SpringBoot的定时任务
springBoot定时任务可分为多线程和单线程,而单线程又分为注解形式,接口形式
1.基于注解形式
基于注解@Scheduled默认为单线程,开启多个任务时,任务的执行时机会受上一个任务执行时间的影响。
1)创建定时器
使用SpringBoot基于注解来创建定时任务非常简单,只需几行代码便可完成。 代码如下
package com.cst.klocwork.service.cron; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.cst.util.string.LocalDateTimes; @Component
@Configuration //1.主要用于标记配置类,兼备Component的效果。
@EnableScheduling // 2.开启定时任务
public class Test {
//3.添加定时任务
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?")
//或直接指定时间间隔,例如:5秒
//@Scheduled(fixedRate=5000)
private void configureTasks() {
f1();
} public void f1() {
System.err.println("执行静态定时任务时间:=== " + LocalDateTimes.nowFormat());
}
}
Cron表达式参数分别表示:
- 秒(0~59) 例如0/5表示每5秒
- 分(0~59)
- 时(0~23)
- 日(0~31)的某天,需计算
- 月(0~11)
- 周几( 可填1-7 或 SUN/MON/TUE/WED/THU/FRI/SAT)
@Scheduled:除了支持灵活的参数表达式cron之外,还支持简单的延时操作,例如 fixedDelay ,fixedRate 填写相应的毫秒数即可。
2)启动测试
启动springBoot项目,可以看到控制台打印出如下信息:
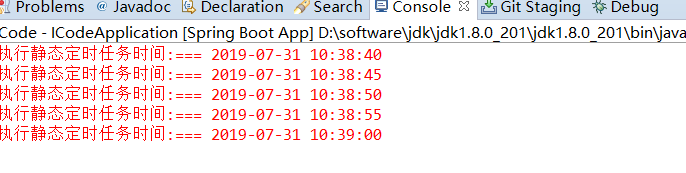
显然,使用@Scheduled 注解很方便,但缺点是当我们调整了执行周期的时候,需要重启应用才能生效,这多少有些不方便。为了达到实时生效的效果,可以使用接口来完成定时任务。
2.基于接口
1)导入依赖包:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent> <dependencies>
<dependency><!--添加Web依赖 -->
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><!--添加MySql依赖 -->
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><!--添加Mybatis依赖 配置mybatis的一些初始化的东西-->
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><!-- 添加mybatis依赖 -->
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2)添加数据库记录:
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS `socks`;
CREATE DATABASE `socks`;
USE `SOCKS`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `cron`;
CREATE TABLE `cron` (
`cron_id` varchar(30) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
`cron` varchar(30) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO `cron` VALUES ('1', '0/5 * * * * ?');
然后在项目中的application.properties添加数据库的配置
3.创建定时器
数据库准备好数据之后,我们编写定时任务,注意这里添加的是TriggerTask,目的是循环读取我们在数据库设置好的执行周期,以及执行相关定时任务的内容。
具体代码如下:
bean类:
package com.cst.klocwork.bean.cron; import com.cst.util.bean.IBean;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Accessors(chain = true)
@Data
public class Cron implements IBean{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String cron_id;
private String cron; }
mapper类:
package com.cst.klocwork.bean.cron;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; @Mapper
@Component
public interface CronMapper extends BaseMapper<Cron>{ @Select("select cron from cron where cron_id = '1'")
String getCron(); }
定时器任务类:
package com.cst.klocwork.service.cron; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.SchedulingConfigurer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.config.ScheduledTaskRegistrar;
import org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronTrigger;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import com.cst.klocwork.bean.cron.CronMapper;
import com.cst.util.string.LocalDateTimes; @Component
@Configuration //1.主要用于标记配置类,兼备Component的效果。
@EnableScheduling // 2.开启定时任务
public class DynamicScheduleTask implements SchedulingConfigurer { @Autowired //注入mapper
private CronMapper cronMapper; /**
* 执行定时任务.
*/
@Override
public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar taskRegistrar) { taskRegistrar.addTriggerTask(
//1.添加任务内容(Runnable)
() -> f1(),
//2.设置执行周期(Trigger)
triggerContext -> {
//2.1 从数据库获取执行周期
String cron = cronMapper.getCron();
//2.2 合法性校验.
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(cron)) {
// Omitted Code ..
}
//2.3 返回执行周期(Date)
return new CronTrigger(cron).nextExecutionTime(triggerContext);
}
);
} public void f1() {
System.err.println("执行动态定时任务: " + LocalDateTimes.nowFormat());
}
}
4)、启动测试
启动springBoot项目后,查看控制台,打印时间是我们预期的每10秒一次:
如果此处想修改运行周期,只需要修改数据库里的时间即可改变运行周期。并且不需要我们重启应用,十分方便。
注意: 如果在数据库修改时格式出现错误,则定时任务会停止,即使重新修改正确;此时只能重新启动项目才能恢复。
3.多线程定时任务
基于注解设定多线程定时任务
1)创建多线程定时任务
//@Component注解用于对那些比较中立的类进行注释;
//相对与在持久层、业务层和控制层分别采用 @Repository、@Service 和 @Controller 对分层中的类进行注释
@Component
@EnableScheduling // 1.开启定时任务
@EnableAsync // 2.开启多线程
public class MultithreadScheduleTask { @Async
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000) //间隔1秒
public void first() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("第一个定时任务开始 : " + LocalDateTime.now().toLocalTime() + "\r\n线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println();
Thread.sleep(1000 * 10);
} @Async
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 2000)
public void second() {
System.out.println("第二个定时任务开始 : " + LocalDateTime.now().toLocalTime() + "\r\n线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println();
}
}
2)启动springBoot项目后
查看控制台
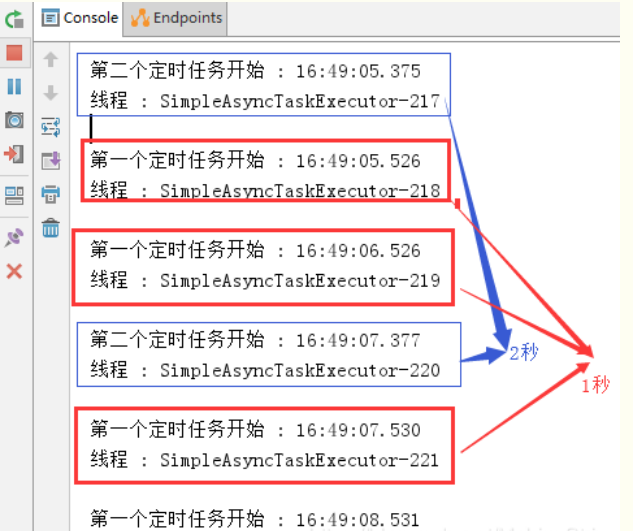
从控制台可以看出,第一个定时任务和第二个定时任务互不影响;
并且,由于开启了多线程,第一个任务的执行时间也不受其本身执行时间的限制,所以需要注意可能会出现重复操作导致数据异常。
SpringBoot的定时任务的更多相关文章
- 玩转SpringBoot之定时任务详解
序言 使用SpringBoot创建定时任务非常简单,目前主要有以下三种创建方式: 一.基于注解(@Scheduled) 二.基于接口(SchedulingConfigurer) 前者相信大家都很熟悉, ...
- SpringBoot 配置定时任务
SpringBoot启用定时任务,其内部集成了成熟的框架,因此我们可以很简单的使用它. 开启定时任务 @SpringBootApplication //设置扫描的组件的包 @ComponentScan ...
- SpringBoot - 添加定时任务
SpringBoot 添加定时任务 EXample1: import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.spri ...
- springboot之定时任务
定时线程 说到定时任务,通常会想到JDK自带的定时线程来执行,定时任务. 回顾一下定时线程池. public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledT ...
- SpringBoot整合定时任务和异步任务处理 3节课
1.SpringBoot定时任务schedule讲解 定时任务应用场景: 简介:讲解什么是定时任务和常见定时任务区别 1.常见定时任务 Java自带的java.util.Timer类 ...
- 十三、springboot集成定时任务(Scheduling Tasks)
定时任务(Scheduling Tasks) 在springboot创建定时任务比较简单,只需2步: 1.在程序的入口加上@EnableScheduling注解. 2.在定时方法上加@Schedule ...
- SpringBoot创建定时任务
之前总结过spring+quartz实现定时任务的整合http://www.cnblogs.com/gdpuzxs/p/6663725.html,而springboot创建定时任务则是相当简单. (1 ...
- springboot开启定时任务 添加定时任务 推送
最近在自学Java的springboot框架,要用到定时推送消息.参考了网上的教程,自己调试,终于调好了.下面将网上的教程归纳下,总结复习下. springboot开启定时任务 在SpringBo ...
- (入门SpringBoot)SpringBoot结合定时任务task(十)
SpringBoot整合定时任务task 使用注解EnableScheduling在启动类上. 定义@Component作为组件被容器扫描. 表达式生成地址:http://cron.qqe2.com ...
- SpringBoot整合定时任务和异步任务处理
SpringBoot定时任务schedule讲解 简介:讲解什么是定时任务和常见定时任务区别 1.常见定时任务 Java自带的java.util.Timer类 timer:配置比较麻烦,时间延后问题, ...
随机推荐
- ssh密码登录
https://stackoverflow.com/a/16928662/8025086 https://askubuntu.com/a/634789/861079 #!/usr/bin/expect ...
- FZU ICPC 2020 寒假训练 5 —— 排序
P1177 [模板]快速排序 题目描述 利用快速排序算法将读入的 N 个数从小到大排序后输出.快速排序是信息学竞赛的必备算法之一.对于快速排序不是很了解的同学可以自行上网查询相关资料,掌握后独立完成. ...
- Hi3516开发笔记(一):海思HI3516DV300芯片介绍,入手开发板以及Demo测试
前言 目前主流国产芯片为RV11XX.RK33XX.Hi35XX系列,本系列开启Hi3516系列的开发教程. Hi3516DV300芯片介绍 Hi3516DV300为专业行Smart IP ...
- 一文分析 Android现状及发展前景
Coding这些年,一直低头"搬砖",好像从未仔细审视过Android的发展现状,亦未好好思考Android的发展前景."低头干活,还要抬头看路",写一篇文章简 ...
- Linux驱动实践:你知道【字符设备驱动程序】的两种写法吗?
作 者:道哥,10+年嵌入式开发老兵,专注于:C/C++.嵌入式.Linux. 关注下方公众号,回复[书籍],获取 Linux.嵌入式领域经典书籍:回复[PDF],获取所有原创文章( PDF 格式). ...
- 提升AI智能化水平,打造智慧新体验
内容来源:华为开发者大会2021 HMS Core 6 AI技术论坛,主题演讲<提升AI智能化水平,打造智慧新体验>. 演讲嘉宾:沈波,华为消费者AI与智慧全场景ML Kit产品总监 今天 ...
- 「后端小伙伴来学前端了」Vuex进阶操作,让你的代码更加高效(简称如何学会偷懒 【手动狗头】)
学妹手机里的美照 前言 前一篇写了Vuex基本使用,用起来还稍稍有些繁琐,代码有很多 冗余的地方,这篇就带着大家用更简单的方式来使用Vuex(其实就是怎么更好的偷懒,用更少的代码来完之前的事情) 进入 ...
- 实践案例1-利用低代码开发平台Odoo快速构建律师事务所管理系统
今年10月份中旬的时候,有一段时间没联系的中学同学,我跟他关系比较好,突然打电话给我,希望我给他夫人的律所开发一个小系统.记得十几年前,当他还在他叔叔公司上班的,他是负责销售的,我们几乎每周都碰面,那 ...
- Linux非root安装Python3以及解决SSL问题
说明 接上一篇. [Linux]非root安装Python3及其包管理 上一篇虽然成功安装了Python3及一些常用的模块,但因为一直装不上SSL模块,导致一些包无法安装,尝试了不少方法都失败了(网上 ...
- 47-Generate Parentheses
Generate Parentheses My Submissions QuestionEditorial Solution Total Accepted: 86957 Total Submissio ...
