output value . Sigmoid neurons are similar to perceptrons, but modified so that small changes in their weights and bias cause only a small change in their output.
http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/chap1.html
. Sigmoid neurons are similar to perceptrons, but modified so that small changes in their weights and bias cause only a small change in their output.
http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/chap3.html


// This is a paper.js widget to show a single neuron learning. In
// particular, the widget is used to show the learning slowdown that
// occurs when the output is saturated.
//
// The same basic widget is used several times, in slightly different
// configurations. paper.js makes it somewhat complex to reuse the
// code, so I have simply duplicated the code. This can give rise to
// bugs if one is not careful to keep the code in sync, so I have
// separated the code into two pieces.
//
// The first piece is the header code. This changes between widgets.
// It sets up things like the starting weight, bias, cost function,
// and so on -- things which may vary betweens widgets.
//
// The second piece is the body code. This is almost exactly the same
// for the different widgets. Note, however, that the costGraphX and
// epochX variables change name, due to a bug in the way paperjs
// handles scope.
//
// We can make these changes by searching on costGraph1 and replacing
// with costGraph2, costGraph3 etc, by replacing epoch1 with epoch2,
// epoch3 etc, and by replcacing cost1 with cost2, cost3 etc.
//
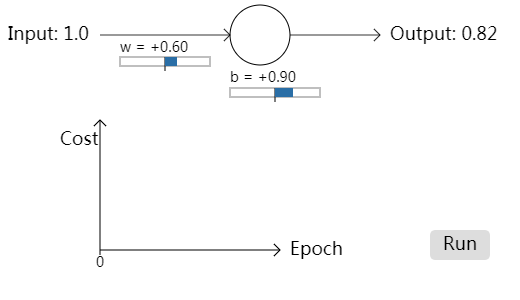
// This separation makes it easy to maintain the duplicated code. // HEADER CODE var startingWeight = 0.6;
var startingBias = 0.9;
var eta = 0.15;
var numFrames = 300; quadratic_cost = {
fn: function(a) {return a*a/2;},
derivative: function(a) {return a*a*(1-a);},
scaling: 240 // used to scale on the graph
} cross_entropy_cost = {
fn: function(a) {return -Math.log(1-a);},
derivative: function(a) {return 1/(1-a);},
scaling: 30
} cost1 = quadratic_cost; // A path for the graph.
costGraph1 = new Path();
costGraph1.strokeColor = "#2A6EA6"; // BODY CODE // STATIC ELEMENTS
//
// Note that this includes some paper.js items which will later be
// modified, e.g., the variables output and weightText. This section
// merely sets the static parts of the elements. var input = new PointText(new Point(8, 40));
input.fontSize = 18;
input.content = "Input: 1.0"; arrow(new Point(100, 35), new Point(230, 35), 0.8); // input arrow var neuron = new Path.Circle(new Point(260, 35), 30);
neuron.strokeColor = "black"; arrow(new Point(290, 35), new Point(380, 35), 0.8); // output arrow // The output text's content will be set dynamically, later
var output = new PointText(new Point(390, 40));
output.fontSize = 18; // The weight text and bar
var weightText = new PointText(new Point(120, 52));
weightText.fontSize=14;
var weightBar = new Path.Rectangle(new Rectangle(120, 57, 90, 9));
weightBar.strokeColor = "grey";
weightBar.strokeWidth = 1;
var weightTick = new Path(new Point(165, 57), new Point(165, 71));
weightTick.strokeColor = "black";
var weightSlider = new Path.Line(
new Point(165, 61.5), new Point(165+weight*20, 61.5));
weightSlider.strokeColor = "#2A6EA6";
weightSlider.strokeWidth = 9; // The bias text and bar
var biasText = new PointText(new Point(230, 82));
biasText.fontSize = 14;
var biasBar = new Path.Rectangle(new Rectangle(230, 88, 90, 9));
biasBar.strokeColor = "grey";
biasBar.strokeWidth = 1;
var biasTick = new Path(new Point(275, 88), new Point(275, 102));
biasTick.strokeColor = "black";
var biasSlider = new Path.Line(
new Point(275, 92.5), new Point(275+bias*20, 92.5));
biasSlider.strokeColor = "#2A6EA6";
biasSlider.strokeWidth = 9; // Axes for the graph
arrow(new Point(100, 250), new Point(100, 120));
arrow(new Point(100, 250), new Point(130+numFrames/2, 250)); // Labels on the axes
var costText = new PointText(new Point(60, 145));
costText.fontSize = 18;
costText.content = "Cost"; var epoch1LabelText = new PointText(new Point(140+numFrames/2, 255));
epoch1LabelText.fontSize = 18;
epoch1LabelText.content = "Epoch"; // Marker for the current epoch
var epoch1Tick = new Path(new Point(100, 250), new Point(100, 255));
epoch1Tick.strokeColor = "black"; var epoch1Number = new PointText(new Point(100, 267));
epoch1Number.fontSize = 14;
epoch1Number.justification = "center"; // We group the epochTick and epochNumber, to make it easy to move
epoch1 = new Group([epoch1Tick, epoch1Number]); // Initialize the dynamic elements. It's convenient to do this in a
// function, so that function can also be called upon a (re)start of
// the widget. var weight, bias;
initDynamicElements(); function initDynamicElements() {
weight = startingWeight;
bias = startingBias;
weightText.content = paramContent("w = ", weight);
weightSlider.segments[1].point.x = 165+weight*20;
biasText.content = paramContent("b = ", bias);
biasSlider.segments[1].point.x = 275+bias*20;
output.content = outputContent(weight, bias);
epoch1.position.x = 100;
epoch1Number.content = "0";
costGraph1.removeSegments();
} function paramContent(s, x) {
sign = (x >= 0)? "+": "";
return s+sign+x.toFixed(2);
} // The run button var runBox = new Path.Rectangle(new Rectangle(430, 230, 60, 30), 5);
runBox.fillColor = "#dddddd"; var runText = new PointText(new Point(460, 250));
runText.justification = "center";
runText.fontSize = 18;
runText.content = "Run"; var runIcon = new Group([runBox, runText]); runIcon.onMouseEnter = function(event) {
runBox.fillColor = "#aaaaaa";
} runIcon.onMouseLeave = function(event) {
runBox.fillColor = "#dddddd";
} var playing = false;
var count = 0; runIcon.onClick = function(event) {
initDynamicElements();
this.visible = false;
weight = startingWeight;
bias = startingBias;
playing = true;
} // The actual procedure function onFrame(event) {
if (playing) {
a = outputValue(weight, bias);
delta = cost1.derivative(a);
weight += -eta*delta;
bias += -eta*delta;
weightText.content = paramContent("w = ", weight);
weightSlider.segments[1].point.x = 165+weight*20;
biasText.content = paramContent("b = ", bias);
biasSlider.segments[1].point.x = 275+bias*20;
output.content = outputContent(weight, bias);
if (count % 2 === 0) {epoch1.position.x += 1;}
costGraph1.add(new Point(epoch1.position.x, 250-cost1.scaling*cost1.fn(a)));
epoch1Number.content = count;
count += 1;
if (count > numFrames) {
count = 0;
runIcon.visible = true;
playing = false;
}
}
} function outputValue(weight, bias) {
return sigmoid(weight+bias);
} function outputContent(weight, bias) {
return "Output: "+outputValue(weight, bias).toFixed(2);
} function sigmoid(z) {
return 1/(1+Math.exp(-z));
} function arrow(point1, point2, width, color) {
if (typeof width === 'undefined') {width=1};
if (typeof color === 'undefined') {color='black'};
delta = point1 - point2;
n = delta/delta.length;
nperp = new Point(-n.y, n.x);
line = new Path(point1, point2);
line.strokeColor = color;
line.strokeWidth = width;
arrow_stroke_1 = new Path(point2, point2+(n+nperp)*6);
arrow_stroke_1.strokeWidth = width;
arrow_stroke_1.strokeColor = color;
arrow_stroke_2 = new Path(point2, point2+(n-nperp)*6);
arrow_stroke_2.strokeWidth = width;
arrow_stroke_2.strokeColor = color;
}
http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/js/saturation4.js
// This is a paper.js widget to show a single neuron learning. In
// particular, the widget is used to show the learning slowdown that
// occurs when the output is saturated.
//
// The same basic widget is used several times, in slightly different
// configurations. paper.js makes it somewhat complex to reuse the
// code, so I have simply duplicated the code. This can give rise to
// bugs if one is not careful to keep the code in sync, so I have
// separated the code into two pieces.
//
// The first piece is the header code. This changes between widgets.
// It sets up things like the starting weight, bias, cost function,
// and so on -- things which may vary betweens widgets.
//
// The second piece is the body code. This is almost exactly the same
// for the different widgets. Note, however, that the costGraphX and
// epochX variables change name, due to a bug in the way paperjs
// handles scope.
//
// We can make these changes by searching on costGraph1 and replacing
// with costGraph2, costGraph3 etc, and by replacing epoch1 with
// epoch2, epoch3 etc.
//
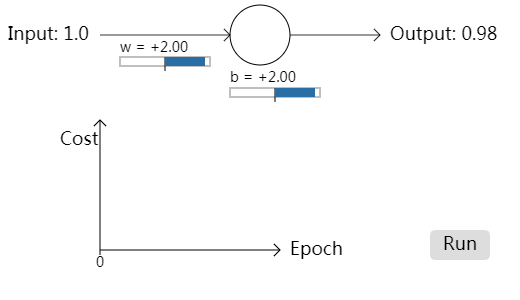
// This separation makes it easy to maintain the duplicated code. // HEADER CODE var startingWeight = 2.0;
var startingBias = 2.0;
var eta = 0.005;
var numFrames = 300; quadratic_cost = {
fn: function(a) {return a*a/2;},
derivative: function(a) {return a*a*(1-a);},
scaling: 240 // used to scale on the graph
} cross_entropy_cost = {
fn: function(a) {return -Math.log(1-a);},
derivative: function(a) {return 1/(1-a);},
scaling: 30
} cost4 = cross_entropy_cost; // A path for the graph.
costGraph4 = new Path();
costGraph4.strokeColor = "#2A6EA6"; // BODY CODE // STATIC ELEMENTS
//
// Note that this includes some paper.js items which will later be
// modified, e.g., the variables output and weightText. This section
// merely sets the static parts of the elements. var input = new PointText(new Point(8, 40));
input.fontSize = 18;
input.content = "Input: 1.0"; arrow(new Point(100, 35), new Point(230, 35), 0.8); // input arrow var neuron = new Path.Circle(new Point(260, 35), 30);
neuron.strokeColor = "black"; arrow(new Point(290, 35), new Point(380, 35), 0.8); // output arrow // The output text's content will be set dynamically, later
var output = new PointText(new Point(390, 40));
output.fontSize = 18; // The weight text and bar
var weightText = new PointText(new Point(120, 52));
weightText.fontSize=14;
var weightBar = new Path.Rectangle(new Rectangle(120, 57, 90, 9));
weightBar.strokeColor = "grey";
weightBar.strokeWidth = 1;
var weightTick = new Path(new Point(165, 57), new Point(165, 71));
weightTick.strokeColor = "black";
var weightSlider = new Path.Line(
new Point(165, 61.5), new Point(165+weight*20, 61.5));
weightSlider.strokeColor = "#2A6EA6";
weightSlider.strokeWidth = 9; // The bias text and bar
var biasText = new PointText(new Point(230, 82));
biasText.fontSize = 14;
var biasBar = new Path.Rectangle(new Rectangle(230, 88, 90, 9));
biasBar.strokeColor = "grey";
biasBar.strokeWidth = 1;
var biasTick = new Path(new Point(275, 88), new Point(275, 102));
biasTick.strokeColor = "black";
var biasSlider = new Path.Line(
new Point(275, 92.5), new Point(275+bias*20, 92.5));
biasSlider.strokeColor = "#2A6EA6";
biasSlider.strokeWidth = 9; // Axes for the graph
arrow(new Point(100, 250), new Point(100, 120));
arrow(new Point(100, 250), new Point(130+numFrames/2, 250)); // Labels on the axes
var costText = new PointText(new Point(60, 145));
costText.fontSize = 18;
costText.content = "Cost"; var epoch4LabelText = new PointText(new Point(140+numFrames/2, 255));
epoch4LabelText.fontSize = 18;
epoch4LabelText.content = "Epoch"; // Marker for the current epoch
var epoch4Tick = new Path(new Point(100, 250), new Point(100, 255));
epoch4Tick.strokeColor = "black"; var epoch4Number = new PointText(new Point(100, 267));
epoch4Number.fontSize = 14;
epoch4Number.justification = "center"; // We group the epochTick and epochNumber, to make it easy to move
epoch4 = new Group([epoch4Tick, epoch4Number]); // Initialize the dynamic elements. It's convenient to do this in a
// function, so that function can also be called upon a (re)start of
// the widget. var weight, bias;
initDynamicElements(); function initDynamicElements() {
weight = startingWeight;
bias = startingBias;
weightText.content = paramContent("w = ", weight);
weightSlider.segments[1].point.x = 165+weight*20;
biasText.content = paramContent("b = ", bias);
biasSlider.segments[1].point.x = 275+bias*20;
output.content = outputContent(weight, bias);
epoch4.position.x = 100;
epoch4Number.content = "0";
costGraph4.removeSegments();
} function paramContent(s, x) {
sign = (x >= 0)? "+": "";
return s+sign+x.toFixed(2);
} // The run button var runBox = new Path.Rectangle(new Rectangle(430, 230, 60, 30), 5);
runBox.fillColor = "#dddddd"; var runText = new PointText(new Point(460, 250));
runText.justification = "center";
runText.fontSize = 18;
runText.content = "Run"; var runIcon = new Group([runBox, runText]); runIcon.onMouseEnter = function(event) {
runBox.fillColor = "#aaaaaa";
} runIcon.onMouseLeave = function(event) {
runBox.fillColor = "#dddddd";
} var playing = false;
var count = 0; runIcon.onClick = function(event) {
initDynamicElements();
this.visible = false;
weight = startingWeight;
bias = startingBias;
playing = true;
} // The actual procedure function onFrame(event) {
if (playing) {
a = outputValue(weight, bias);
delta = cost4.derivative(a);
weight += -eta*delta;
bias += -eta*delta;
weightText.content = paramContent("w = ", weight);
weightSlider.segments[1].point.x = 165+weight*20;
biasText.content = paramContent("b = ", bias);
biasSlider.segments[1].point.x = 275+bias*20;
output.content = outputContent(weight, bias);
if (count % 2 === 0) {epoch4.position.x += 1;}
costGraph4.add(new Point(epoch4.position.x, 250-cost4.scaling*cost4.fn(a)));
epoch4Number.content = count;
count += 1;
if (count > numFrames) {
count = 0;
runIcon.visible = true;
playing = false;
}
}
} function outputValue(weight, bias) {
return sigmoid(weight+bias);
} function outputContent(weight, bias) {
return "Output: "+outputValue(weight, bias).toFixed(2);
} function sigmoid(z) {
return 1/(1+Math.exp(-z));
} function arrow(point1, point2, width, color) {
if (typeof width === 'undefined') {width=1};
if (typeof color === 'undefined') {color='black'};
delta = point1 - point2;
n = delta/delta.length;
nperp = new Point(-n.y, n.x);
line = new Path(point1, point2);
line.strokeColor = color;
line.strokeWidth = width;
arrow_stroke_1 = new Path(point2, point2+(n+nperp)*6);
arrow_stroke_1.strokeWidth = width;
arrow_stroke_1.strokeColor = color;
arrow_stroke_2 = new Path(point2, point2+(n-nperp)*6);
arrow_stroke_2.strokeWidth = width;
arrow_stroke_2.strokeColor = color;
}
output value . Sigmoid neurons are similar to perceptrons, but modified so that small changes in their weights and bias cause only a small change in their output.的更多相关文章
- 使用神经网络识别手写数字Using neural nets to recognize handwritten digits
The human visual system is one of the wonders of the world. Consider the following sequence of handw ...
- chapter1:using neural nets to recognize handwritten digits
two important types of artificial neuron :the perceptron and the sigmoid neuron Perceptrons 感知机的输入个数 ...
- 提高神经网络的学习方式Improving the way neural networks learn
When a golf player is first learning to play golf, they usually spend most of their time developing ...
- 神经网络和Deep Learning
参考资料: 在线免费书籍 http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/chap1.html Chapter 1 1. perceptron 感知机 it's a ...
- (六)6.16 Neurons Networks linear decoders and its implements
Sparse AutoEncoder是一个三层结构的网络,分别为输入输出与隐层,前边自编码器的描述可知,神经网络中的神经元都采用相同的激励函数,Linear Decoders 修改了自编码器的定义,对 ...
- [LeetCode] Similar RGB Color 相似的红绿蓝颜色
In the following, every capital letter represents some hexadecimal digit from 0 to f. The red-green- ...
- CS229 6.16 Neurons Networks linear decoders and its implements
Sparse AutoEncoder是一个三层结构的网络,分别为输入输出与隐层,前边自编码器的描述可知,神经网络中的神经元都采用相同的激励函数,Linear Decoders 修改了自编码器的定义,对 ...
- Digital Adjustment of DC-DC Converter Output Voltage in Portable Applications
http://pdfserv.maximintegrated.com/en/an/AN818.pdf http://www.maximintegrated.com/app-notes/index.mv ...
- Simple Addition Permits Voltage Control Of DC-DC Converter's Output
http://electronicdesign.com/power/simple-addition-permits-voltage-control-dc-dc-converters-output In ...
随机推荐
- 通过Linux定时任务实现定时轮询数据库及发送Http请求
通过Linux定时任务实现定时轮询数据库及发送Http请求 概述 有时需要临时增加一个定时任务(需要根据数据库查询结果然后发送HTTP请求),如果在项目中额外增加(Java+Spring+Quartz ...
- 使用BAT编译,链接,执行汇编代码
大家都知道汇编程序(MASM)的上机过程,先要对源代码进行汇编. 连接,然后再执行,而这中间有很多环节需要输入很多东西,麻烦的很(只有经历过的朋友才懂得).如何使这个过程变的简单呢?在我们搞汇编课程设 ...
- SSO单点登录系列4:cas-server登录页面自定义修改过程(jsp页面修改)
落雨 cas 单点登录 SSO单点登录系列4:cas-server登录页面自定义修改过程,全新DIY. 目标: 下面是正文: 打开cas的默认首页,映入眼帘的是满眼的中文and英文混杂体,作为一 ...
- ElasticSearch Java Api-删除索引
删除可以是删除整个索引库,也可以根据文档id删除索引库下的文档,还可以通过query查询条件删除所有符合条件的数据. 一.删除整个索引库 下面的例子会删除indexName索引: DeleteInde ...
- SpringMVC处理MySQL BLOB字段的下载
任务: uos.docfile的content字段是longblob类型,通过Web点击链接能下载到存储在这个字段里的文件.Web点击链接类似如下形式: http://localhost:8080/d ...
- 不在JPA 的 persistence.xml 文件里配置Entity class的解决的方法
在Spring 集成 Hibernate 的JPA方式中,须要在persistence配置文件里定义每个实体类.这样很地不方便.2种方法能够解决此问题: 这2种方式都能够实现不用在persist ...
- node - 关于package.json
2018-8-3(首次更新) 一.关于版本号: 文章来自:https://blog.csdn.net/yancloudfrontend/article/details/72867314 指定版本:比如 ...
- ionic准备之angular基础——dom操作相关(6)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- IOS压缩解压缩
#import <zlib.h> 压缩 -(NSData *)compressData:(NSData *)uncompressedData { if ([uncompressedData ...
- VMware下的ubuntu12.04不识别usb设备问题的解决方法
情况一:U盘通过USB连接到Ubuntu后,点击VM—removable devices,无usb信息? 解决方法: 在“服务”中启动“VMware USB Arbitration Service”服 ...
