STL——容器(Map & multimap)的查找
- map.find(key); //查找键key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回map.end();
- map.count(key); //返回容器中键值为key的对组个数。对map来说,要么是0,要么是1;对multimap来说,值>=0。
- map.lower_bound(keyElem); //返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。
- map.upper_bound(keyElem); // 返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。
- map.equal_range(keyElem); //返回容器中key与keyEl相等的上下限的两个迭代器。上限是闭区间,下限是开区间,如[beg,end)。
1. map.find(key);
find(); 的所有返回值均为 key 的 iterator 类型迭代器




代码示例:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <map>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 map<int, string> mapStu1;
9
10 mapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "内容A"));
11 mapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "内容B"));
12 mapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容C"));
13 mapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容D"));
14 mapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(5, "内容E"));
15
16 map<int, string>::iterator it_1 = mapStu1.find(3); //将返回值赋值给 iterator 类型的 it
17
18 if (it_1 != mapStu1.end()) //由于 find 为全部遍历,如果没有找到元素, 会返回 end()
19 {
20 cout << "key值: " << it_1->first << " 对应的velue为:" << it_1->second << endl;
21 }
22 else
23 {
24 cout << "没有找到对应的" << it_1->first << endl;
25 }
26
27 map<int, string>::iterator it_2 = mapStu1.find(6);
28
29 if (it_2 != mapStu1.end())
30 {
31 cout << "key值: " << it_2->first << " 对应的velue为:" << it_2->second << endl;
32 }
33 else
34 {
35 cout << "没有找到对应的key" << endl;
36 }
37
38 return 0;
39 }
打印结果:

由于 map 的 key具有唯一性, multimap 这种具有多个相同的 key 如何解决, 示例代码如下:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <map>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 multimap<int, string> multimapStu1;
9
10 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "内容A"));
11 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "内容B"));
12 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容C"));
13 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容D"));
14 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容E"));
15 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容F"));
16
17 map<int, string>::iterator it_1 = multimapStu1.find(3); //将返回值赋值给 iterator 类型的 it
18
19 if (it_1 != multimapStu1.end())
20 {
21 for (; it_1 != multimapStu1.end(); it_1++)
22 {
23 if (it_1->first == 3)
24 {
25 cout << "key值: " << it_1->first << " 对应的velue为:" << it_1->second << endl;
26 }
27 }
28 }
29
30 return 0;
31 }
打印结果:

2. map.count(key);
统计拥有 key 的数量, 示例代码如下:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <map>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 multimap<int, string> multimapStu1;
9
10 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "内容A"));
11 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "内容B"));
12 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容C"));
13 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容D"));
14 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容E"));
15
16 map<int, string>::iterator it_1 = multimapStu1.find(3);
17
18 int count = multimapStu1.count(3);
19 cout << "找到" << count << "个相关元素" << endl;
20
21 if (it_1 != multimapStu1.end())
22 {
23 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
24 {
25 cout << "key值: " << it_1->first << " 对应的velue为:" << it_1->second << endl;
26 }
27 }
28 else
29 {
30 cout << "没找到" << endl;
31 }
32
33 return 0;
34 }
打印结果:

3. map.lower_bound(keyElem);
返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器,示例代码如下:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <map>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 multimap<int, string> multimapStu1;
9
10 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "内容A"));
11 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "内容B"));
12 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容C"));
13 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容D"));
14 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容DD"));
15 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容DDD"));
16 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(5, "内容E"));
17
18 //map<int, string>::iterator it_1 = multimapStu1.lower_bound(4);
19
20 cout << "输出 key 值大等于4以后的内容" << endl;
21
22 for (map<int, string>::iterator it = multimapStu1.lower_bound(3); it != multimapStu1.end(); it++)
23 {
24 if (it->first == 4)
25 {
26 cout << "第一个 key 为:" << it->first << " 其内容为:" << it->second << endl;
27 }
28 }
29
30 return 0;
31 }
打印结果:

4. map.upper_bound(keyElem);
返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器,代码示例:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <map>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 multimap<int, string> multimapStu1;
9
10 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "内容A"));
11 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "内容B"));
12 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容C"));
13 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容D"));
14 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容DD"));
15 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容DDD"));
16 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(5, "内容E"));
17
18 cout << "输出 key 值大等于4以后的内容" << endl;
19
20 for (map<int, string>::iterator it = multimapStu1.upper_bound(3); it != multimapStu1.end(); it++)
21 {
22 if (it->first == 4)
23 {
24 cout << "第一个 key 为:" << it->first << " 其内容为:" << it->second << endl;
25 }
26 }
27
28 return 0;
29 }
打印结果:

5. map.equal_range(keyElem);
返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。上限是闭区间,下限是开区间,如[beg,end)。代码如下:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <map>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 multimap<int, string> multimapStu1;
9
10 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "内容A"));
11 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "内容B"));
12 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容C"));
13 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容CC"));
14 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "内容CCC"));
15 multimapStu1.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "内容D"));
16
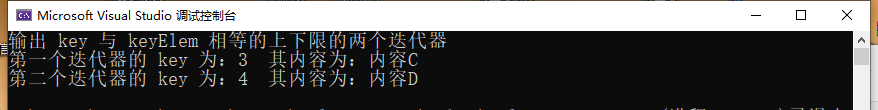
17 cout << "输出 key 与 keyElem 相等的上下限的两个迭代器" << endl;
18
19 pair<multimap<int, string>::iterator, multimap<int, string>::iterator> mmit = multimapStu1.equal_range(3);
20
21 if (mmit.first != multimapStu1.end())
22 {
23 cout << "第一个迭代器的 key 为:" << (*mmit.first).first << " 其内容为:" << (*mmit.first).second << endl;
24 }
25
26 if (mmit.second != multimapStu1.end())
27 {
28 cout << "第二个迭代器的 key 为:" << (*mmit.second).first << " 其内容为:" << (*mmit.second).second << endl;
29 }
30
31 return 0;
32 }
打印结果:
==========================================================================================================================
STL——容器(Map & multimap)的查找的更多相关文章
- STL:map/multimap用法详解
map/multimap 使用map/multimap之前要加入头文件#include<map>,map和multimap将key/value当作元素,进行管理.它们可根据key的排序准则 ...
- STL之map&multimap使用简介
map 1.insert 第一种:用insert函数插入pair数据 #include <map> #include <string> #include <iostrea ...
- STL容器 -- Map
核心描述: map 就是从键(key) 到 值(value) 的一个映射.且键值不可重复,内部按照键值排序. 头文件: #include <map> 拓展: multimap 是一个多重映 ...
- STL容器Map
Map的常见函数 Map的实现机制 STL中的Map底层实现机制是RB树(红-黑树)
- 【STL】-Map/Multimap的用法
初始化: map<string,double> salaries; 算法: 1. 赋值.salaries[ "Pat" ] = 75000.00; 2. 无效的索引将自 ...
- STL - 容器 - Map(二)
把Map用作关联式数组 MapAdvanceTest.cpp #include <map> #include <string> #include <iostream> ...
- STL - 容器 - Map(一)
MapTest.cpp #include <map> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <algo ...
- iBinary C++STL模板库关联容器之map/multimap
目录 一丶关联容器map/multimap 容器 二丶代码例子 1.map的三种插入数据的方法 3.map集合的遍历 4.验证map集合数据是否插入成功 5.map数据的查找 6.Map集合删除元素以 ...
- C++STL容器(lower_bound,upper_bound)
C++STL容器中有三种二分查找函数,这里分享其中的两个 这两个函数其实都可以理解为不破坏数组次序的前期下能将目标元素插入到数组的第几个位置,不过在细节上两个函数有所差异 int d[6]={0,2, ...
随机推荐
- CSS属性(字体与文本属性)
1.字体属性 (1)font-family 把要对这个网站要设置的字体都写上,如果这个浏览器支持第一个字体,则会用,如果不支持则会尝试第二个,如果设置的字体系统都不支持则会使用系统默认的字体作为网站的 ...
- 网页中Office和pdf相关文件导出
最近被派去维护和开发一些做了一半.年久失修的项目.有一部分内容是关于word文件导出,顺带着把excel.pdf文件的导出也调研下吧,我想未来开发我应该会遇到的,遂做了下笔记分享给需要的人. 由于项目 ...
- wordpress 博客环境安装
WordPress是使用PHP语言开发的博客平台,用户可以在支持PHP和MySQL数据库的服务器上架设属于自己的网站.也可以把 WordPress当作一个内容管理系统(CMS)来使用. 1.数据库环境 ...
- Hadoop大数据平台之HBase部署
环境:CentOS 7.4 (1708 DVD) 工具:Xshell+Xftp 1. 使用xftp将hbase上传到/usr/local目录下,将其解压并重命名. 2. 配置conf目录下的hbas ...
- html页面转PDF、图片操作记录
前言 日常开发中,我们有可能会碰到从系统中导出数据并打印的需要,打印的格式是常规的表格形式,例如: 本文记录使用js库html2canvas + jspdf实现html转PDF.图片,并下载 画出页面 ...
- CDR简单制作透明字体【6·18特惠倒计时3天!】
将图片剪贴到文字中是平面设计常用的一种处理方法之一,一般是将图片置入到该文字,且图片的外轮廓是沿着文字的形状剪贴的,这种处理手法被广泛应用于排版设计中.本教程结合蒙版功能加阴影效果做出特殊的视觉效果. ...
- Django踩坑记录2
错误如下 OperationalError no such table 解决方法: 首先执行: python manage.py makemigrations 再执行 python manage.py ...
- 移动自动化测试框架--openatx
之前学习并使用appium进行移动端测试,对于使用appium的一些体会与感受是否与我相似 1. appium启动服务和app程序非常慢 2. appium搭建环境较复杂 3. appium必须连接u ...
- php进阶学习-单例设计模式
什么是单例模式(singleton)? 在整个应用程序的生命周期中,任何一个时刻,单例类的实例都只存在一个,同时这个类还必须提供一个访问该类的全局访问点. 单例模式的特点 一个类只有一个实例 私有克隆 ...
- 终于有人把鸿蒙OS讲明白了,大佬讲解!快收藏!
来自 | GitHub科技 本文面向的是开发人员,主要想通过科普让大家了解一下鸿蒙开发.接下来,我想给大家科普一下这个这么火的鸿蒙系统. 到底什么是鸿蒙 OS 在官网上看到鸿蒙 OS 的简介是,分布式 ...
