子线程调用invalidate()产生“Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.”原因分析
备注:本文基于sdk28, ViewActivity页面禁用了硬件加速(AndroidManifest.xml中添加了android:hardwareAccelerated="false")。
1、异常出处
ViewActivity代码链接:https://gitee.com/2820174512/application/blob/master/app/src/main/java/com/example/myapplication/threadcheck/ViewActivity.java
点击Hello,World!后报如下异常:
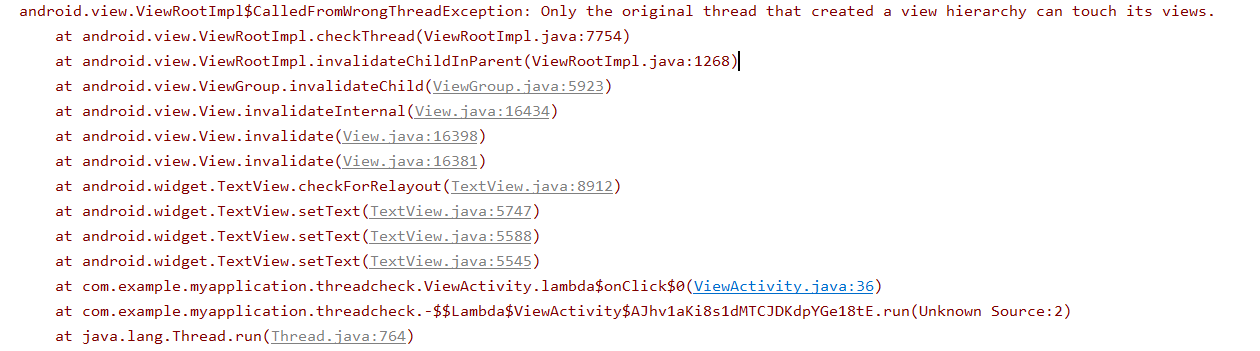
从图片中可以看出异常在ViewRootImpl类的invalidateChildInParent方法中进行检查的,判断当前线程是否是创建线程(View类一般是在主线程创建的),部分代码如下, 可以看出就是在checkThread方法中抛出的异常。
@Override
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(int[] location, Rect dirty) {
checkThread();
if (DEBUG_DRAW) Log.v(mTag, "Invalidate child: " + dirty);
...
return null;
}
void checkThread() {
if (mThread != Thread.currentThread()) {
throw new CalledFromWrongThreadException(
"Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.");
}
}
2、从View.invalidate()方法开始分析
先看下TextView.invalidate()方法(View的invalidate()方法)
public void invalidate() {
invalidate(true);
}
public void invalidate(boolean invalidateCache) {
invalidateInternal(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop, invalidateCache, true);
}
void invalidateInternal(int l, int t, int r, int b, boolean invalidateCache,
boolean fullInvalidate) {
...
// Reset content capture caches
mCachedContentCaptureSession = null;
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)
|| (invalidateCache && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)
|| (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != PFLAG_INVALIDATED
|| (fullInvalidate && isOpaque() != mLastIsOpaque)) {
...
// Propagate the damage rectangle to the parent view.
final AttachInfo ai = mAttachInfo;
final ViewParent p = mParent;
if (p != null && ai != null && l < r && t < b) {
final Rect damage = ai.mTmpInvalRect;
damage.set(l, t, r, b);
p.invalidateChild(this, damage);
}
...
}
}
主要执行逻辑:向上请求父View执行invalidateChild()方法,
该方法为ViewParent接口的方法,ViewGroup类实现了该接口的invalidateChild方法
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null && attachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated) {
// HW accelerated fast path
onDescendantInvalidated(child, child);
return;
}
ViewParent parent = this;
if (attachInfo != null) {
...
do {
View view = null;
if (parent instanceof View) {
view = (View) parent;
}
if (drawAnimation) {
if (view != null) {
view.mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION;
} else if (parent instanceof ViewRootImpl) {
((ViewRootImpl) parent).mIsAnimating = true;
}
}
...
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);
if (view != null) {
// Account for transform on current parent
Matrix m = view.getMatrix();
if (!m.isIdentity()) {
RectF boundingRect = attachInfo.mTmpTransformRect;
boundingRect.set(dirty);
m.mapRect(boundingRect);
dirty.set((int) Math.floor(boundingRect.left),
(int) Math.floor(boundingRect.top),
(int) Math.ceil(boundingRect.right),
(int) Math.ceil(boundingRect.bottom));
}
}
} while (parent != null);
}
}
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(final int[] location, final Rect dirty) {
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)) != 0) {
...
return mParent;
}
return null;
}
do while循环一层层向上请求重绘,最终应该是到ViewRootImpl类的invalidateChildInParent方法
3、ViewRootImpl如何与View进行关联:从Activity的setContentView开始分析
3.1 最顶层的View——DecorView
要将View显示到界面上,需要在Activity中执行setContentView,这里主要分析setContentView(View)方法
public void setContentView(View view) {
getWindow().setContentView(view);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
public Window getWindow() {
return mWindow;
}
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
...
}
mWindow属性在android.app.Activity#attach方法中进行赋值, 实现类为PhoneWindow,而PhoneWindow的setContentView实现如下:
// This is the top-level view of the window, containing the window decor.
private DecorView mDecor;
@Override
public void setContentView(View view) {
setContentView(view, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
@Override
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
view.setLayoutParams(params);
final Scene newScene = new Scene(mContentParent, view);
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mContentParent.addView(view, params);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}
private void installDecor() {
mForceDecorInstall = false;
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor(-1);
mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) {
mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable);
}
} else {
mDecor.setWindow(this);
}
...
}
protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) {
// System process doesn't have application context and in that case we need to directly use
// the context we have. Otherwise we want the application context, so we don't cling to the
// activity.
Context context;
if (mUseDecorContext) {
Context applicationContext = getContext().getApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext == null) {
context = getContext();
} else {
context = new DecorContext(applicationContext, getContext());
if (mTheme != -1) {
context.setTheme(mTheme);
}
}
} else {
context = getContext();
}
return new DecorView(context, featureId, this, getAttributes());
}
可以看出mDecor为View树中最顶层的View,是DecorView类的一个实例。
3.2 DecorView与ViewRootImpl进行关联
这里我是通过搜索“DecorView如何与ViewRootImpl进行关联”才知道具体关联代码,见链接https://www.cnblogs.com/huansky/p/11911549.html
主要在ActivityThread类的handleResumeActivity方法中
@Override
public void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token, boolean finalStateRequest, boolean isForward,
String reason) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
// TODO Push resumeArgs into the activity for consideration
final ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, finalStateRequest, reason);
if (r == null) {
// We didn't actually resume the activity, so skipping any follow-up actions.
return;
}
final Activity a = r.activity;
if (localLOGV) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Resume " + r + " started activity: " + a.mStartedActivity
+ ", hideForNow: " + r.hideForNow + ", finished: " + a.mFinished);
}
final int forwardBit = isForward
? WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION : 0;
// If the window hasn't yet been added to the window manager,
// and this guy didn't finish itself or start another activity,
// then go ahead and add the window.
boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
if (!willBeVisible) {
try {
willBeVisible = ActivityManager.getService().willActivityBeVisible(
a.getActivityToken());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (r.mPreserveWindow) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
r.mPreserveWindow = false;
// Normally the ViewRoot sets up callbacks with the Activity
// in addView->ViewRootImpl#setView. If we are instead reusing
// the decor view we have to notify the view root that the
// callbacks may have changed.
ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl();
if (impl != null) {
impl.notifyChildRebuilt();
}
}
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
if (!a.mWindowAdded) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);
} else {
// The activity will get a callback for this {@link LayoutParams} change
// earlier. However, at that time the decor will not be set (this is set
// in this method), so no action will be taken. This call ensures the
// callback occurs with the decor set.
a.onWindowAttributesChanged(l);
}
}
// If the window has already been added, but during resume
// we started another activity, then don't yet make the
// window visible.
} else if (!willBeVisible) {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Launch " + r + " mStartedActivity set");
r.hideForNow = true;
}
...
}
一般执行流程: 获取Activity实例a对应的WindowManager实例wm,然后addView。
Activity的attach方法中对mWindowManager对象赋值,mWindowManager对象从mWindow对象中获得
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
...
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
...
}
mWindow对象为Window类,getWindowManager实现如下,则ActivityThread类中handleResumeActivity获取的wm对象实现类为WindowManagerImpl类
public WindowManager getWindowManager() {
return mWindowManager;
}
public void setWindowManager(WindowManager wm, IBinder appToken, String appName,
boolean hardwareAccelerated) {
mAppToken = appToken;
mAppName = appName;
mHardwareAccelerated = hardwareAccelerated
|| SystemProperties.getBoolean(PROPERTY_HARDWARE_UI, false);
if (wm == null) {
wm = (WindowManager)mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
}
mWindowManager = ((WindowManagerImpl)wm).createLocalWindowManager(this);
}
WindowManagerImpl类addView(View, ViewGroup.LayoutParams)实现如下
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);
}
委托给WindowManagerGlobal类的addView(View, ViewGroup.LayoutParams, Display, Window)实现,最终调用ViewRootImpl的setView方法关联DecorView与ViewRootImpl
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
...
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
...
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
4、其他
4.1 获取DecorView与ViewRootImpl的直接方法
在View中mParent只有一处赋值,就是在void assignParent(ViewParent parent)方法中,可以在这里添加一个条件断点 parent instanceof ViewRootImpl, 就可以获取对应的调用信息
4.2 硬件加速相关以及invalidate()流程图
ViewGroup类的invalidateChild部分代码如下,
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null && attachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated) {
// HW accelerated fast path
onDescendantInvalidated(child, child);
return;
}
...
do {
View view = null;
if (parent instanceof View) {
view = (View) parent;
}
if (drawAnimation) {
if (view != null) {
view.mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION;
} else if (parent instanceof ViewRootImpl) {
((ViewRootImpl) parent).mIsAnimating = true;
}
}
// If the parent is dirty opaque or not dirty, mark it dirty with the opaque
// flag coming from the child that initiated the invalidate
if (view != null) {
if ((view.mViewFlags & FADING_EDGE_MASK) != 0 &&
view.getSolidColor() == 0) {
opaqueFlag = PFLAG_DIRTY;
}
if ((view.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) != PFLAG_DIRTY) {
view.mPrivateFlags = (view.mPrivateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | opaqueFlag;
}
}
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);
if (view != null) {
// Account for transform on current parent
Matrix m = view.getMatrix();
if (!m.isIdentity()) {
RectF boundingRect = attachInfo.mTmpTransformRect;
boundingRect.set(dirty);
m.mapRect(boundingRect);
dirty.set((int) Math.floor(boundingRect.left),
(int) Math.floor(boundingRect.top),
(int) Math.ceil(boundingRect.right),
(int) Math.ceil(boundingRect.bottom));
}
}
} while (parent != null);
}
其中attachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated表示启用硬件加速,如果启用硬件加速,子线程invalidate()不会产生异常(genymotion9.0模拟器中未产生异常,genymotion6.0模拟器中会产生异常)。
本文开始在activity中禁用硬件加速就是因为这个原因,而像子线程中requestLayout、addView等硬件没有加速问题,一定会报异常。
invalidate()执行后方法调用流程图如下:

4.3 View加载线程问题
只要View没有添加到Window中View就可以在子线程中操作,不过会有线程安全问题。
子线程调用invalidate()产生“Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.”原因分析的更多相关文章
- 开发错误记录1:解决:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.
今天在项目中要使用圆角头像,导入开源 CircleImageView ,然后setImageBitmap()时 运行时就会发现,它会报一个致命性的异常:: · ERROR/AndroidRuntime ...
- 浅析Android中的消息机制-解决:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.
在分析Android消息机制之前,我们先来看一段代码: public class MainActivity extends Activity implements View.OnClickListen ...
- Android: Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views 异常
最近自己再写一个小项目练手,创建一个线程从网络获取数据然后显示在 recyclerView 上.写好后发现页面能够显示,但是有时候会把请求的数据显示过来,有时候不会.点开 android monito ...
- Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views解决办法
这周操作系统作业布置了一个作业,内容是做个小软件,来模拟消费者生产者问题,作业实现起来不来,因为之前写过这个算法,所以关键步骤就是在消费和生产的时候更新缓存区的UI控件就行,之后问题就来了,出现了标题 ...
- 错误:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views——Handler的使用
在跟随教程学习到显示web页面的html源码时报错:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views ...
- Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views
在调试软件的时候出现如下的错误: 01-05 20:53:36.492: E/ZZShip(2043): android.view.ViewRootImpl$CalledFromWrongThread ...
- 解决Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views
这种异常出现在子线程中处理UI操作产生的异常,将UI操作放在主线程中就OK了
- andriod 错误:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views——Handler的使用
package com.example.yanlei.myapplication; import android.media.MediaMetadataRetriever; import androi ...
- "Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.” 解决方法
这个主要总是,开启的线程和 UI 线程(主线程)不是同一个线程.可以Runnable方式避免,如下例所示就可以解决这个问题了. public static void updateText(Activi ...
随机推荐
- 001 发大招了 神奇的效率工具--Java代码转python代码
今天发现一个好玩的工具: 可以直接将java转成python 1. 安装工具(windows 环境下面) 先下载antlr: 下载链接如下: http://www.antlr3.org/downloa ...
- 在 Visual Studio 中创建一个简单的 C# 控制台应用程序
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43994242/article/details/87260824 快速入门:使用 Visual Studio 创建第一个 C# 控制台应用 h ...
- ATMEGA的SPI总线 - 第1部分
转自: 1. https://www.yiboard.com/thread-782-1-1.html 2.https://mansfield-devine.com/speculatrix/2018/0 ...
- PADS Layout VX.2.3 修改层名
操作系统:Windows 10 x64 工具1:PADS Layout VX.2.3 点击菜单Setup > Layer Definition... 在Layers Setup窗口中,选择相应的 ...
- C语言中最常用的标准库函数
标准头文件包括: <asset.h> <ctype.h> <errno.h> <float.h> <limits ...
- pycharm 解决PEP8问题,配置autopep8到菜单栏
autopep8是一个可以将Python代码自动排版为PEP8风格第三方包,使用它可以轻松地排版出格式优美整齐的代码.网络上有很多介绍如何在pycharm中配置autopep8的方案,但很多方案中还是 ...
- tu
1 第五章 图 2 //结构定义 3 #define MaxVertexNum 100 //图中顶点数目的最大值 4 typedef struct ArcNode{ //边表节点 5 int adjv ...
- Linux 下 svn 场景实例及常用命令详解
一.SVN使用场景实例 问题: 在使用svn做为版本控制系统的软件开发中,经常会有这样的需求:在工作复本目录树的不同目录中增加了很多文件,但未纳入版本控制系统,这时如果使用svn add命令一个一个的 ...
- Dotnet Core使用特定的SDK&Runtime版本
Dotnet Core的SDK版本总在升级,怎么使用一个特定的版本呢? 假期过完了,心情还在.今天写个短的. 一.前言 写这个是因为昨天刷微软官方文档,发现global.json在 SDK 3.0 ...
- k8s集群调度方案
Scheduler是k8s集群的调度器,主要的任务是把定义好的pod分配到集群节点上 有以下特征: 1 公平 保证每一个节点都能被合理分配资源或者能被分配资源 2 资源高效利用 集群所有资 ...
