Spring boot启动原理
1.入口类
/**
* springboot应用的启动入口
*/
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication
public class SampleApplication { @RequestMapping("/")
public String sayhello(){
return "hello world";
} public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub SpringApplication.run(SampleApplication.class, args);
} }
Spring Boot程序的启动入口就一行代码,SpringApplication.run(SampleApplication.class,args)
2.执行过程
2.1SpringApplication的实例化
SpringApplication的静态run方法内部其实是new了一个SpringApplication的实例,构造函数保存了SourceClass。在SpringApplication实例初始化的时候,它做了几件事情:
- 推断应用类型是standard还是Web。根据classpath里面是否存在某个特征类(org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)来决定是否应该创建一个为Web应用使用的ApplicationContext类型。
- 使用SpringFactoriesLoader在应用的classpath中查找并加载所有可用的ApplicationContextInitializer。SpringFactoriesLoader从类路径下各个jar的配置文件META-INF/spring.factories加载配置
- 使用SpringFactoriesLoader在应用的classpath中查找并加载所有可用的ApplicationListener。
推断应用入口类
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
下面具体从源码来看看每一步是怎么做的
2.1 推断应用类型是Standard还是Web
private WebApplicationType deduceWebApplicationType() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
//相关常量
private static final String REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS = "org.springframework."
+ "web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS = "org.springframework."
+ "web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String[] WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
可能会出现三种结果:
- WebApplicationType.REACTIVE - 当类路径中存在REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS并且不存在MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS时
- WebApplicationType.NONE - 也就是非Web型应用(Standard型),此时类路径中不包含WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES中定义的任何一个类时
- WebApplicationType.SERVLET - 类路径中包含了WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES中定义的所有类型时
2.2 设置初始化器ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
这里出现了一个新的概念 - 初始化器。
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
// 这里的入参type就是ApplicationContextInitializer.class
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
这里面首先会根据入参type读取所有的names(是一个String集合),然后根据这个集合来完成对应的实例化操作。
// 这里的入参type就是ApplicationContextInitializer.class
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null)
return result;
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
List<String> factoryClassNames = Arrays.asList(
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue()));
result.addAll((String) entry.getKey(), factoryClassNames);
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
/**
* The location to look for factories.
* <p>Can be present in multiple JAR files.
*/
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
这个方法会尝试从类路径的META-INF/spring.factories处读取相应配置文件,然后进行遍历,读取配置文件中Key为:org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的value。以spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包为例,它的META-INF/spring.factories部分定义如下所示:
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.AutoConfigurationReportLoggingInitializer因此这两个类名会被读取出来,然后放入到集合中,准备开始下面的实例化操作:
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args,
Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass
.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
类加载,确认被加载的类确实是org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的子类,然后就是得到构造器进行初始化,最后放入到实例列表中。
因此,所谓的初始化器就是org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类,这个接口是这样定义的:
public interface ApplicationContextInitializer<C extends ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
/**
* Initialize the given application context.
* @param applicationContext the application to configure
*/
void initialize(C applicationContext);
}
根据类文档,这个接口的主要功能是:
在Spring上下文被刷新之前进行初始化的操作。典型地比如在Web应用中,注册Property Sources或者是激活Profiles。Property Sources比较好理解,就是配置文件。Profiles是Spring为了在不同环境下(如DEV,TEST,PRODUCTION等),加载不同的配置项而抽象出来的一个实体。
2.3 设置监听器ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 这里的入参type是:org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener.class
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
} private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
可以发现,这个加载相应的类名,然后完成实例化的过程和上面在设置初始化器时如出一辙,同样,还是以spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包中的spring.factories为例,看看相应的Key-Value:
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer至于ApplicationListener接口,它是Spring框架中一个相当基础的接口了,代码如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener { /**
* Handle an application event.
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event); }
2.4 推断应用入口类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
这个方法的实现有点意思:
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
它通过构造一个运行时异常,通过异常栈中方法名为main的栈帧来得到入口类的名字。
至此,对于SpringApplication实例的初始化过程就结束了。
2.2 执行SpringApplication实例的run方法
SpringApplication实例的run方法内部都做了哪些呢:
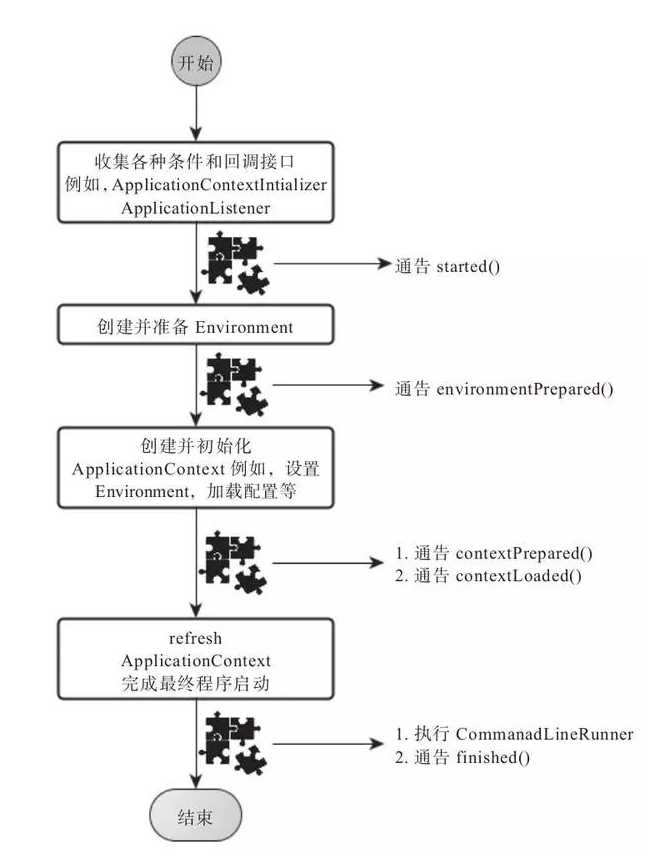
1.创建SpringApplication自己的SpringApplicationRunListener。遍历执行所有通过SpringFactoriesLoader可以查找到并加载的SpringApplicationRunListener。调用.它们的started()方法,告诉这些SpringApplicationRunListener,“嘿,SpringBoot应用要开始执行咯!”。
2.创建并配置当前Spring Boot应用将要使用的Environment(包括配置要使用的PropertySource以及Profile)。
3. 遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的environmentPrepared()的方法,告诉他们:“当前SpringBoot应用使用的Environment准备好了咯!”。
4. 如果SpringApplication的showBanner属性被设置为true,则打印banner。
5.创建ApplicationContext,因为现在应用类型是Servlet,创建的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
6.对ApplicationContext进行配置,将之前准备好的Environment设置给创建好的ApplicationContext使用。还有配置BeanNameGenerator、ResourceLoader等。
7.ApplicationContext创建好之后,然后遍历ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize(applicationContext)方法来对已经创建好的ApplicationContext进行进一步的处理。这里的ApplicationContextInitializer就是创建SpringApplication实例时设置的初始化器。
8. 遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared()方法。
9. 最核心的一步,将之前通过@EnableAutoConfiguration获取的所有配置以及其他形式的IoC容器配置加载到已经准备完毕的ApplicationContext。
10.遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()方法。
11.启动ApplicationContext,AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext继承了SpringFrameWork本身提供的GenericWebApplicationContext提供的功能并进行了扩展,以支持配置并启动Embed Tomcat。
(1)、对BeanFactory进行一些初始化配置。
(2)、执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor,其中包括对BeanDefinition的进一步处理。最重要的是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,用来解析处理所有@Configuration标签类,并将Bean定义注册到BeanFactory中。因为@SpringBootApplication中包含了@EnableAutoConfiguration的meta-annotation,会进行自动配置处理,基本原理是判断工程依赖了哪些第三方组件并对其进行自动化配置,这样处理完@Configuration标签后,BeanFactory中就已经有大量的Bean定义了。
(3)、注册BeanPostProcessor,这些Processor会在首次getBean时执行。主要功能包括进行Autowire、Required等标签的处理,完成自动绑定等功能。也有特殊的关于WebServleterFactory的后续处理。
(4)、在ApplicationContext的onRefresh方法中会对Web容器(Tomcat)进行配置,包括注册Servlet、Filter、Listener等。
(5)、在ApplicationContext的finishRefresh方法中启动Web容器(Tomcat),完成应用的启动。
3. 总结
Spring boot启动原理的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot启动原理解析
Spring Boot启动原理解析http://www.cnblogs.com/moonandstar08/p/6550758.html 前言 前面几章我们见识了SpringBoot为我们做的自动配置 ...
- spring boot启动原理步骤分析
spring boot最重要的三个文件:1.启动类 2.pom.xml 3.application.yml配置文件 一.启动类->main方法 spring boot启动原理步骤分析 1.spr ...
- Spring Boot 启动原理分析
https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/6056 转 在spring boot里,很吸引人的一个特性是可以直接把应用打包成为一个jar/war,然后这个jar/war是可以直接启 ...
- spring boot 启动原理详细解析
我们开发任何一个Spring Boot项目,都会用到如下的启动类 1 @SpringBootApplication 2 public class Application { 3 public stat ...
- spring boot 启动原理
https://www.processon.com/view/link/59812124e4b0de2518b32b6e https://www.cnblogs.com/trgl/p/7353782. ...
- [Spring Boot] Spring Boot启动过程源码分析
关于Spring Boot,已经有很多介绍其如何使用的文章了,本文从源代码(基于Spring-boot 1.5.6)的角度来看看Spring Boot的启动过程到底是怎么样的,为何以往纷繁复杂的配置到 ...
- Spring Boot 运作原理
Spring Boot 运作原理 1.Spring Boot 简介 SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程.该框架使用了 ...
- Spring Boot启动过程源码分析--转
https://blog.csdn.net/dm_vincent/article/details/76735888 关于Spring Boot,已经有很多介绍其如何使用的文章了,本文从源代码(基于Sp ...
- Spring Boot核心原理
Spring Boot核心原理 spring-boot-starter-xxx 方便开发和配置 1.没有depoy setup tomcat 2.xml文件里面的没有没有了 @SpringBootA ...
随机推荐
- hdu1199 线段树
这题说的是给了 n 个操作. 每个操作会把 [a,b] 之间的球 涂为黑色或者 白色, 然后最后问 最长的连续的白色的 球有多少个,初始的时候全是黑的. 我们将所有的点离散化, 记得离散 a-1, b ...
- 587. Erect the Fence(凸包算法)
问题 给定一群树的坐标点,画个围栏把所有树围起来(凸包). 至少有一棵树,输入和输出没有顺序. Input: [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]] Output: ...
- maven和gradle中,dependency和plugin的区别
dependency引入的东西 作用:代码编译/运行时所需要的东西 打包:项目打包后这些东西基本都在(一般都在). 例如:JSON工具包GSON(com.google.code.gson),不仅开发时 ...
- 20145314郑凯杰《网络对抗技术》可选实验 shellcode注入与Return-to-libc攻击实验
20145314郑凯杰<网络对抗技术>可选实验 shellcode注入与Return-to-libc攻击实验 1.0 实践内容 Return-to-libc攻击是一种特殊的缓冲区溢出攻击, ...
- 20145221 《Java程序设计》第二周学习总结
20145221 <Java程序设计>第二周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第二周内容已在假期完成,详见博客: <Java程序设计>第三章-基础语法 代码调试中的问题和解决过程 第 ...
- 【转载】通过JSFL让Flash Professional CS4或CS5拥有批量FLA导出SVG的功能
近期一个项目要求博主爱吾所爱(爱生活=爱技术)将 所有的.fla源文件里的图形都转为.svg矢量图,经常一番搜索之后,发现新版本的Flash Professional CC已经有此功能,但无奈我等用的 ...
- windows10如何安装cpu版本tensorflow
1.获取anaconda https://repo.continuum.io/archive/Anaconda3-2018.12-Windows-x86_64.exe (这个版本内置python3.7 ...
- [参考]用递归的方法获取 字符 对应的 二进制字符串 (C/C++)
将字符转换为16进制字符串.十进制字符串可以参考这里:https://www.cnblogs.com/stxs/p/8846545.html 代码及调试结果 举例:字符'a',查ASCII码表它对应的 ...
- spark内存管理分析
前言 下面的分析基于对spark2.1.0版本的分析,对于1.x的版本可以有区别. 内存配置 key 默认 解释 spark.memory.fraction 0.6 spark可以直接使用的内存大小系 ...
- Spring Cloud 开发的一些推荐规划
1.提供一个统一的 父 pom 依赖 作用:统一版本与引入必要依赖 2.提供一个模板模型. 作用: 开发人员不必关系具体基础启动项 3.提供一个统一基础配置模型 作用: 开发人员不比太过关注与必 ...
