1); for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) {
matrixY.setAsDouble(samples.get(i).getY(), i, 0);
}
// System.out.println(matrixY); // 对X进行转置
Matrix matrixXTrans = matrixX.transpose();
// System.out.println(matrixXTrans); // 乘积运算:x*转转置后x:matrixXTrans*matrixX
Matrix matrixMtimes = matrixXTrans.mtimes(matrixX);
System.out.println(matrixMtimes); System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
// 求逆
Matrix matrixMtimesInv = matrixMtimes.inv();
System.out.println(matrixMtimesInv); // x转置后结果*求逆结果
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
Matrix matrixMtimesInvMtimes = matrixMtimesInv.mtimes(matrixXTrans);
System.out.println(matrixMtimesInvMtimes); System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
Matrix theta = matrixMtimesInvMtimes.mtimes(matrixY);
System.out.println(theta);
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* y=ax+b
*
* a(0,1] b[5,20]
*
* x[0,500] y>=5
*/
// y= 0.8d*x+15
// 当x不变动时,y对应有多个值;此时把y求均值。
List<Sample> samples = new ArrayList<Sample>();
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 1 + 15 + 1, 1d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 4 + 15 + 0.8, 4d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 3 + 15 + 0.7, 3d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 24 + 15 + 0.4, 24d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 5 + 15 + 0.3, 5d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 10 + 15 + 0.4, 10d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 14 + 15 + 0.2, 14d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 7 + 15 + 0.3, 7d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 1000 + 23 + 0.3, 70d));
int sampleCount = samples.size();
int fetureCout = 2;
leastsequare(sampleCount, fetureCout, samples);
}
过滤样本中的噪点:
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* y=ax+b
*
* a(0,1] b[5,20]
*
* x[0,500] y>=5
*/
// y= 0.8d*x+15
// 当x不变动时,y对应有多个值;此时把y求均值。
List<Sample> samples = new ArrayList<Sample>();
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 1 + 15 + 1, 1d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 4 + 15 + 0.8, 4d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 3 + 15 + 0.7, 3d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 24 + 15 + 0.4, 24d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 5 + 15 + 0.3, 5d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 10 + 15 + 0.4, 10d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 14 + 15 + 0.2, 14d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 7 + 15 + 0.3, 7d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 1000 + 23 + 0.3, 70d));
// samples = filterSample(samples);
sortSample(samples);
FilterSampleByGradientResult result = filterSampleByGradient(0, samples);
while (result.isComplete() == false) {
List<Sample> newSamples=result.getSamples();
sortSample(newSamples);
result = filterSampleByGradient(result.getIndex(), newSamples);
}
samples = result.getSamples();
for (Sample sample : samples) {
System.out.println(sample);
}
int sampleCount = samples.size();
int fetureCout = 2;
leastsequare(sampleCount, fetureCout, samples);
}
/**
* 对采样点进行排序,按照x排序,升序排列
* @param samples 采样点集合
* **/
private static void sortSample(List<Sample> samples) {
samples.sort(new Comparator<Sample>() {
public int compare(Sample o1, Sample o2) {
if (o1.getX() > o2.getX()) {
return 1;
} else if (o1.getX() <= o2.getX()) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
});
}
/**
* 过滤采样点中的噪点(采样过滤方式:double theta=(y2-y1)/(x2-x1),theta就是一个斜率,根据该值范围来过滤。)
* @param index 记录上次过滤索引
* @param samples 采样点集合(将从其中过滤掉噪点)
* **/
private static FilterSampleByGradientResult filterSampleByGradient(int index, List<Sample> samples) {
int sampleSize = samples.size();
for (int i = index; i < sampleSize - 1; i++) {
double delta_x = samples.get(i).getX() - samples.get(i + 1).getX();
double delta_y = samples.get(i).getY() - samples.get(i + 1).getY();
// 距离小于2米
if (Math.abs(delta_x) < 1) {
double newY = (samples.get(i).getY() + samples.get(i + 1).getY()) / 2;
double newX = samples.get(i).getX();
samples.remove(i);
samples.remove(i + 1);
samples.add(new Sample(newY, newX));
return new FilterSampleByGradientResult(false, i, samples);
} else {
double gradient = delta_y / delta_x;
if (gradient > 1.5) {
if (i == 0) {
// double newY = (samples.get(i).getY() + samples.get(i
// + 1).getY()) / 2;
// double newX = (samples.get(i).getX() + samples.get(i
// + 1).getX()) / 2;
// samples.remove(i);
// samples.add(new Sample(newY, newX));
} else {
samples.remove(i + 1);
}
return new FilterSampleByGradientResult(false, i, samples);
}
}
}
return new FilterSampleByGradientResult(true, 0, samples);
}
使用距离来处理过滤:
private static List<Sample> filterSample(List<Sample> samples) {
// x={x1,x2,x3...xn}
// u=E(x) ---x的期望(均值)为 u
// 6=sqrt(pow((x1-u),2)+pow((x2-u),2)+pow((x3-u),2)+...+pow((xn-u),2))
// 6为x的标准差,标准差=sqrt(方差)
// 剔除噪点可以采用:
// 若xi不属于(u-3*6,u+3*6),则认为它是噪点。
// 另外一种方案,对x/y都做上边的处理,之后如果两个结果为and 或者 or操作来选取是否剔除。
// 用点的方式来过滤数据,求出一个中值点,求其他点到该点的距离。
int sampleCount = samples.size();
double sumX = 0d;
double sumY = 0d;
for (Sample sample : samples) {
sumX += sample.getX();
sumY += sample.getY();
}
// 求中心点
double centerX = (sumX / sampleCount);
double centerY = (sumY / sampleCount);
List<Double> distanItems = new ArrayList<Double>();
// 计算出所有点距离该中心点的距离
for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) {
Sample sample = samples.get(i);
Double xyPow2 = Math.pow(sample.getX() - centerX, 2) + Math.pow(sample.getY() - centerY, 2);
distanItems.add(Math.sqrt(xyPow2));
}
// 以下对根据距离(所有点距离中心点的距离)进行筛选
double sumDistan = 0d;
double distanceU = 0d;
for (Double distance : distanItems) {
sumDistan += distance;
}
distanceU = sumDistan / sampleCount;
double deltaPowSum = 0d;
double distanceTheta = 0d;
// sqrt(pow((x1-u),2)+pow((x2-u),2)+pow((x3-u),2)+...+pow((xn-u),2))
for (Double distance : distanItems) {
deltaPowSum += Math.pow((distance - distanceU), 2);
}
distanceTheta = Math.sqrt(deltaPowSum);
// 剔除噪点可以采用:
// 若xi不属于(u-3*6,u+3*6),则认为它是噪点。
double minDistance = distanceU - 0.5 * distanceTheta;
double maxDistance = distanceU + 0.5 * distanceTheta;
List<Integer> willbeRemoveIdxs = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = distanItems.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Double distance = distanItems.get(i);
if (distance <= minDistance || distance >= maxDistance) {
willbeRemoveIdxs.add(i);
System.out.println("will be remove " + i);
}
}
for (int willbeRemoveIdx : willbeRemoveIdxs) {
samples.remove(willbeRemoveIdx);
}
return samples;
}
实际业务测试:
package com.zjanalyse.spark.maths; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List; import org.ujmp.core.DenseMatrix;
import org.ujmp.core.Matrix; public class LastSquare {
/**
* y=ax+b a(0,1] b[5,20] x[0,500] y>=5
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// y= 0.8d*x+15
// 当x不变动时,y对应有多个值;此时把y求均值。
List<Sample> samples = new ArrayList<Sample>();
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 11 + 15 + 1, 11d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 24 + 15 + 0.8, 24d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 33 + 15 + 0.7, 33d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 24 + 15 + 0.4, 24d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 47 + 15 + 0.3, 47d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 60 + 15 + 0.4, 60d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 14 + 15 + 0.2, 14d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 57 + 15 + 0.3, 57d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 70 + 60 + 0.3, 70d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 80 + 60 + 0.3, 80d));
samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 40 + 30 + 0.3, 40d)); sortSample(samples);
System.out.println("原始样本数据");
for (Sample sample : samples) {
System.out.println(sample);
} System.out.println("开始“所有点”通过“业务数据取值范围”剔除:");
// 按照业务过滤。。。
filterByBusiness(samples);
System.out.println("结束“所有点”通过“业务数据取值范围”剔除:"); for (Sample sample : samples) {
System.out.println(sample);
} int sampleCount = samples.size();
int fetureCout = 2;
System.out.println("第一次拟合。。。");
Matrix theta = leastsequare(sampleCount, fetureCout, samples); double wear_loss = theta.getAsDouble(0, 0);
double path_loss = theta.getAsDouble(1, 0); System.out.println("wear loss " + wear_loss);
System.out.println("path loss " + path_loss); System.out.println("开始“所有点”与“第一多项式拟合结果直线方式距离方差”剔除:");
samples = filterSample(wear_loss, path_loss, samples);
System.out.println("结束“所有点”与“第一多项式拟合结果直线方式距离方差”剔除:"); for (Sample sample : samples) {
System.out.println(sample);
} System.out.println("第二次拟合。。。");
sampleCount = samples.size();
fetureCout = 2; if (sampleCount >= 2) {
theta = leastsequare(sampleCount, fetureCout, samples); wear_loss = theta.getAsDouble(0, 0);
path_loss = theta.getAsDouble(1, 0); System.out.println("wear loss " + wear_loss);
System.out.println("path loss " + path_loss);
}
System.out.println("complete...");
} /**
* 按照业务过滤有效值范围
*/
private static void filterByBusiness(List<Sample> samples) {
for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) {
double x = samples.get(i).getX();
double y = samples.get(i).getY();
if (x >= 500) {
System.out.println(x + " x值超出有效值范围[0,500)");
samples.remove(i);
i--;
}
// y= 0.8d*x+15
else if (y < 0 * x + 5 || y > 1 * x + 30) {
System.out.println(
y + " y值超出有效值范围[(0*x+5),(1*x+30)]其中x=" + x + ",也就是:[" + (0 * x + 5) + "," + (1 * x + 30) + ")");
samples.remove(i);
i--;
}
}
} /**
* Description 点到直线的距离
*
* @param x1
* 点横坐标
* @param y1
* 点纵坐标
* @param A
* 直线方程一般式系数A
* @param B
* 直线方程一般式系数B
* @param C
* 直线方程一般式系数C
* @return 点到之间的距离
* @see 点0,1到之前y=x+0的距离 <br>
* double distance = getDistanceOfPerpendicular(0,0, -1, 1, 0);<br>
* System.out.println(distance);<br>
*/
private static double getDistanceOfPerpendicular(double x1, double y1, double A, double B, double C) {
double distance = Math.abs((A * x1 + B * y1 + C) / Math.sqrt(A * A + B * B));
return distance;
} private static List<Sample> filterSample(double wear_loss, double path_loss, List<Sample> samples) {
// x={x1,x2,x3...xn}
// u=E(x) ---x的期望(均值)为 u
// 6=sqrt(pow((x1-u),2)+pow((x2-u),2)+pow((x3-u),2)+...+pow((xn-u),2))
// 6为x的标准差,标准差=sqrt(方差)
// 剔除噪点可以采用:
// 若xi不属于(u-3*6,u+3*6),则认为它是噪点。 // 求出所有点距离第一次拟合结果的直线方程的距离
int sampleCount = samples.size();
List<Double> distanItems = new ArrayList<Double>();
// 计算出所有点距离该中心点的距离
for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) {
Sample sample = samples.get(i);
double distance = getDistanceOfPerpendicular(sample.getX(), sample.getY(), path_loss, -1, wear_loss);
distanItems.add(Math.sqrt(distance));
} // 以下对根据距离(所有点距离中心点的距离)进行筛选
double sumDistan = 0d;
double distanceU = 0d;
for (Double distance : distanItems) {
sumDistan += distance;
}
distanceU = sumDistan / sampleCount; double deltaPowSum = 0d;
double distanceTheta = 0d;
// sqrt(pow((x1-u),2)+pow((x2-u),2)+pow((x3-u),2)+...+pow((xn-u),2))
for (Double distance : distanItems) {
deltaPowSum += Math.pow((distance - distanceU), 2);
}
distanceTheta = Math.sqrt(deltaPowSum); // 剔除噪点可以采用:
// 若xi不属于(u-3*6,u+3*6),则认为它是噪点。
double minDistance = distanceU - 0.25 * distanceTheta;
double maxDistance = distanceU + 0.25 * distanceTheta;
List<Integer> willbeRemoveIdxs = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = distanItems.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Double distance = distanItems.get(i);
if (distance <= minDistance || distance >= maxDistance) {
System.out.println(distance + " out of range [" + minDistance + "," + maxDistance + "]");
willbeRemoveIdxs.add(i);
} else {
System.out.println(distance);
}
} for (int willbeRemoveIdx : willbeRemoveIdxs) {
Sample sample = samples.get(willbeRemoveIdx);
System.out.println("remove " + sample);
samples.remove(willbeRemoveIdx);
} return samples;
} /**
* 对采样点进行排序,按照x排序,升序排列
*
* @param samples
* 采样点集合
**/
private static void sortSample(List<Sample> samples) {
samples.sort(new Comparator<Sample>() {
public int compare(Sample o1, Sample o2) {
if (o1.getX() > o2.getX()) {
return 1;
} else if (o1.getX() <= o2.getX()) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
});
} /**
* Description 采用最小二乘法多项式拟合方式,获取多项式的系数。
*
* @param sampleCount
* 采样点个数
* @param fetureCount
* 多项式的系数
* @param samples
* 采样点集合
**/
private static Matrix leastsequare(int sampleCount, int fetureCout, List<Sample> samples) {
// 构件 2*2矩阵 存储X,元素值都为1.0000的矩阵
Matrix matrixX = DenseMatrix.Factory.ones(sampleCount, fetureCout); for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) {
matrixX.setAsDouble(samples.get(i).getX(), i, 1);
} // System.out.println(matrixX);
// System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
// 构件 2*2矩阵 存储X
Matrix matrixY = DenseMatrix.Factory.ones(sampleCount, 1); for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) {
matrixY.setAsDouble(samples.get(i).getY(), i, 0);
}
// System.out.println(matrixY); // 对X进行转置
Matrix matrixXTrans = matrixX.transpose();
// System.out.println(matrixXTrans); // 乘积运算:x*转转置后x:matrixXTrans*matrixX
Matrix matrixMtimes = matrixXTrans.mtimes(matrixX);
// System.out.println(matrixMtimes); // System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
// 求逆
Matrix matrixMtimesInv = matrixMtimes.inv();
// System.out.println(matrixMtimesInv); // x转置后结果*求逆结果
// System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
Matrix matrixMtimesInvMtimes = matrixMtimesInv.mtimes(matrixXTrans);
// System.out.println(matrixMtimesInvMtimes); // System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
Matrix theta = matrixMtimesInvMtimes.mtimes(matrixY);
// System.out.println(theta); return theta;
}
}
最小二乘法多项式拟合的Java实现的更多相关文章
- matlab最小二乘法数据拟合函数详解
定义: 最小二乘法(又称最小平方法)是一种数学优化技术.它通过最小化误差的平方和寻找数据的最佳函数匹配.利用最小二乘法可 以简便地求得未知的数据,并使得这些求得的数据与实际数据之间误差的平方和为最小. ...
- 数据拟合:多项式拟合polynomial curve fitting
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/49804441 常见的曲线拟合方法 1.使偏差绝对值之和最小 2.使偏差绝对值最大的最小 3 ...
- 最小二乘法多项式曲线拟合原理与实现 zz
概念 最小二乘法多项式曲线拟合,根据给定的m个点,并不要求这条曲线精确地经过这些点,而是曲线y=f(x)的近似曲线y= φ(x). 原理 [原理部分由个人根据互联网上的资料进行总结,希望对大家能有用] ...
- matlab练习程序(最小二乘多项式拟合)
最近在分析一些数据,就是数据拟合的一些事情,用到了matlab的polyfit函数,效果不错. 因此想了解一下这个多项式具体是如何拟合出来的,所以就搜了相关资料. 这个文档介绍的还不错,我估计任何一本 ...
- numpy多项式拟合
关于解决使用numpy.ployfit进行多项式拟合的时候请注意数据类型,解决问题的思路就是统一把数据变成浮点型,就可以了.这是numpy里面的一个bug,非常low希望后面改善. # coding: ...
- MATLAB多项式及多项式拟合
多项式均表示为数组形式,数组元素为多项式降幂系数 1. polyval函数 求多项式在某一点或某几个点的值. p = [1,1,1];%x^2+x+1 x = [-1,0,1];y = po ...
- Matlab多项式拟合測试
x=0:0.2:4; %生成等差数列 rnd=rand(1,size(x,2))*5; %生成一组随机数 y=x.*x.*x+x.*x+6+rnd; %生成y=x^3+x^2+6函数在垂直方向5个尺度 ...
- 多项式拟合的cpp实现
当我们拥有一组散点图数据时,通常更愿意看到其走势. 对现有数据进行拟合,并输出拟合优度是常用的方法之一. 拟合结果正确性的验证,可以使用excel自带的功能. 下面是c++代码的实现: #ifndef ...
- python多项式拟合:np.polyfit 和 np.polyld
python数据拟合主要可采用numpy库,库的安装可直接用pip install numpy等. 1. 原始数据:假如要拟合的数据yyy来自sin函数,np.sin import numpy as ...
随机推荐
- IE 兼容 getElementsByClassName
getElementsByClassName 通过class获取节点,是很多新人练习原生JS都用到的,项目中也会写,当项目进行到一定程度时,测试IE低版本,忽然发现不支持的时候,瞬间感觉整个人都不好了 ...
- NGUI_Depth
四.深度(Depth)概念; 1. (1).每一个UIPanel和每一个UI控件都一定会有一个Depth,深度值大代表显示的优先级高(会趋向于在界面更上层显示) (2).Depth决定的是UI的显示层 ...
- Web开发中Listener、Filter、Servlet的初始化及调用
我们在使用Spring+SpringMVC开发项目中,web.xml中一般的配置如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8&qu ...
- maven compile启动报错
ERROR] Failed to execute goal org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.3:compile (default-co ...
- 【openvpn】转载:烂泥:ubuntu 14.04搭建OpenVPN服务器
地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ilanni/p/4681740.html (1)安装openVpn软件后.在openVpn的配置目录下添加配置文件: ca.crt client ...
- python基础学习笔记二之列表
1.列表 ①列表的创建: ②列表的查询(索引): ③列表的切片操作: 此处要注意到:返回索引0到3的元素,顾头不顾尾. ④列表的增加: s.append() #直接在结尾追加 s.insert() ...
- 【SSH/SFTP】SSH协议和SFTP
[SSH和SFTP] ■ 设置一个只允许访问部分目录的SFTP服务器 由于SSH和SFTP之间的紧密联系,一个SFTP服务器必然会导致开放一定的SSH服务,而SSH的风险显然比SFTP要大一些.自然, ...
- Android学习笔记2——shape
Android有很多特别的xml文件,如常用的selector.style以及shape,熟练使用这些xml可以是我们的项目变得更个性化. 一.子标签(corners.gradient.padding ...
- Lucene教程 -------(一、初始Lucene)
一.lucene的介绍 lucene是一个全文检索的框架,apache组织提供了一个用java实现的全文检索的开源项目.功能非常的强大,api非常简单,并且有了全文检索的功能支持可以非常方便的实现根据 ...
- 数据库(Mongodb)
1.MongoClient()函数 In [8]: import pymongo In [9]: con = pymongo.MongoClient('localhost') #建立连接 In [10 ...
