pytest测试框架 -- assert断言和fixture固件
一、断言
(1)使用assert语句进行断言
# test_run.py @pytest.mark.assert
def test_assert(self):
r = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com")
assert r.status_code == 100
# pytest常用的python断言:
1)assert xx:判断xx为真
2)assert not xx:判断xx不为真
3)assert a in b:判断b包含a
4)assert a not in b: 判断b不包含a
5)assert a == b:判断a等于b
6)assert a !=b:判断a不等于b
(2)使用pytest.raises触发期望异常的断言
# test_run.py @pytest.mark.arrser
def test_assert(self):
r = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com")
with pytest.raises(AssertionError) as excinfo:
assert r.status_code == 201 # 此处可能存在异常,所以主动raises抛出
print("This will be not execute") # 此处未被执行
assert excinfo.type == AssertionError # 此处被执行
assert "" in str(excinfo.value) # 此处被执行
print("This will be execute") # 此处被执行
excinfo 是一个异常信息实例,它是围绕实际引发的异常的包装器。主要属性是.type、 .value 和 .traceback
注意:断言type的时候,异常类型是不需要加引号的,断言value值的时候需转str。
二、fixture的使用
(1)fixture的作用
- 完成setup和teardown操作,处理数据库、文件等资源的打开和关闭
- 完成大部分测试用例需要完成的通用操作,例如login、设置config参数、环境变量等
- 准备测试数据,将数据提前写入到数据库,或者通过params返回给test用例,等
(2)fixture的优势
- 命名方式灵活,不局限于setup和teardown这几个命名
- conftest.py 配置里可以实现数据共享,不需要import就能自动找到一些配置
- scope="function",若多个用例都调用了fixture函数,则此fixture在每个用例开始前都执行一次
- scope="class",如果一个class的多个用例都调用了次fixture,则此fixture仅在第一次调用开始前执行一次,后续调用不执行
- scope="module" 在当前.py脚本里面所有用例开始前只执行一次。
- scope="session" 以实现多个.py跨文件使用一个session来完成多个用例
(3)fixture源码详解
fixture(scope='function',params=None,autouse=False,ids=None,name=None):
scope:有四个级别参数"function"(默认),"class","module","session"
params:一个可选的参数列表,它将导致多个参数调用fixture功能和所有测试使用它。
autouse:如果True,则为所有测试激活fixture func可以看到它。如果为False则显示需要参考来激活fixture
ids:每个字符串id的列表,每个字符串对应于params这样他们就是测试ID的一部分。如果没有提供ID它们将从params自动生成
name:fixture的名称。这默认为装饰函数的名称。如果fixture在定义它的统一模块中使用,夹具的功能名称将被请求夹具的功能arg遮蔽,解决这个问题的一种方法时将装饰函数命令"fixture_<fixturename>"然后使用"@pytest.fixture(name='<fixturename>')"。
(4)源码演示
1、若scope="function"
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print("登录操作!") def test_01(login):
print("执行用例01,需先登录") def test_02():
print("执行用例02,不需登录") def test_03(login):
print("执行用例03,需先登录"
输出结果:

2、若scope="class"
@pytest.fixture(scope='class')
def login():
print("登录操作!") class TestFixture1():
def test_01(self, login):
print("执行用例01,需先登录")
def test_02(self):
print("执行用例02,不需登录")
def test_03(self, login):
print("执行用例03,需先登录") class TestFixture2():
def test_01(self, login):
print("执行用例01,需先登录")
def test_02(self):
print("执行用例02,不需登录")
def test_03(self, login):
print("执行用例03,需先登录")
输出结果:

3、若scope="module"
@pytest.fixture(scope='module')
def login():
print("登录操作!") class TestFixture1():
def test_01(self, login):
print("执行用例01,需先登录")
def test_02(self):
print("执行用例02,不需登录")
def test_03(self, login):
print("执行用例03,需先登录") class TestFixture2():
def test_01(self, login):
print("执行用例01,需先登录")
def test_02(self):
print("执行用例02,不需登录")
def test_03(self, login):
print("执行用例03,需先登录")
输出结果:

4、若scope="session"
fixture为session级别是可以跨.py模块调用的,也就是当我们有多个.py文件的用例的时候,如果多个用例只需调用一次fixture,那就可以设置为scope="session",并且写到conftest.py文件里。
conftest.py文件名称时固定的,pytest会自动识别该文件。放到项目的根目录下就可以全局调用了,如果放到某个package下,那就在该package内有效。
一个工程下可以建多个conftest.py的文件,一般在工程根目录下设置的conftest文件起到全局作用。在不同子目录下也可以放conftest.py的文件,作用范围只能在该层级以及以下目录生效。
# conftest.py
import pytest @pytest.fixture(scope='session')
def test1():
print("登录操作")
# test_fixture1.py
import pytest
def test_01(test1):
print("用例01,需要先登录") def test_02(test1):
print("用例02,需要先登录") if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(['-s', 'test_fixture1.py'])
pytest.main(['-s', 'test_fixture2.py'])
# test_fixture2.py
import pytest
class TestCase():
def test_03(self, test1):
print("用例03,需先登录") def test_04(self, test1):
print("用例04,需先登录") if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(['-s', 'test_fixture2.py'])
(1)若pycharm下运行test_fixture1.py,则输出结果如下:
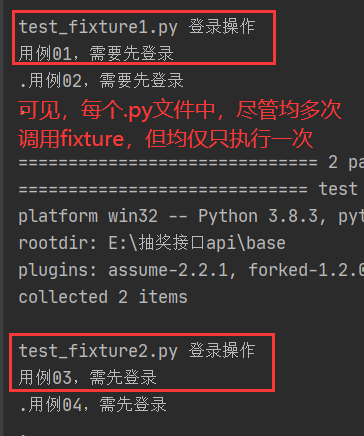
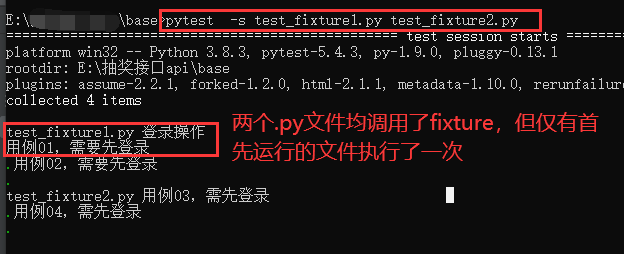
(2)若在命令行下同时运行test_fixture1.py 和test_fixture2.py两个文件,则结果输出如下:
三、使用装饰器@pytest.mark.usefixtures()修饰需要运行的用例
如果一个方法或者一个class用例想要同时调用多个fixture,可以使用@pytest.mark.usefixture()进行叠加。注意叠加顺序,先执行的放底层,后执行的放上层。
import pytest @pytest.fixture()
def test1():
print("执行function1") @pytest.fixture()
def test2():
print("执行function2") @pytest.mark.usefixtures('test1')
def test_01():
print("---用例a执行---") @pytest.mark.usefixtures('test1') # 后执行
@pytest.mark.usefixtures('test2') # 先执行
class TestCase():
def test_02(self):
print("---用例b执行---") def test_03(self):
print("---用例c执行---") 输出结果:
test_fixture2.py 执行function1
---用例a执行---
.执行function2
执行function1
---用例b执行---
.执行function2
执行function1
---用例c执行---
usefixtures与传fixture区别
(1)如果fixture有返回值,那么usefixture就无法获取到返回值,这个是装饰器usefixture与用例直接传fixture参数的区别。
(2)当fixture需要用到return出来的参数时,只能将参数名称直接当参数传入,不需要用到return出来的参数时,两种方式都可以。
四、使用pytestmark或autouse使得每个函数都调用该固件
(1)如果你想要模块中的每个函数都调用该固件,你也可以使用pytestmark标记(注意:pytestmark变量名不可更改)
import pytest @pytest.fixture()
def test2():
print("执行function2") pytestmark = pytest.mark.usefixtures('test2') def test_01():
print("---用例a执行---") class TestCase():
def test_02(self):
print("---用例b执行---") def test_03(self):
print("---用例c执行---") 输出结果:
test_fixture2.py 执行function2
---用例a执行---
.执行function2
---用例b执行---
.执行function2
---用例c执行---
(2)使用@pytest.fixture()中的参数autouse(自动使用),将其设为true(默认为false),这样每个函数都会自动调用该前置函数了:
import pytest @pytest.fixture(autouse='true')
def test1():
print("执行function1") def test_01():
print("---用例a执行---") class TestCase():
def test_02(self):
print("---用例b执行---") def test_03(self):
print("---用例c执行---") 输出结果:
test_fixture2.py 执行function1
---用例a执行---
.执行function1
---用例b执行---
.执行function1
---用例c执行---
五、params参数化
params参数可以实现前置函数的参数化,调用前置函数的测试用例可以根据前置函数不同的参数执行多次。
在fixture标签中的params参数传入了列表类型的参数列表;我们又在前置函数中传入了request参数;最后在测试函数中我们通过request.param来表示参数(参数列表中的每个值)
import pytest @pytest.fixture(params=['参数1','参数2'])
def test1(request):
print("执行前置函数, %s" % request.param) def test_01(test1): # 注意,此时test1未用引号
print("---用例a执行---") class TestCase():
def test_02(self):
print("---用例b执行---") def test_03(self):
print("---用例c执行---") 输出结果:
test_fixture2.py 执行前置函数, 参数1
---用例a执行---
.执行前置函数, 参数2
---用例a执行---
.---用例b执行---
.---用例c执行-- 或者:
import pytest
import requests url_datas = ["http://www.baidu.com", "http://www.weibo.com"] @pytest.fixture(params=url_datas)
def get_url(request):
return request.param def test_get_status_code(get_url):
r = requests.get(get_url)
print(r.status_code) if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(['-s', 'test_fixture1.py']) 输出结果:
test_fixture1.py 200
.200
.
使用yield实现前置和后置函数(如setUp和tearDown)。
yield相当于 return 返回一个值,并且记住这个返回的位置,下次迭代时,代码从yield的下一条语句开始执行。
import pytest def connect():
print("连接数据库") def disconnect():
print("断开数据库") @pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def databases():
connect() # 前置函数
yield
disconnect() # 后置函数 def test_01(databases):
print("执行用例a") class TestCase(): def test_02(self, databases):
print("执行用例b") def test_03(self, databases):
print("执行用例c") if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(['-s', 'test_fixture1.py']) 运行结果:
连接数据库
执行用例a
.断开数据库
连接数据库
执行用例b
.执行用例c
.断开数据库
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/huizaia/p/10331469.html
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39721240/article/details/88650329
pytest测试框架 -- assert断言和fixture固件的更多相关文章
- Pytest测试框架(三):pytest fixture 用法
xUnit style 结构的 fixture用于初始化测试函数, pytest fixture是对传统的 xUnit 架构的setup/teardown功能的改进.pytest fixture为测试 ...
- 『德不孤』Pytest框架 — 1、Pytest测试框架介绍
目录 1.什么是单元测试框架 2.单元测试框架主要做什么 3.单元测试框架和自动化测试框架有什么关系 4.Pytest测试框架说明 5.Pytest框架和Unittest框架区别 (1)Unittes ...
- Pytest测试框架(一):pytest安装及用例执行
PyTest是基于Python的开源测试框架,语法简单易用,有大量的插件,功能非常多.自动检测测试用例,支持参数化,跳过特定用例,失败重试等功能. 安装 pip install -U pytest ...
- Pytest测试框架(二):pytest 的setup/teardown方法
PyTest支持xUnit style 结构, setup() 和 teardown() 方法用于初始化和清理测试环境,可以保证测试用例的独立性.pytest的setup/teardown方法包括:模 ...
- Pytest测试框架(五):pytest + allure生成测试报告
Allure 是一款轻量级.支持多语言的开源自动化测试报告生成框架,由Java语言开发,可以集成到 Jenkins. pytest 测试框架支持Allure 报告生成. pytest也可以生成juni ...
- pytest测试框架 -- 简介
一.pytest测试框架简介: (1)pytest是python的第三方测试框架,是基于unittest的扩展框架,比unittest更简洁,更高效. (2)pytest框架可以兼容unittest用 ...
- 技术面试没过,居然是没有用pytest测试框架
1.引言 我有一个朋友是做Python自动化测试的.前几天他告诉我去参加一个大厂面试被刷了. 我问他是有没有总结被刷下来的原因.他说面试官问了一些 pytest 单元测试框架相关的知识,包括什么插件系 ...
- Pytest 测试框架
一 . Pytest 简介 Pytest是python的一种单元测试框架. 1. pytest 特点 入门简单,文档丰富 支持单元测试,功能测试 支持参数化,重复执行,部分执行,测试跳过 兼容其他测试 ...
- 【pytest系列】- pytest测试框架介绍与运行
如果想从头学起pytest,可以去看看这个系列的文章! https://www.cnblogs.com/miki-peng/category/1960108.html 前言 目前有两种纯测试的测 ...
随机推荐
- 四种方法求Capacitated Facility Location Problem问题
问题详情 1. 贪心算法 1.1 算法框架 此题可以利用贪心算法来求解, 可以假设只关注顾客的cost, 当仓库满了就在下一个仓库里 具体解决方案: 将每个顾客到工厂的cost 由小到大进行排序 从第 ...
- Linux根目录下文件夹用途解释
root目录:主要用于存放root用户相关文件的目录: usr目录:安装一个软件时,linux指定的此软件默认安装的目录: home目录:用于存放普通用户的相关文件的目录:例如:我使用adduser ...
- iOS Abort问题系统性解决方案
一.背景 崩溃(Crash),即闪退,多指移动设备(如iOS.Android设备)在打开/使用应用程序的过程中,突然出现意外退出/中断的情况.如果App线上版本频繁发生崩溃,会极大地影响用户体验,甚至 ...
- 【转载】PyChram简单使用教程
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yamei/p/5519818.html 一.PyChram下载官网:http://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm Win ...
- Android Studio 突然无法识别真机问题
最近在赶项目,今天AS突然疯狂跟我作对,森气!! 平时连接手机没有问题,今天突然各种识别不到真机!! 1.数据线,check.没有问题. 2.重启AS,还是不行. 3.安装驱动,行不通. 4.已经弹出 ...
- 关于Exceptionless日志收集框架会被Fiddler抓包,从而获取到ApiKey的问题
关于Exceptionless日志收集框架会被Fiddler抓包,从而获取到ApiKey的问题 环境:Exceptionless5.0.0.Linux.WPF客户端.Fiddler 问题:在使用Exc ...
- VScode+PicGo+Github+jsdelivr使用图床书写Markdown
本文讲述使用Github作为图床,VScode搭配Picgo插件书写Markdown,并使用jsdelivr进行CDN加速的配置流程. 准备阶段 首先进行以下准备工作,都很简单,不再赘述. 注册Git ...
- vmware 虚拟机共享 windows 目录
1.vmware 配置: 2.虚拟机进行配置: 虚拟机安装vmware-tools 3.虚拟机中挂载sr0(cdrom): [root@bogon ~]# mount /dev/sr0 /mnt/ m ...
- SCE信号期末复习省流小助手(懒人版)
XDU-SCE网信院信号期末复习省流小助手(懒人版) 本人根据西安电子科技大学网络与信息安全18年期末考试整理的考点和题型 以下题型代表了信号与系统课程的 精髓 若能掌握以下知识点和题型,80分稳有: ...
- go语言之文件操作
一: 相关的API 1func Create(name string) (file *File, err Error) 根据提供的文件名创建新的文件,返回一个文件对象,默认权限是0666 2 func ...
