[转]what’s the difference between @Component ,@Repository & @Service annotations in Spring
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/6070314.html
@Component is equivalent to
<bean>@Service, @Controller , @Repository = {@Component + some more special functionality}
That mean Service,Controller and Repository are functionally the same.
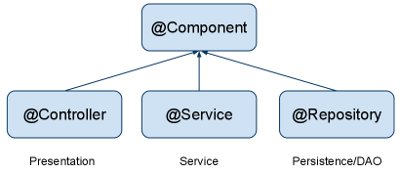
The three annotations are used to separate "Layers" in your application,
- Controllers just do stuff like dispatching, forwarding, calling service methods etc.
- Service Hold business Logic, Calculations etc.
- Repository are the DAOs(Data Access Objects), they access the database directly.
Now you may ask why separate them:(I assume you know AOP-Aspect Oriented Programming)
Lets say you want to Monitors the Activity of the DAO Layer only. You will write an Aspect(A class) class that does some logging before and after every method of your DAO is invoked, you are able to do that using AOP as you have three distinct Layers and are not mixed.
So you can do logging of DAO "around", "before" or "after" the DAO methods. You could do that because you had a DAO in the first place. What you just achieved is Separation of concerns or tasks.
Imagine if there were only one annotation @Controller, then this component will have dispatching, business logic and accessing database all mixed, so dirty code!
Above mentioned is one very common scenario, there are many more use cases of why to use three annotations.
In Spring @Component, @Service, and @Controller. @Component are Stereotype annotations which is used for:
@Controller: where your request mapping from presentation page done i.e. Presentation layer won't go to any other file it goes directly to @Controller class and check for requested path in @RequestMapping annotation which written before method calls if necessary.
@Service: All business logic is here i.e. Data related calculations and all.This annotation of business layer in which our user not directly call persistence method so it will call this methods using this annotation. It will request @Repository as per user request
@Repository:This is Persistence layer(Data Access Layer) of application which used to get data from database. i.e. all the Database related operations are done by repository.
@Component - Annotate your other components (for example REST resource classes) with component stereotype.
From Spring Documentation:
In Spring 2.0 and later, the @Repository annotation is a marker for any class that fulfills the role or stereotype (also known as Data Access Object or DAO) of a repository. Among the uses of this marker is the automatic translation of exceptions.
Spring 2.5 introduces further stereotype annotations: @Component, @Service, and @Controller. @Component is a generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component. @Repository, @Service, and @Controller are specializations of @Component for more specific use cases, for example, in the persistence, service, and presentation layers, respectively.
Therefore, you can annotate your component classes with @Component, but by annotating them with @Repository, @Service, or @Controller instead, your classes are more properly suited for processing by tools or associating with aspects. For example, these stereotype annotations make ideal targets for pointcuts.
Thus, if you are choosing between using @Component or @Service for your service layer, @Service is clearly the better choice. Similarly, as stated above, @Repository is already supported as a marker for automatic exception translation in your persistence layer.
| Annotation | Meaning |
+------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| @Component | generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component |
| @Repository| stereotype for persistence layer |
| @Service | stereotype for service layer |
| @Controller| stereotype for presentation layer (spring-mvc) |Spring 2.5 introduces further stereotype annotations: @Component, @Service and @Controller. @Component serves as a generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component; whereas, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller serve as specializations of @Component for more specific use cases (e.g., in the persistence, service, and presentation layers, respectively). What this means is that you can annotate your component classes with @Component, but by annotating them with @Repository, @Service, or @Controller instead, your classes are more properly suited for processing by tools or associating with aspects. For example, these stereotype annotations make ideal targets for pointcuts. Of course, it is also possible that @Repository, @Service, and @Controller may carry additional semantics in future releases of the Spring Framework. Thus, if you are making a decision between using @Component or @Service for your service layer, @Service is clearly the better choice. Similarly, as stated above, @Repository is already supported as a marker for automatic exception translation in your persistence layer.
@Component – Indicates a auto scan component.
@Repository – Indicates DAO component in the persistence layer.
@Service – Indicates a Service component in the business layer.
@Controller – Indicates a controller component in the presentation layer.
reference :- http://static.springsource.org/spring/docs/3.0.0.M3/reference/html/ch04s12.html
总的来说就是 @Service, @Controller , @Repository = {@Component + 特殊的功能} ,文章提到我们应该结合Spring中到的切面编程思想(AOP), 我们的controller 承担着分发请求的任务后,又要处理业务逻辑,同时还要与数据库持久层作交互,这样的代码是糟糕的,所以文档中主张是使用这几个注解类,更好地区分开各自的功能
- @Component : 将自动扫描组件
- @Repository : 指示为在持久层的Dao层的组件(它的好处是捕抓到持久层交互中出现的异常,并把异常友好地表示出来,假如没有这个注释,数据库抛出的异常常常难以理解)
- @Service : 业务逻辑
- @Controller : 分发请求
[转]what’s the difference between @Component ,@Repository & @Service annotations in Spring的更多相关文章
- What's the difference between @Component, @Repository & @Service annotations in Spring?
@Component is equivalent to <bean> @Service, @Controller , @Repository = {@Component + some mo ...
- 【转载】@Component, @Repository, @Service的区别
@Component, @Repository, @Service的区别 官网引用 引用spring的官方文档中的一段描述: 在Spring2.0之前的版本中,@Repository注解可以标记在任何 ...
- SpringAnnotation注解之@Component,@Repository,@Service,@Controller
@Component:组件,表示此写上了此注解的bean,作为一个组件存在于容器中.这样的话别的地方就可以使用@Resource这个注解来把这个组件作为一个资源来使用了.初始化bean的名字为类名首字 ...
- @Component @Repository @Service @Controller
Spring 2.5 中除了提供 @Component 注释外,还定义了几个拥有特殊语义的注释,它们分别是:@Repository.@Service 和 @Controller.在目前的 Spring ...
- @Component, @Repository, @Service的区别
注解 含义 @Component 最普通的组件,可以被注入到spring容器进行管理 @Repository 作用于持久层 @Service 作用于业务逻辑层 @Controller 作用于表现层(s ...
- @Component, @Repository, @Service,@Controller的区别
@Component, @Service, @Controller, @Repository是spring注解,注解后可以被spring框架所扫描并注入到spring容器来进行管理 @Componen ...
- 从头认识Spring-2.7 自己主动检測Bean(1)-@Component @Repository @Service @Controller
这一章节我们来讨论一下自己主动检測Bean. 1.domain 厨师类: package com.raylee.my_new_spring.my_new_spring.ch02.topic_1_19; ...
- @Component @Controller @Service @Repository@Resourse
@Component @Controller @Service @Repository@Resourse这些全部是Spring提供的注解. 其中@Component用来表示把一个类纳入spring容器 ...
- Spring注解详解@Repository、@Component、@Service 和 @Constroller
概述 注释配置相对于 XML 配置具有很多的优势: 它可以充分利用 Java 的反射机制获取类结构信息,这些信息可以有效减少配置的工作.如使用 JPA 注释配置 ORM 映射时,我们就不需要指定 PO ...
随机推荐
- 【题解】 UVa11729 Commando War
题目大意 你有n个部下,每个部下需要完成一项任务.第i个部下需要你花Bj分钟交代任务,然后他就会立刻独立地.无间断地执行Ji分钟后完成任务.你需要选择交代任务的顺序,使得所有任务尽早执行完毕(即最后一 ...
- ocp题库变化,052新加的考试题及答案整理-32
32. Examine these commands and their output: • SQL> SELECT * FROM emp; • ENO ENAME • ---- ----- • ...
- 小记 Linux 之 Vim
小记 Linux 之 Vim 使用vim用来进行文本流查询,是非常重要的部分. 技巧一:使用 '#' 系统将列出文档相同字符,在代码时很重要. 技巧二:使用 ']I' 具体操作是先使用 ? 或 \ 进 ...
- nginx负载均衡配合keepalived服务案例实战
本实验用4台 centos6 虚拟机,2台做负载均衡,2台做web服务器,都先装上nginx lb01:192.168.0.235 --主负载均衡器 lb02:192.168.0.236 --备负 ...
- 2016级算法第五次上机-G.ModricWang的撒币游戏
1062 ModricWang的撒币游戏 思路 此题为2017年ACM-ICPC亚洲区域赛乌鲁木齐赛区的A题,现场94个队中有38个队做出此题.在这里作为满分以外的题,是为了让大家看一下外面一些题的风 ...
- (STM32F4) Timer 基本操作
Timer (計時器) 就是慢慢數時間,在timer內部有一個計數器. 而計數器會數到Register的value當數值數到設定值Timer就會發起IRQ 而程式就會轉跳到中斷向量裡頭去執行想要做的事 ...
- PHP 数组与CSV文件互转
项目说明 数组导出CSV,ZIP文件,CSV,ZIP文件还原数组(Array export file,file restore array)适用于导入导出会员,商品信息注意:读取中文文件名文件.数据时 ...
- Opencv ValueError: not enough values to unpack (expected 3, got 2)解决办法
问题背景 有些人在用我去年的毕设运行时(感谢QAQ),报错 Opencv ValueError: not enough values to unpack (expected 3, got 2) 当时就 ...
- C++标准库类模板vector
vector是C++标准库STL中的一个重要的类模板,相当于一个更加健壮的,有很多附加能力的数组 使用vector前首先要包含头文件 #include<vector> 1.vector的 ...
- vue中nextTick的使用(转载)
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/chaoyuehedy/p/8985425.html 简介 vue是非常流行的框架,他结合了angular和react的优点,从而形成了一个轻量 ...
