81-POJ-Wall(计算几何)
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 41143 | Accepted: 14068 |
Description

Your task is to help poor Architect to save his head, by writing a program that will find the minimum possible length of the wall that he could build around the castle to satisfy King's requirements.
The task is somewhat simplified by the fact, that the King's castle has a polygonal shape and is situated on a flat ground. The Architect has already established a Cartesian coordinate system and has precisely measured the coordinates of all castle's vertices in feet.
Input
Next N lines describe coordinates of castle's vertices in a clockwise order. Each line contains two integer numbers Xi and Yi separated by a space (-10000 <= Xi, Yi <= 10000) that represent the coordinates of ith vertex. All vertices are different and the sides of the castle do not intersect anywhere except for vertices.
Output
Sample Input
9 100
200 400
300 400
300 300
400 300
400 400
500 400
500 200
350 200
200 200
Sample Output
1628
Hint
Source
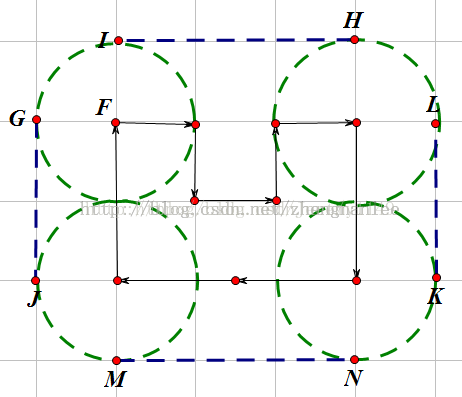
证明:

先从简单的例子看起:假设现在的凸包有四个顶点构成,可以就一个顶点来观察,我们可以看到此处的周角由四个部分组成:2个直角,一个凸包内角,一个圆弧对应的圆心角。
同理每个顶点都有类似的关系,同时周角固定为360度,而凸包内角和为(4-2)*180 ;
所以总的圆弧对应的圆心角 = 4个周角 - 4 * 2个直角 - 4个凸包内角 = 4 * 360 - 4 * 2 * 90 - (4-2)*180 = 1440-720-360 =360度。
现在推广到n个顶点的凸包:
则所有内角和 = 周角 * n - n * 2个直角 - (n-2)*180 = 360*n - n *180 - n*180 + 360 = 360度。
故对于任意的凸包,所有的圆弧对应的圆心角之和都为360度,它们构成一个完整的圆。
ac代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#define N 10005
const double PI = acos(-1.0); int n,tot;//n为二维平面上点的个数,tot为凸包上点的个数
struct node {
int x,y;
}a[N],p[N]; //p[]用来储存凸包 double dis(node a1,node b1){ //两点间距离公式
return sqrt((a1.x-b1.x)*(a1.x-b1.x)+(a1.y-b1.y)*(a1.y-b1.y) + 0.00);
} //叉积:返回结果为正说明p2在向量p0p1的左边(三点构成逆时针方向);
//为负则相反;为0则三点共线(叉积的性质很重要)
double multi(node p0,node p1,node p2){ //
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
} //极角排序:极角排序是根据坐标系内每一个点与x轴所成的角,逆时针比较。按照角度从小到大的方式排序
int cmp(node p1,node p2){ //极角排序;
int x=multi(p1,p2,a[0]);
if(x>0||(x==0&&dis(p1,a[0])<dis(p2,a[0])))
return 1;
return 0;
} void Graham(){ //求凸包
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) //找到最下最左的一个点
if(a[i].y<a[k].y||(a[i].y==a[k].y&&a[i].x<a[k].x))
k=i;
swap(a[0],a[k]); //将其设置为第一个点
sort(a+1,a+n,cmp);
tot=2,p[0]=a[0],p[1]=a[1]; //p[]模拟栈,用来储存凸包
for(int i=2;i<n;i++){
while(tot>1&&multi(p[tot-1],p[tot-2],a[i])>=0)
tot--; //右拐就回退
p[tot++]=a[i]; //左拐就放入
}
} double getArea(){
struct node b[3];
b[0] = p[0], b[1] = p[1], b[2] = p[2];
double area = 0;
for(int i = 2; i < tot; i++){
area += multi(b[0], b[1], p[i]) / 2.0;
b[1] = p[i];
}
return area;
} double getGirth(){
double rt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < tot; i++){
rt += dis(p[i], p[(i+1)%tot]);
}
return rt;
} int main(){
double L;
while(cin >> n >> L){
tot = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y;
}
Graham();
double res = getGirth();
res += 2*PI*L;
cout << int(res + 0.5) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
81-POJ-Wall(计算几何)的更多相关文章
- POJ 1113 Wall(计算几何の凸包)
Description Once upon a time there was a greedy King who ordered his chief Architect to build a wall ...
- POJ 1556 计算几何+最短路
代码1: #include<iostream> #include<stdio.h> #include<string> #include<string.h> ...
- POJ 2954-Triangle(计算几何+皮克定理)
职务地址:POJ 2954 意甲冠军:三个顶点的三角形,给出,内部需求格点数. 思考:就像POJ 1265. #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h& ...
- poj 1410 计算几何
/** 注意: 千万得小心..就因为一个分号,调了一个晚上... **/ #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using name ...
- poj 2653 计算几何
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> ...
- poj 1269 计算几何
/** 判断直线位置关系 **/ #include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <cstdio> using name ...
- poj 3304 计算几何
大意: 是否存在一条直线,使所有线段在直线上的投影至少交与一点 思路: 转换为是否存在一条直线与所有的线段相交,做这条直线的垂线,那么垂线即为所求 **/ #include <iostream& ...
- poj 2398 计算几何
#include <iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include <algorithm> ...
- BZOJ 1113 Wall ——计算几何
凸包第一题. 自己认为自己写的是Andrew 其实就是xjb写出来居然过掉了测试. 刚开始把pi定义成了int,调了半天 #include <map> #include <cmath ...
- POJ 3855 计算几何·多边形重心
思路: 多边形面积->任选一个点,把多边形拆成三角,叉积一下 三角形重心->(x1+x2+x3)/3,(y1+y2+y3)/3 多边形重心公式题目中有,套一下就好了 计算多边形重心方法: ...
随机推荐
- bzoj 3994 [SDOI2015]约数个数和——反演
题目:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3994 \( d(i*j)=\sum\limits_{x|i}\sum\limits_{y|j ...
- sphinx-1.3.0扩展在pPHP 7.0.7版本编译不通过
在这个网友也是在php7上面编译插件不通过 https://bugs.php.net/bug.php?id=71586 下php7对应的扩展文件即可 http://git.php.net/?p=pec ...
- CRC 自动判断大端 小端
/* aos_crc64.c -- compute CRC-64 * Copyright (C) 2013 Mark Adler * Version 1.4 16 Dec 2013 Mark Adle ...
- 安装ecb
mac emacs上安装ecb,通过elpa折腾得要死,死活无法使用. 解决办法:下载https://github.com/alexott/ecb,添加路径,(require 'ecb),直接ok.
- Go的List操作上的一个小“坑”
转自http://sharecore.net/blog/2014/01/09/the-trap-in-golang-list/ 一直想不清楚一个问题,简单设计的东西到底是“坑多”还是“坑少”呢? 复杂 ...
- ssi框架学习总结
框架简介: 相信大家对于mvc的三层架构已经灰常熟悉了,在这就不细讲了,个人感觉ssi的框架结构还是比较典型的mvc三层架构,还是比较容易上手的.关于这块的入门我想特别感谢下FrankHui童鞋,在他 ...
- GOF23设计模式之外观模式(facade)
一.外观模式概述 外观模式也称为门面模式. 核心:为了系统提供统一的入口,封装子系统的复杂性,便于客户端调用. 二.外观模式场景导入与示例代码 场景:要想自己去注册一个公司,首先去工商局检测命名是否合 ...
- CSS 基本知识梳理-续
CSS 基本知识 1.CSS 简介 CSS 指层叠样式表 (Cascading Style Sheets),是一种用来表现 HTML 文档样式的语言,样式定义如何显示 HTML 元素,是能够真正做到网 ...
- Druid.io系列(四):索引过程分析
原文链接: https://blog.csdn.net/njpjsoftdev/article/details/52956083 Druid底层不保存原始数据,而是借鉴了Apache Lucene.A ...
- 第二章:Android Studio概述(二)[学习Android Studio汉化教程]
The Main Menu Bar 主菜单栏 主菜单栏位于Android Studio的最上面,你几乎可以利用主菜单和其子菜单来执行任何操作.不像Android Studio中其他的一些菜单,主菜单 ...
