05-树9 Huffman Codes及基本操作
哈夫曼树与哈弗曼编码
- 哈夫曼树
带权路径长度(WPL):设二叉树有n个叶子结点,每个叶子结点带有权值 Wk,从根结点到每个叶子结点的长度为 Lk,则每个叶子结点的带权路径长度之和就是:
WPL = 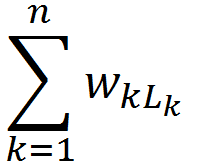
最优二叉树或哈夫曼树: WPL最小的二叉树
- 哈夫曼树的特点:
①没有度为1的结点
②n个叶子结点的哈夫曼树共有2n-1个结点
③哈夫曼树的任意非叶节点的左右子树交换后仍是哈夫曼树
④对同一组权值{w1 ,w2 , …… , wn},存在不同构的两棵哈夫曼树
- 哈夫曼树的构造
每次把权值最小的两颗二叉树合并.(利用堆)

基本操作
- HuffmanTree的建立
- 带权路径的求解
- HuffmanCoding
#include<limits.h> /* INT_MAX等 */
#include<stdio.h> /* EOF(=^Z或F6),NULL */
typedef struct
{
unsigned int weight;
unsigned int parent,lchild,rchild;
}HTNode,*HuffmanTree; /* 动态分配数组存储赫夫曼树 */
typedef char **HuffmanCode; /* 动态分配数组存储赫夫曼编码表 */
int min1(HuffmanTree t,int i)
{ /* 函数void select()调用 */
int j,flag;
unsigned int k=UINT_MAX; /* 取k为不小于可能的值 */
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
if(t[j].weight<k&&t[j].parent==0)
k=t[j].weight,flag=j;
t[flag].parent=1;
return flag;
}
void select(HuffmanTree t,int i,int *s1,int *s2)
{ /* s1为最小的两个值中序号小的那个 */
int j;
*s1=min1(t,i);
*s2=min1(t,i);
if(*s1>*s2)
{
j=*s1;
*s1=*s2;
*s2=j;
}
}
void HuffmanCoding(HuffmanTree *HT,HuffmanCode *HC,int *w,int n)
{ /* w存放n个字符的权值(均>0),构造赫夫曼树HT,并求出n个字符的赫夫曼编码HC */
int m,i,s1,s2;
unsigned c,cdlen;
HuffmanTree p;
char *cd;
if(n<=1)
return;
m=2*n-1;
*HT=(HuffmanTree)malloc((m+1)*sizeof(HTNode)); /* 0号单元未用 */
for(p=*HT+1,i=1;i<=n;++i,++p,++w)
{
(*p).weight=*w;
(*p).parent=0;
(*p).lchild=0;
(*p).rchild=0;
}
for(;i<=m;++i,++p)
(*p).parent=0;
for(i=n+1;i<=m;++i) /* 建赫夫曼树 */
{ /* 在HT[1~i-1]中选择parent为0且weight最小的两个结点,其序号分别为s1和s2 */
select(*HT,i-1,&s1,&s2);
(*HT)[s1].parent=(*HT)[s2].parent=i;
(*HT)[i].lchild=s1;
(*HT)[i].rchild=s2;
(*HT)[i].weight=(*HT)[s1].weight+(*HT)[s2].weight;
}
/* 以下为无栈非递归遍历赫夫曼树,求赫夫曼编码*/
*HC=(HuffmanCode)malloc((n+1)*sizeof(char*));
/* 分配n个字符编码的头指针向量([0]不用) */
cd=(char*)malloc(n*sizeof(char)); /* 分配求编码的工作空间 */
c=m;
cdlen=0;
for(i=1;i<=m;++i)
(*HT)[i].weight=0; /* 遍历赫夫曼树时用作结点状态标志 */
while(c)
{
if((*HT)[c].weight==0)
{ /* 向左 */
(*HT)[c].weight=1;
if((*HT)[c].lchild!=0)
{
c=(*HT)[c].lchild;
cd[cdlen++]='0';
}
else if((*HT)[c].rchild==0)
{ /* 登记叶子结点的字符的编码 */
(*HC)[c]=(char *)malloc((cdlen+1)*sizeof(char));
cd[cdlen]='\0';
strcpy((*HC)[c],cd); /* 复制编码(串) */
}
}
else if((*HT)[c].weight==1)
{ /* 向右 */
(*HT)[c].weight=2;
if((*HT)[c].rchild!=0)
{
c=(*HT)[c].rchild;
cd[cdlen++]='1';
}
}
else
{ /* HT[c].weight==2,退回 */
(*HT)[c].weight=0;
c=(*HT)[c].parent;
--cdlen; /* 退到父结点,编码长度减1 */
}
}
free(cd);
}
void main()
{
HuffmanTree HT;
HuffmanCode HC;
int *w,n,i;
printf("请输入权值的个数(>1):");
scanf("%d",&n);
w=(int *)malloc(n*sizeof(int));
printf("请依次输入%d个权值(整型):\n",n);
for(i=0;i<=n-1;i++)
scanf("%d",w+i);
HuffmanCoding(&HT,&HC,w,n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
puts(HC[i]);
}
题目
- Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives an integer NN (2\le N\le 632≤N≤63), then followed by a line that contains all the NN distinct characters and their frequencies in the following format:
c[1] f[1] c[2] f[2] ... c[N] f[N]
where c[i] is a character chosen from {'0' - '9', 'a' - 'z', 'A' - 'Z', '_'}, and f[i] is the frequency of c[i] and is an integer no more than 1000. The next line gives a positive integer MM (\le 1000≤1000), then followed by MM student submissions. Each student submission consists of NN lines, each in the format:
c[i] code[i]
where c[i] is the i-th character and code[i] is an non-empty string of no more than 63 '0's and '1's.
- Output Specification:
For each test case, print in each line either "Yes" if the student's submission is correct, or "No" if not.
Note: The optimal solution is not necessarily generated by Huffman algorithm. Any prefix code with code length being optimal is considered correct.
Sample Input:
7
A 1 B 1 C 1 D 3 E 3 F 6 G 6
4
A 00000
B 00001
C 0001
D 001
E 01
F 10
G 11
A 01010
B 01011
C 0100
D 011
E 10
F 11
G 00
A 000
B 001
C 010
D 011
E 100
F 101
G 110
A 00000
B 00001
C 0001
D 001
E 00
F 10
G 1
- Sample Output:
Yes
Yes
No
No
AC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define MAXSIZE 64
int nodenum;
int c[64];
char f[64];
typedef struct TNode* HuffTree;
struct TNode
{
HuffTree left;
HuffTree right;
int freq;
};
struct heap
{
HuffTree* data;
int size;
int capacity;
};
typedef struct heap* Minheap;
Minheap CreatHeap()
{
Minheap H = new struct heap;
H->data = new HuffTree[MAXSIZE];
H->size = 0;
H->capacity = MAXSIZE;
H->data[0] = new struct TNode;
H->data[0]->freq = -1;
return H;
}
bool Insert(Minheap H, HuffTree f)
{
int i;
if (H->size == H->capacity){
printf("minheap is full");
return false;
}
i = ++H->size;
for (; H->data[i / 2]->freq > f->freq; i /= 2)
H->data[i] = H->data[i / 2];
H->data[i] = f;
return true;
}
bool IsEmpty(Minheap H)
{
return (H->size == 0);
}
HuffTree DeleteMin(Minheap H)
{
int Parent, Child;
HuffTree MinItem, X;
if (IsEmpty(H)) {
printf("minheap is empty");
}
MinItem = H->data[1];
X = H->data[H->size--];
for (Parent = 1; Parent * 2 <= H->size; Parent = Child) {
Child = Parent * 2;
if ((Child != H->size) && (H->data[Child]->freq > H->data[Child + 1]->freq))
Child++;
if (X->freq <= H->data[Child]->freq) break;
else
H->data[Parent] = H->data[Child];
}
H->data[Parent] = X;
return MinItem;
}
HuffTree HuffmanTree()
{
Minheap h = CreatHeap();
for (int i = 0; i < nodenum; i++)
{
HuffTree f = new struct TNode;
f->freq = c[i]; //全局变量赋值
f->left = NULL;
f->right = NULL;
if (!Insert(h, f))
break;
}
for (;;)
{
if (h->size == 1) break;
HuffTree f = new struct TNode;
f->left = DeleteMin(h);
f->right = DeleteMin(h);
f->freq = f->left->freq + f->right->freq;
Insert(h, f);
//printf("fleft=%d,fright=%d,ffreq=%d\n",f->left->freq,f->right->freq,f->freq);
}
return DeleteMin(h);
}
int WPL(HuffTree tree, int depth)
{
if ((!tree->left) && (!tree->right))
{
//printf("depth:%d,leaf->freq:%d\n",depth,tree->freq);
return depth*(tree->freq);
}
else
{
//printf("depth:%d,tree->freq:%d\n",depth,tree->freq);
return WPL(tree->left, depth + 1) + WPL(tree->right, depth + 1);
}
}
bool check(HuffTree tree, string s)
{
bool flag = false;
HuffTree p = tree;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if (s[i] == '0')
{
if (!p->left)
{
p->left = new TNode;
p->left->left = NULL;
p->left->right = NULL;
p = p->left;
flag = true;
}
else
{
p = p->left;
}
}
else if (s[i] == '1')
{
if (!p->right)
{
p->right = new TNode;
p->right->left = NULL;
p->right->right = NULL;
p = p->right;
flag = true;
}
else
{
p = p->right;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
int main()
{
int case_;
cin >> nodenum;
for (int i = 0; i < nodenum; i++)
{
cin >> f[i] >> c[i];
}
HuffTree tree = HuffmanTree();
int wpl = WPL(tree, 0); //权值可以放在建HufumanTree的时候计算
cin >> case_;
for (int j = 0; j < case_; j++)
{
HuffTree root = new TNode;
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL;
int s_wpl = 0;
string judge = "";
for (int i = 0; i<nodenum; i++)
{
char ch;
string s;
cin >> ch >> s;
if (s.size()>nodenum - 1){
judge = "No";
break;
}
s_wpl += s.size()*c[i];
if (!check(root, s)) //判断序列是否满足要求
judge = "No";
}
if (judge.empty() && s_wpl == wpl)
judge = "Yes";
else
judge = "No";
cout << judge << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- 补充
//补充,理解思路,时间复杂度O(N*logN)
HuffTree HuffmanTree(Minheap H)
{
//假设H->size个权值已经在H->data->frq里
int i;
HuffTree T;
BuildMinTree(H); //将H->data[]按权值调整为最小堆
for (i = 0; i < H->size;i++)
{
T = malloc(sizeof(struct TNode));
T->left = DeleteMin(H); //从最小堆中删除一个结点,作为新T的左子结点
T->right = DeleteMin(H); //从最小堆中删除一个结点,作为新T的右子节点
T->freq = T->left->freq + T->right->freq; //计算新权值
Insert(H, T);
}
T = DeleteMin(H);
return T;
}
题目来源
Reference
05-树9 Huffman Codes
05-树9 Huffman Codes (用优先队列实现)
05-树9 Huffman Codes及基本操作的更多相关文章
- PAT 05-树8 Huffman Codes
以现在的生产力,是做不到一天一篇博客了.这题给我难得不行了,花了两天时间在PAT上还有测试点1没过,先写上吧.记录几个做题中的难点:1.本来比较WPL那块我是想用一个函数实现的,无奈我对传字符串数组无 ...
- 05-树9 Huffman Codes
哈夫曼树 Yes 需满足两个条件:1.HuffmanTree 结构不同,但WPL一定.子串WPL需一致 2.判断是否为前缀码 开始判断用的strstr函数,但其传值应为char *,不能用在strin ...
- pta5-9 Huffman Codes (30分)
5-9 Huffman Codes (30分) In 1953, David A. Huffman published his paper "A Method for the Const ...
- PTA 05-树9 Huffman Codes (30分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/671 5-9 Huffman Codes (30分) In 1953, David ...
- 数据结构慕课PTA 05-树9 Huffman Codes
题目内容 In 1953, David A. Huffman published his paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Re ...
- 哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)与哈夫曼编码
哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)与哈夫曼编码(Huffman coding)
- 05-树9 Huffman Codes (30 分)
In 1953, David A. Huffman published his paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redunda ...
- 05-树9 Huffman Codes (30 分)
In 1953, David A. Huffman published his paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redunda ...
- Huffman codes
05-树9 Huffman Codes(30 分) In 1953, David A. Huffman published his paper "A Method for the Const ...
随机推荐
- java多线程快速入门(四)
通过匿名内部类的方法创建多线程 package com.cppdy; //通过匿名内部类的方法创建多线程 public class ThreadDemo2 { public static void m ...
- pytest九:使用自定义标记 mark
pytest 可以支持自定义标记,自定义标记可以把一个 web 项目划分多个模块,然后指定模块名称执行.app 自动化的时候,如果想android 和 ios 公用一套代码时,也可以使用标记功能,标明 ...
- PyCharm 新建文件时默认添加作者时间等
将内容添加到Python Script 右侧的文本框中: 路径: File → Setting → Editor → File and Code Templates → Python Script # ...
- python 全栈开发,Day59(小米商城)
一.小米商城 准备工作: 访问iconfont,官网链接: http://www.iconfont.cn/ 登录之后,找到需要的图标 将图标下载到本地,解压,重命名为font创建几个空文件夹:css, ...
- 【C++ Primer | 06】 函数
contexpr函数 const用于运行期常量,constexpr用于编译期常量 • [test1.cpp] #include <iostream> using namespace std ...
- (转载)关于一些对location认识的误区
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/4169396.html 关于一些对location认识的误区 1. location 的匹配顺序是“先匹配正则,再匹配普通”. ...
- C# 线程本地存储 调用上下文 逻辑调用上下文
线程本地存储 using System; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleAppTest ...
- 51Nod 算法马拉松28 A题 先序遍历与后序遍历 分治
欢迎访问~原文出处——博客园-zhouzhendong 去博客园看该题解 题目传送门 - 51Nod1832 题意概括 对于给定的一个二叉树的先序遍历和后序遍历,输出有多少种满足条件的二叉树. 两棵二 ...
- BZOJ1258 [CQOI2007]三角形tri 模拟
欢迎访问~原文出处——博客园-zhouzhendong 去博客园看该题解 题目传送门 - BZOJ1258 题意概括 这种图中,一个三角形的三边如果被其他某一个三角形的一条边包括,那么我们说该三角形和 ...
- Floyd-傻子也能看懂的弗洛伊德算法(转)
暑假,小哼准备去一些城市旅游.有些城市之间有公路,有些城市之间则没有,如下图.为了节省经费以及方便计划旅程,小哼希望在出发之前知道任意两个城市之前的最短路程. ...
