【LeetCode】426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List 解题报告 (C++)
- 作者: 负雪明烛
- id: fuxuemingzhu
- 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/
题目描述
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers as synonymous to the previous and next pointers in a doubly-linked list.
Let’s take the following BST as an example, it may help you understand the problem better:
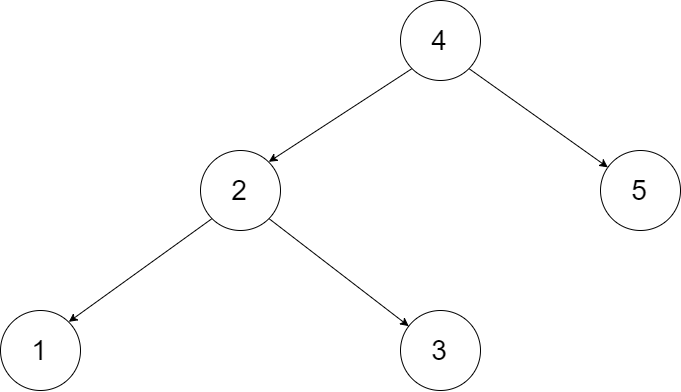
We want to transform this BST into a circular doubly linked list. Each node in a doubly linked list has a predecessor and successor. For a circular doubly linked list, the predecessor of the first element is the last element, and the successor of the last element is the first element.
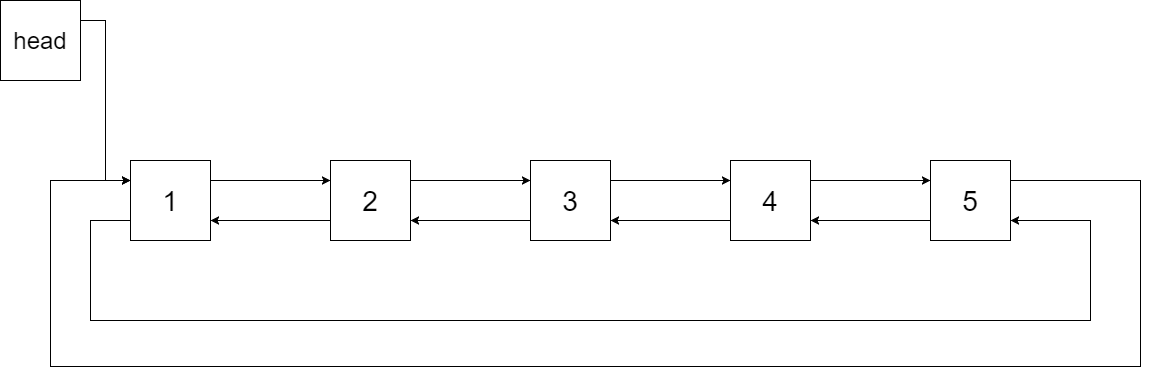
The figure below shows the circular doubly linked list for the BST above. The “head” symbol means the node it points to is the smallest element of the linked list.
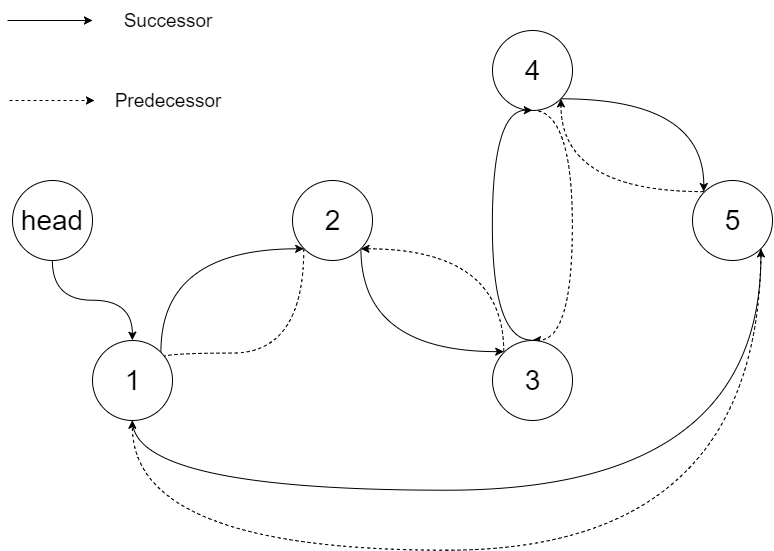
Specifically, we want to do the transformation in place. After the transformation, the left pointer of the tree node should point to its predecessor, and the right pointer should point to its successor. We should return the pointer to the first element of the linked list.
The figure below shows the transformed BST. The solid line indicates the successor relationship, while the dashed line means the predecessor relationship.
题目大意
将一个BST转换为有序的双向链表,并返回该双向链表的头指针。
解题方法
递归
看到BST就想到中序遍历是有序的。
中序遍历有两种做法:递归和迭代。递归的方式做法比较常见。
这里相对于普通的中序遍历的修改是对当前节点进行判断,如果有pre的话需要修改pre和当前node的指针。head节点的定义是左下角节点,也是真正处理的第一个节点。last节点是最后的一个节点。
当递归结束之后,需要把head和last拼接到一起。
C++代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (!root) return nullptr;
Node* head = nullptr;
Node* pre = nullptr;
Node* last = nullptr;
inorder(root, head, pre, last);
last->right = head;
head->left = last;
return head;
}
void inorder(Node* node, Node* &head, Node* &pre, Node* &last) {
if (!node) return;
inorder(node->left, head, pre, last);
if (pre) {
pre->right = node;
node->left = pre;
}
pre = node;
if (!head)
head = node;
last = node;
inorder(node->right, head, pre, last);
}
};
迭代
迭代的方法是通过一个栈来实现的,先把最左下角的节点放入栈中,然后依次出栈,出栈的时候处理该栈,并且把这个节点的右节点放入栈中。
C++代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (!root) return nullptr;
Node* head = nullptr;
Node* pre = nullptr;
Node* last = nullptr;
stack<Node*> st;
Node* p = root;
while (!st.empty() || p) {
if (p) {
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
} else {
Node* node = st.top(); st.pop();
if (!node) continue;
p = node->right;
if (!head)
head = node;
if (pre) {
pre->right = node;
node->left = pre;
}
pre = node;
last = node;
}
}
last->right = head;
head->left = last;
return head;
}
};
相似题目:94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
参考资料:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/solution/liang-chong-jie-fa-by-jason-2-11/
日期
2019 年 9 月 21 日 —— 莫生气,我若气病谁如意
【LeetCode】426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List 解题报告 (C++)的更多相关文章
- LeetCode 426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/ 题目: C ...
- [leetcode]426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List二叉搜索树转有序双向链表
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers ...
- 426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List把bst变成双向链表
[抄题]: Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right po ...
- [LC] 426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers ...
- [LeetCode] Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List 将二叉搜索树转为有序双向链表
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers ...
- LeetCode426.Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List
题目 Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right point ...
- [LeetCode] 272. Closest Binary Search Tree Value II 最近的二叉搜索树的值 II
Given a non-empty binary search tree and a target value, find k values in the BST that are closest t ...
- 【LeetCode】430. Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]430. Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): LeetCode 作者: 负雪明烛 id: ...
- [LeetCode#272] Closest Binary Search Tree Value II
Problem: Given a non-empty binary search tree and a target value, find k values in the BST that are ...
随机推荐
- Anaconda 安装与卸载
Anaconda是一个免费开源的Python和R语言的发行版本,用于计算科学(数据科学.机器学习.大数据处理和预测分析),Anaconda致力于简化软件包管理系统和部署.Anaconda的包使用软件包 ...
- RabbitMQ消息中介之Python使用
本文介绍RabbitMQ在python下的基本使用 1. RabbitMQ安装,安装RabbitMQ需要预安装erlang语言,Windows直接下载双击安装即可 RabbitMQ下载地址:http: ...
- php导出pdf,dompdf中文字体乱码解决办法(特别是代码迁移引起的乱码)
dompdf\lib\fonts\dompdf_font_family_cache.php记住这个文件里面存放的是字体生成的缓存,迁移时如果覆盖了这个文件会导致乱码而且很难找到出错的地方,相信我... ...
- Mybatis-运行原理
一.mybatis分层图 二.运行流程 根据全局配置文件创建sqlSessionFactory对象 根据全局配置文件的io流来构建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象: 解析(XmlC ...
- ganglia -api
setup 命令: virtualenv ve source ve/bin/activate pip install -r requirements.txt python ganglia/gangli ...
- 使用NSURLSessionDownloadTask实现大文件下载-监听下载进度
- 5.1 涉及知识点(1)创建NSURLSession并设置代理,通过NSURLSessionDownloadTask并以代理的方式来完成大文件的下载 //1.创建NSURLSession,设置代理 ...
- 收集linux网络配置信息的shell脚本
此脚本已在CentOS/ RHEL和Fedora Linux操作系统下进行测试过.可用于当前网络配置信息. 代码: #!/bin/bash # HWINF=/usr/sbin/hwinfo IFCFG ...
- 【Python】【Module】os
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录:相当于shell下cd os.curd ...
- 南京邮电大学CTF密码学之MD5-golang与php代码实现
题目内容:这里有一段丢失的md5密文 e9032???da???08????911513?0???a2 要求你还原出他并且加上nctf{}提交 已知线索 明文为: TASC?O3RJMV?WDJKX? ...
- ExecutorService 线程池详解
1.什么是ExecutorService,为什么要使用线程池? 许多服务器应用程序都面向处理来自某些远程来源的大量短小的任务,每当一个请求到达就创建一个新线程,然后在新线程中为请求服务,但是频繁创建新 ...
