『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_锚框生成
Github地址:Mask_RCNN
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_论文学习
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_项目文档翻译
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其一:总览
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其二:基于ReNet101的FPN共享网络
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其三:RPN锚框处理和Proposal生成
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其四:FPN和ROIAlign的耦合
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其五:目标检测结果精炼
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其六:Mask生成
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络终篇:使用detect方法进行推断
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_锚框生成
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_训练网络其一:数据集与Dataset类
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_训练网络其二:train网络结构&损失函数
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_训练网络其三:训练Model
一、和SSD锚框对比
Mask_RCNN的锚框本质上来说和SSD的是一样的(『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其三:锚框生成),
中心点的个数等于特征层像素数
框体生成是围绕中心点的
最终的框体坐标需要归一化到01之间,都是对于输入图片的相对大小
RCNN系列一般都是一个共享特征,但在Mask_RCNN结构引入了FPN结构后,和SSD一样,使用了多层特征,这样两者的锚框生成算法可以说是如出一辙了,只不过是生成策略有所微调:
SSD中不同特征层对应着不同的网格增强比例参数;Mask_RCNN不通层的比例(anchor_ratios)则完全一致
SSD每一层每一个中心点生成该层ratio+2个框;Mask_RCNN生成固定3个框
SSD中心点为feat像素偏移0.5步长;Mask_RCNN中心点直接选为feat像素位置
而基本生成方式两者完全一致:
- h乘anchor_ratios**0.5
- w除anchor_ratios**0.5
h、w初始值为给定的参考尺寸,即感受野控制实际依赖的参数为每一层的anchor_ratios和参考尺寸,对SSD:
anchor_sizes=[(21., 45.),
(45., 99.),
(99., 153.),
(153., 207.),
(207., 261.),
(261., 315.)]
anchor_ratios=[[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5],
[2, .5]]
对Mask_RCNN(h、w参考尺寸大小一致):
self.config.BACKBONE_STRIDES = [4, 8, 16, 32, 64] # 特征层的下采样倍数,中心点计算使用
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS = [0.5, 1, 2] # 特征层锚框生成参数
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = [32, 64, 128, 256, 512] # 特征层锚框感受野
二、锚框生成
锚框生成入口函数位于model.py中的get_anchor函数,需要参数image_shape,保证含有[h, w]即可,也可以包含[h, w, c],
def get_anchors(self, image_shape):
"""Returns anchor pyramid for the given image size."""
# [N, (height, width)]
backbone_shapes = compute_backbone_shapes(self.config, image_shape)
# Cache anchors and reuse if image shape is the same
if not hasattr(self, "_anchor_cache"):
self._anchor_cache = {}
if not tuple(image_shape) in self._anchor_cache:
# Generate Anchors: [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
a = utils.generate_pyramid_anchors(
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES, # (32, 64, 128, 256, 512)
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS, # [0.5, 1, 2]
backbone_shapes, # with shape [N, (height, width)]
self.config.BACKBONE_STRIDES, # [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE) # 1
# Keep a copy of the latest anchors in pixel coordinates because
# it's used in inspect_model notebooks.
# TODO: Remove this after the notebook are refactored to not use it
self.anchors = a
# Normalize coordinates
self._anchor_cache[tuple(image_shape)] = utils.norm_boxes(a, image_shape[:2])
return self._anchor_cache[tuple(image_shape)]
调用函数compute_backbone_shapes计算各个特征层shape:
def compute_backbone_shapes(config, image_shape):
"""Computes the width and height of each stage of the backbone network. Returns:
[N, (height, width)]. Where N is the number of stages
"""
if callable(config.BACKBONE):
return config.COMPUTE_BACKBONE_SHAPE(image_shape) # Currently supports ResNet only
assert config.BACKBONE in ["resnet50", "resnet101"]
return np.array(
[[int(math.ceil(image_shape[0] / stride)),
int(math.ceil(image_shape[1] / stride))]
for stride in config.BACKBONE_STRIDES]) # [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]
调用函数utils.generate_pyramid_anchors生成全部锚框:
def generate_pyramid_anchors(scales, ratios, feature_shapes, feature_strides,
anchor_stride):
"""Generate anchors at different levels of a feature pyramid. Each scale
is associated with a level of the pyramid, but each ratio is used in
all levels of the pyramid. Returns:
anchors: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]. All generated anchors in one array. Sorted
with the same order of the given scales. So, anchors of scale[0] come
first, then anchors of scale[1], and so on.
"""
# Anchors
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
anchors = []
for i in range(len(scales)):
anchors.append(generate_anchors(scales[i],
ratios,
feature_shapes[i],
feature_strides[i],
anchor_stride))
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
return np.concatenate(anchors, axis=0)
utils.generate_pyramid_anchors会调用utils.generate_anchors来生成每一层的锚框(这一步较多的使用了函数meshgrid,介绍见『Numpy』np.meshgrid):
def generate_anchors(scales, ratios, shape, feature_stride, anchor_stride):
"""
scales: 1D array of anchor sizes in pixels. Example: [32, 64, 128]
ratios: 1D array of anchor ratios of width/height. Example: [0.5, 1, 2]
shape: [height, width] spatial shape of the feature map over which
to generate anchors.
feature_stride: Stride of the feature map relative to the image in pixels.
anchor_stride: Stride of anchors on the feature map. For example, if the
value is 2 then generate anchors for every other feature map pixel.
"""
# Get all combinations of scales and ratios
scales, ratios = np.meshgrid(np.array(scales), np.array(ratios))
scales = scales.flatten()
ratios = ratios.flatten() # Enumerate heights and widths from scales and ratios
heights = scales / np.sqrt(ratios)
widths = scales * np.sqrt(ratios) # Enumerate shifts in feature space
shifts_y = np.arange(0, shape[0], anchor_stride) * feature_stride
shifts_x = np.arange(0, shape[1], anchor_stride) * feature_stride
shifts_x, shifts_y = np.meshgrid(shifts_x, shifts_y) # Enumerate combinations of shifts, widths, and heights
box_widths, box_centers_x = np.meshgrid(widths, shifts_x) # (n, 3) (n, 3)
box_heights, box_centers_y = np.meshgrid(heights, shifts_y) # (n, 3) (n, 3) # Reshape to get a list of (y, x) and a list of (h, w)
# (n, 3, 2) -> (3n, 2)
box_centers = np.stack([box_centers_y, box_centers_x], axis=2).reshape([-1, 2])
box_sizes = np.stack([box_heights, box_widths], axis=2).reshape([-1, 2]) # Convert to corner coordinates (y1, x1, y2, x2)
boxes = np.concatenate([box_centers - 0.5 * box_sizes,
box_centers + 0.5 * box_sizes], axis=1)
# 框体信息是相对于原图的, [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
return boxes
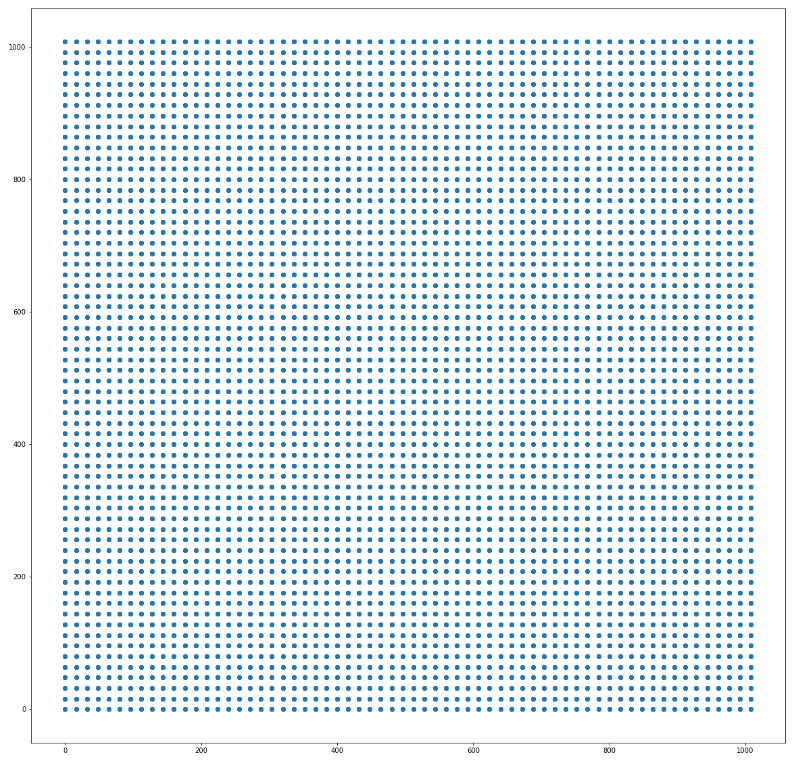
模拟某层的中心点分布
最后回到get_anchor,调用utils.norm_boxes将锚框坐标化为01之间:
def norm_boxes(boxes, shape):
"""Converts boxes from pixel coordinates to normalized coordinates.
boxes: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in pixel coordinates
shape: [..., (height, width)] in pixels Note: In pixel coordinates (y2, x2) is outside the box. But in normalized
coordinates it's inside the box. Returns:
[N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates
"""
h, w = shape
scale = np.array([h - 1, w - 1, h - 1, w - 1])
shift = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
return np.divide((boxes - shift), scale).astype(np.float32)
最终返回相对坐标下的锚框,shape:[anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]。
『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_锚框生成的更多相关文章
- 『计算机视觉』经典RCNN_其二:Faster-RCNN
项目源码 一.Faster-RCNN简介 『cs231n』Faster_RCNN 『计算机视觉』Faster-RCNN学习_其一:目标检测及RCNN谱系 一篇讲的非常明白的文章:一文读懂Faster ...
- 『计算机视觉』经典RCNN_其一:从RCNN到Faster-RCNN
RCNN介绍 目标检测-RCNN系列 一文读懂Faster RCNN 一.目标检测 1.两个任务 目标检测可以拆分成两个任务:识别和定位 图像识别(classification)输入:图片输出:物体的 ...
- 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN
一.Mask-RCNN流程 Mask R-CNN是一个实例分割(Instance segmentation)算法,通过增加不同的分支,可以完成目标分类.目标检测.语义分割.实例分割.人体姿势识别等多种 ...
- 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其三:RPN锚框处理和Proposal生成
一.RPN锚框信息生成 上文的最后,我们生成了用于计算锚框信息的特征(源代码在inference模式中不进行锚框生成,而是外部生成好feed进网络,training模式下在向前传播时直接生成锚框,不过 ...
- 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其六:Mask生成
一.Mask生成概览 上一节的末尾,我们已经获取了待检测图片的分类回归信息,我们将回归信息(即待检测目标的边框信息)单独提取出来,结合金字塔特征mrcnn_feature_maps,进行Mask生成工 ...
- 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_从服装关键点检测看KeyPoints分支
下图Github地址:Mask_RCNN Mask_RCNN_KeyPoints『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_论文学习『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_项目文档翻译『计算机视觉』Mas ...
- 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_训练网络其三:训练Model
Github地址:Mask_RCNN 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_论文学习 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_项目文档翻译 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其一:总览 『计算机视觉』M ...
- 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_训练网络其二:train网络结构&损失函数
Github地址:Mask_RCNN 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_论文学习 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_项目文档翻译 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其一:总览 『计算机视觉』M ...
- 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_训练网络其一:数据集与Dataset类
Github地址:Mask_RCNN 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_论文学习 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_项目文档翻译 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其一:总览 『计算机视觉』M ...
随机推荐
- ZOJ 3829 Known Notation(贪心)题解
题意:给一串字符,问你最少几步能变成后缀表达式.后缀表达式定义为,1 * 1 = 1 1 *,题目所给出的字串不带空格.你可以进行两种操作:加数字,交换任意两个字符. 思路:(不)显然,最终结果数字比 ...
- div包裹页面后多余部分没有显示,也没滚动条 overflow 属性设置
今天弄个div套着一个页面结果那个页面超出范围后页面没有滚动条可以滚动浏览下面的内容,原来是设置了overflow的hidden属性 visible 默认值.内容不会被修剪,会呈现在元素框之外. hi ...
- 题解——CodeForces 438D The Child and Sequence
题面 D. The Child and Sequence time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
- awk 基础入门
简介 awk是一个强大的文本分析工具,相对于grep的查找,sed的编辑,awk在其对数据分析并生成报告时,显得尤为强大.简单来说awk就是把文件逐行的读入,以空格为默认分隔符将每行切片,切开的部分再 ...
- ComponentOne 2017 V1 发布
在刚刚庆祝完Visual Studio20周年之后,我们迎来了ComponentOne 2017年第一个重要的版本. ComponentOne Studio与Visual Studio 2017配合发 ...
- ISTQB学习笔记
学习ISTQB大纲此文记录初次阅读时不够明确的地方 第一章:软件测试基础1. 引起软件缺陷的原因人都会犯错误(error,mistake),因此人设计的代码或文档中会引入缺陷(defect, faul ...
- 文档对象模型DOM
文档对象模型 DOM 1 DOM概述 1.1 什么是DOM 文档对象模型 Document Object Model 提供给用户操作document obj 的标准接口 文档对象模型 是表示和操作 H ...
- ZOJ 3987 Numbers(Java枚举)
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=3987 题意:给出一个数n,现在要将它分为m个数,这m个数相加起来必须等于n ...
- Ajax - 汇总
1,什么是ajax? 为什么要使用ajax? 1.ajax是"asynchornous javascript and xml "的缩写,指一种创建交互式网页应用的网页开发技术. 2 ...
- border:none和border:0的区别
C:当定义border:none时,表示无边框样式,浏览器并不会对边框进行渲染,也就没有实际的宽度: D:定义边框时,除了设置宽度外,还必须设置边框的样式才能显示出来. border:0;浏 ...
