C. Hongcow Builds A Nation
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Hongcow is ruler of the world. As ruler of the world, he wants to make it easier for people to travel by road within their own countries.
The world can be modeled as an undirected graph with n nodes and m edges. k of the nodes are home to the governments of the k countries that make up the world.
There is at most one edge connecting any two nodes and no edge connects a node to itself. Furthermore, for any two nodes corresponding to governments, there is no path between those two nodes. Any graph that satisfies all of these conditions is stable.
Hongcow wants to add as many edges as possible to the graph while keeping it stable. Determine the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add.
The first line of input will contain three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of vertices and edges in the graph, and the number of vertices that are homes of the government.
The next line of input will contain k integers c1, c2, ..., ck (1 ≤ ci ≤ n). These integers will be pairwise distinct and denote the nodes that are home to the governments in this world.
The following m lines of input will contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n). This denotes an undirected edge between nodes ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the graph described by the input is stable.
Output a single integer, the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add to the graph while keeping it stable.
4 1 2
1 3
1 2
2
3 3 1
2
1 2
1 3
2 3
0
For the first sample test, the graph looks like this:
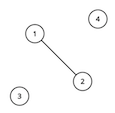 Vertices 1 and 3 are special. The optimal solution is to connect vertex 4 to vertices 1 and 2. This adds a total of 2 edges. We cannot add any more edges, since vertices 1 and 3 cannot have any path between them.
Vertices 1 and 3 are special. The optimal solution is to connect vertex 4 to vertices 1 and 2. This adds a total of 2 edges. We cannot add any more edges, since vertices 1 and 3 cannot have any path between them.
For the second sample test, the graph looks like this:
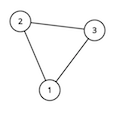 We cannot add any more edges to this graph. Note that we are not allowed to add self-loops, and the graph must be simple.
We cannot add any more edges to this graph. Note that we are not allowed to add self-loops, and the graph must be simple.
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<string.h>
3 #include<algorithm>
4 #include<queue>
5 #include<math.h>
6 #include<stdlib.h>
7 #include<stack>
8 #include<stdio.h>
9 #include<ctype.h>
10 #include<map>
11 #include<vector>
12 using namespace std;
13 typedef long long LL;
14 int c[100005];
15 int bin[100005];
16 int du[100005];
17 vector<int>vec[100005];
18 int fin(int x);
19 int ask[100005];
20 int id[100005];
21 map<int,int>my;
22 LL bian[100005];
23 int main(void)
24 {
25 int n,m,k;
26 int i,j;
27
28 while(scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&k)!=EOF)
29 {
30 my.clear();
31 memset(bian,0,sizeof(bian));
32 for(i = 0; i <100005; i++)vec[i].clear(),bin[i] = i,du[i] = 1;
33 for(i = 1; i <=k; i++)
34 scanf("%d",&c[i]);
35 while(m--)
36 {
37 int x,y;
38 scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
39 vec[x].push_back(y);
40 vec[y].push_back(x);
41 int xx = fin(x);
42 int yy = fin(y);
43 if(xx!=yy)
44 {
45 if(du[xx] > du[yy])
46 {
47 du[xx] += du[yy],bin[yy] = xx;
48 bian[xx]+=bian[yy];
49 bian[xx]++;
50 }
51 else
52 {
53 du[yy] += du[xx],bin[xx] = yy;
54 bian[yy]+=bian[xx];
55 bian[yy]++;
56 }
57 }
58 else bian[xx]++;
59 }
60 for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
61 {
62 ask[i] = fin(i);
63 }
64 LL maxx = 0;
65 LL b;
66 for(i = 1; i <= k; i++)
67 {
68 my[ask[c[i]]] = 1;
69 if(du[ask[c[i]]]>maxx)
70 {
71 maxx = max((LL)du[ask[c[i]]],maxx);
72 b = bian[ask[c[i]]];
73 }
74 }
75 LL cnt = 0;
76 LL mc = 0;
77 for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
78 {
79 if(!my.count(ask[i]))
80 {
81 cnt+=du[ask[i]];
82 my[ask[i]] = 1;
83 mc+=bian[ask[i]];
84 }
85 }//printf("%lld\n",maxx);
86 LL acc = cnt*(cnt-1)/(LL)2;
87 LL akk = acc;
88 acc+=maxx*cnt;
89 acc-=mc;
90 for(i = 1;i <= k;i++)
91 {
92 acc+=(LL)du[ask[c[i]]]*(LL)(du[ask[c[i]]]-1)/(LL)2;
93 acc-=bian[ask[c[i]]];
94 }
95 printf("%lld\n",acc);
96 }
97 return 0;
98 }
99 int fin(int x)
100 {
101 int i;
102 for(i = x; i!=bin[i];)
103 i = bin[i];
104 return i;
105 }
C. Hongcow Builds A Nation的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 744A. Hongcow Builds A Nation
A. Hongcow Builds A Nation 题意: 现在有 n 个点 ,m 条边组成了一个无向图 , 其中有 k 个特殊点, 这些特殊点之间不能连通 ,问可以再多加几条边? 因为$x^2+y ...
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) Hongcow Builds A Nation —— 图论计数
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/745/problem/C C. Hongcow Builds A Nation time limit per test 2 se ...
- Codeforces 745C:Hongcow Builds A Nation(并查集)
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/744/A 题意:在一个图里面有n个点m条边,还有k个点是受限制的,即不能从一个受限制的点走到另外一个受限制的点(有路 ...
- C. Hongcow Builds A Nation 并查集
http://codeforces.com/contest/745/problem/C 把他们并查集后, 其他没有连去government的点,全部放去同一个并查集,然后选择一个节点数最多的gover ...
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) C - Hongcow Builds A Nation
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/745/problem/C 题意:给出n个点m条边,还有k个不能连通的点,问最多能添加几条边. 要知道如果有n个点最多的边是n*( ...
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) A,B,C 暴力,模拟,并查集
A. Hongcow Learns the Cyclic Shift time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes ...
- Codeforces Round #385 //再遇状压
敲完三题挂机一小时..... 也没懂DE什么意思 rank600上了一波分... A. Hongcow Learns the Cyclic Shift 给一个字符串,每次可以把最后一个字符拿到开头 ...
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2)A B C 模拟 水 并查集
A. Hongcow Learns the Cyclic Shift time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes ...
- cf744
Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 1) <br > A.Hongcow Builds A Nation 贪心. 显然就是凑成一个最大的块即可 那么首先并查集处理已经确 ...
随机推荐
- Ansi,UTF8,Unicode,ASCII编码的区别
Ansi,UTF8,Unicode,ASCII编码的区别 近日需要不同的编码,关于上述编码,一直迷迷糊糊,查了些资料,总算大致了解了, 下面全是从网上搜来的: 1. ASCII和Ansi编码 ...
- 学习Java的第三天
一.今日收获 1.今天家里有白事,忙了一整天,也没有看更多的资料 二.今日问题 无 三.明日目标 补全今天耽误的功课,继续学习java!
- day34 前端基础之JavaScript
day34 前端基础之JavaScript ECMAScript 6 尽管 ECMAScript 是一个重要的标准,但它并不是 JavaScript 唯一的部分,当然,也不是唯一被标准化的部分.实际上 ...
- ERROR 1690 (22003): BIGINT UNSIGNED value is out of range in..的错误 [转]
问题: ERROR 1690 (22003): BIGINT UNSIGNED value is out of range in..的错误 解决方法: 把没被singed的变量临时变更signed去处 ...
- SSH服务及通过SSH方式登录linux
SSH服务及通过SSH方式登录linux 1.检查SSH服务转自:[1]Linux之sshd服务https://www.cnblogs.com/uthnb/p/9367875.html[2]Linux ...
- java打jar包和运行jar包的两种方式
java打jar包和运行jar包的两种方式更详细的打包方式请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/mq0036/p/8566427.html 一.java类不依赖第三方jar包以简单的一 ...
- GCD的补充
1-1 关于GCD中的创建和释放 在iOS6.0之前,在GCD中每当使用带creat单词的函数创建对象之后,都应该对其进行一次release操作. 在iOS6.0之后,GC ...
- 什么是maven(一)
转自博主--一杯凉茶 我记得在搞懂maven之前看了几次重复的maven的教学视频.不知道是自己悟性太低还是怎么滴,就是搞不清楚,现在弄清楚了,基本上入门了.写该篇博文,就是为了帮助那些和我一样对于m ...
- java中二维数组初始化的几种方法
/* 第一种方式 */ int tdarr1[][] = { { 1, 3, 5 }, { 5, 9, 10 } }; /* 第二种方式 */ int tdarr2[][] = new int[][] ...
- 为什么企业全面云化需要IT战略支撑和驱动?
引子:为什么传统企业全面云化一直磨磨唧唧举步维艰? 笔者将企业上云大体上分为几个阶段: 第一个阶段是基础设施虚拟化.即将应用从物理机搬到(lift and shift migration)虚拟机上.基 ...
