DS实验题 Dijkstra算法
参考:Dijkstra算法
数据结构来到了图论这一章节,网络中的路由算法基本都和图论相关。于是在拿到DS的实验题的时候,决定看下久负盛名的Dijkstra算法。
Dijkstra的经典应用是开放最短路径优先路由算法(OSPF)。
题目:

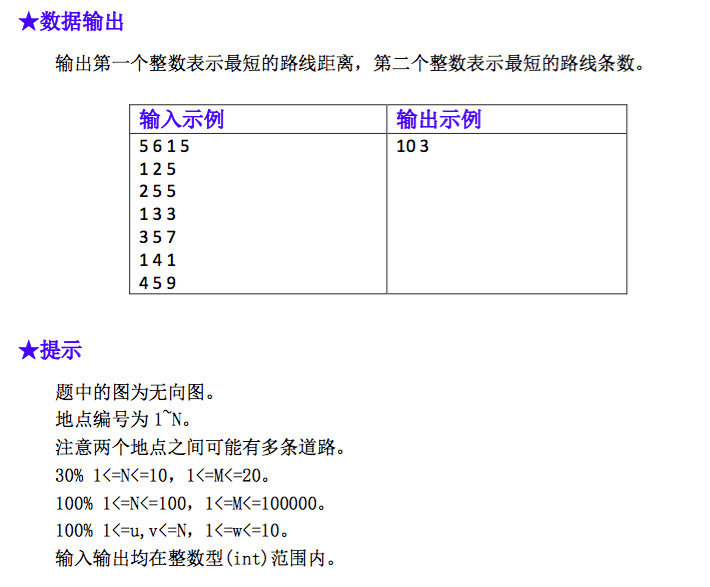
第一种实现的算法(错误):
在看过相关的Dijkstra算法解析之后,决定自己尝试写个算法,不过很遗憾,考虑并不全面,理解也不是特别深刻。
最后决定还是贴出来。
算法思想:
1.建立邻接表(后面用二维数组实现,相对来说轻松很多)
2.维护三个数组:dist代表从源点到某个节点的最短路径长度;ins代表这个节点是否已经被查询过;pre记录最短路径。
3.算法主体:
-1.当前节点 = 源节点。
-2.从当前节点出发,遍历邻接节点,找到离它最近的节点,且这个节点尚未遍历过,同时更新dist。
-3.跳转到找到的最近节点,先前节点的ins置1,回到2。
-4.当当前节点附近没有未遍历的节点时,break。
算法代码如下:
//
// main.cpp
// Gank_Dijkstra
//
// Created by wasdns on 16/11/15.
// Copyright © 2016年 wasdns. All rights reserved.
//
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 100000000;
struct edge {
edge *next;
int num;
int len;
} eg[100000];
struct head {
edge *next;
int num;
} h[100000];
void IniList(int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
h[i].next = NULL;
h[i].num = i;
}
}
void CreatList(int n, int m)
{
int i;
int x, y, leng;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
h[i].next = NULL;
h[i].num = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> x >> y >> leng;
edge *p1, *p2;
p1 = new edge;
p1 -> next = NULL;
p1 -> num = y;
p1 -> len = leng;
p2 = new edge;
p2 -> next = NULL;
p2 -> num = x;
p2 -> len = leng;
edge *p3, *p4;
p3 = h[x].next;
if (p3 == NULL) {
h[x].next = p1;
}
else
{
while (p3 -> next != NULL) {
p3 = p3 -> next;
}
p3 -> next = p1;
}
p4 = h[y].next;
if (p4 == NULL) {
h[y].next = p2;
}
else
{
while (p4 -> next != NULL) {
p4 = p4 -> next;
}
p4 -> next = p2;
}
}
}
void PrintList(int n)
{
int i;
edge *p;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
p = h[i].next;
cout << "Node:" << h[i].num << endl;
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p -> num << " " << p -> len << " ";
p = p -> next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int pre[105];
int dist[105];
bool ins[105];
void Initial(int b, int n)
{
int i;
memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre));
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
dist[i] = 10000000;
ins[i] = false;
}
dist[b] = 0;
pre[b] = b;
}
int Dijkstra(int b, int n, int end)
{
Initial(b, n);
int cnt = 0;
int turn = b;
while (cnt < n)
{
edge *p;
p = h[turn].next;
int minlen = maxn;
int tnext = turn;
while (p != NULL)
{
if (ins[p -> num]) {
p = p -> next;
continue;
}
int t = dist[turn] + p -> len;
if (t < dist[p -> num]) {
dist[p -> num] = t;
pre[p -> num] = turn;
}
if (t < minlen) {
minlen = t;
tnext = p -> num;
}
p = p -> next;
}
ins[turn] = true;
cnt++;
if (turn == tnext) {
turn = b;
}
turn = tnext;
}
return dist[end];
}
int main()
{
int n, m, s, e;
cin >> n >> m >> s >> e;
CreatList(n, m);
PrintList(n);
cout << Dijkstra(s, n, e) << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
5 6 1 5
1 2 5
2 5 5
1 3 3
3 5 7
1 4 1
4 5 9
6 9 1 6
1 3 3
1 2 6
2 3 2
2 4 5
3 4 3
3 5 4
4 5 2
4 6 3
5 6 5
5 6 1 5
1 2 7
1 3 1
1 4 3
2 5 1
3 5 10
4 5 9
*/
算法缺陷:
测试一下下面这个样例,
5 6 1 5
1 2 7
1 3 1
1 4 3
2 5 1
3 5 10
4 5 9
答案应该为8,但是结果为11。
原因在于,当以上算法经过:1 -> 3 -> 5 -> 2 最终来到节点2的时候,节点2附近没有未遍历的节点了(节点2),跳出循环。
第二种算法:
//
// main.cpp
// Dijkstra
//
// Created by wasdns on 16/11/16.
// Copyright © 2016年 wasdns. All rights reserved.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int DijGraph[105][105]; //节点i和j之间的距离:DijGraph[i][j]
int pre[105]; //最短路节点的前继节点(查询最短路)
int dist[105]; //源点到每个节点的最短路距离
bool ins[105]; //节点i是否位于已查询节点集合S
/*
初始化函数
*/
void Initial(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ins[i] = false;
pre[i] = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (i == j) DijGraph[i][j] = 0;
else DijGraph[i][j] = 1000000;
}
}
}
int cnt = 1; //记录到目的节点的条数
int belen = 1000000; //到目的节点的最短路长度
void Dijkstra(int n, int b, int e)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //根据图的信息初始化dist数组
dist[i] = DijGraph[b][i];
}
dist[b] = 0;
ins[b] = true; //源节点加入集合S
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) //集合V一共有n-1个节点
{
int next = b; //记录此时V中最靠近源点的节点
int minlen = 1000000; //以及源点到该节点的长度
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) //源点从V中挑一个最近节点
{
if (ins[j]) continue; //这个节点在S中,跳过
if (dist[j] < minlen) { //找到一个目前到源点距离最小的
next = j;
minlen = dist[j]; //更新离源点最近节点的信息
}
}
ins[next] = true; //最近节点离开V加入S
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) //新来的节点向外得到路径信息
{ //并维护dist
if (ins[j]) continue;
/* 从源点到当前节点next的距离 + 当前节点next到某个相邻节点j的距离。*/
/* 如果小于目前源点到节点j的最短距离dist[j],更新dist[j]。*/
/* 另外,需要在这个时候记录到目的点的最短距离,以及路径条数。*/
int t = dist[next] + DijGraph[next][j];
if (t <= dist[j])
{
if (t < dist[j])
{
dist[j] = t;
pre[j] = next;
if (j == e) {
cnt = 1;
belen = dist[j];
}
}
else
{
if (j == e) cnt++;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i, n, m, s, e;
cin >> n >> m >> s >> e;
int x, y, len;
Initial(n);
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> x >> y >> len;
DijGraph[x][y] = len;
DijGraph[y][x] = len;
}
Dijkstra(n, s, e);
cout << belen << " " << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
2016/11/15
DS实验题 Dijkstra算法的更多相关文章
- DS实验题 融合软泥怪-2 Heap实现
题目和STL实现:DS实验题 融合软泥怪-1 用堆实现优先队列 引言和堆的介绍摘自:Priority Queue(Heaps)--优先队列(堆) 引言: 优先队列是一个至少能够提供插入(Insert) ...
- DS实验题 Old_Driver UnionFindSet结构 指针实现邻接表存储
题目见前文:DS实验题 Old_Driver UnionFindSet结构 这里使用邻接表存储敌人之间的关系,邻接表用指针实现: // // main.cpp // Old_Driver3 // // ...
- 经典算法题每日演练——第十七题 Dijkstra算法
原文:经典算法题每日演练--第十七题 Dijkstra算法 或许在生活中,经常会碰到针对某一个问题,在众多的限制条件下,如何去寻找一个最优解?可能大家想到了很多诸如“线性规划”,“动态规划” 这些经典 ...
- DS实验题 sights
算法与数据结构实验题 6.3 sights ★实验任务 美丽的小风姑娘打算去旅游散心,她走进了一座山,发现这座山有 n 个景点, 由于山路难修,所以施工队只修了最少条的路,来保证 n 个景点联通,娇弱 ...
- DS实验题 order
算法与数据结构 实验题 6.4 order ★实验任务 给出一棵二叉树的中序遍历和每个节点的父节点,求这棵二叉树的先序和后序遍历. ★数据输入 输入第一行为一个正整数n表示二叉树的节点数目,节点编号从 ...
- DS实验题 Inversion
题目: 解题过程: 第一次做这题的时候,很自然的想到了冒泡和选择,我交的代码是用选择写的.基本全WA(摊手). 贴上第一次的代码: // // main.cpp // sequenceschange ...
- DS实验题 融合软泥怪-1
题目 思路 很容易想到第一种做法,用Huffman算法,从森林中找出两个值最小的节点,合并再加入森林,在这个过程中不断记录. 但是每一次需要sort一遍,将最小的两个值节点置于头两个节点,最坏情况下复 ...
- DS实验题 PlayGame Kruskal(UnionFindSet)
题目: 思路: 有两种做法,一种是Prim算法,另外一种则是我所使用的Kruskal算法,Kruskal的算法实现可以参考:最小生成树-Prim算法和Kruskal算法,讲的已经是十分清楚了. 具体算 ...
- DS实验题 Order 已知父节点和中序遍历求前、后序
题目: 思路: 这题是比较典型的树的遍历问题,思路就是将中序遍历作为位置的判断依据,假设有个节点A和它的父亲Afa,那么如果A和Afa的顺序在中序遍历中是先A后Afa,则A是Afa的左儿子,否则是右儿 ...
随机推荐
- UEditor插入表格没有边框但有间距
百度编辑器ueditor插入一个表格后,在编辑过程中有表格,但是保存后,在前台网页中没有边框,但有间距,设置方法如下: 在UEditor文件夹下打开ueditor.all.js文件,找到UE.comm ...
- JQuery的AJAX封装加例子
将json字符串转换为javascript对象有两种方法:var strs = eval("(" + data + ")");var strs = $.pars ...
- 菜鸟学Linux命令:find命令 查找文件
find命令是Linux下最常用的命令之一,灵活的使用find命令,你会发现查找文件变得十分简单. 命令格式 find [指定查找目录] [查找规则(选项)] [查找完后执行的动作] 参数规则 - ...
- linux tricks 之 bitmap分析.
------------------------------------------- 本文系作者原创, 欢迎大家转载! 转载请注明出处:netwalker.blog.chinaunix.net -- ...
- hdu 4006 优先队列 2011大连赛区网络赛F **
签到题都要想一会 #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstri ...
- nohup之no hang up, kill, ps -ef, ps aux, grep
背景:今天在安装hudson时,每次启动时都必须在linux终端(SecureCRT)执行: java -jar hudson.war --httpPort=18080 --jp13Port=1800 ...
- 浅谈K-SVD
由于工作需要,最近刚刚看了一些K-SVD的介绍,这里给自己做一下小节. K-SVD我们一般是用在字典学习.稀疏编码方面,它可以认为是K-means的一种扩展,http://en.wikipedia.o ...
- 下拉更新列表Android-PullToRefresh
项目地址:https://github.com/chrisbanes/Android-PullToRefresh
- BZOJ3532 : [Sdoi2014]Lis
f[i]表示以i为结尾的LIS长度 对于所有f[i]=1的,由S向i连边 对于所有f[i]=maxf的,由i向T连边 对于j<i,a[j]<a[i],且f[j]+1=f[i]的,j向i连边 ...
- JS正则表达式验证数字(很全)
1.<script type="text/javascript"> 2. function validate(){ 3. var reg = new ...
