Spring IOC 源码简单分析 04 - bean的初始化
### 准备
## 目标
##测试代码
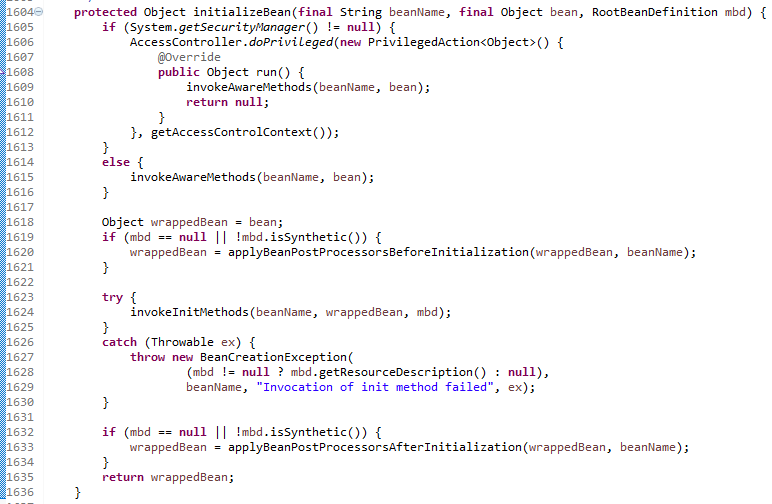
### 分析
## 文档描述
- BeanNameAware's setBeanName
- BeanClassLoaderAware's setBeanClassLoader
- BeanFactoryAware's setBeanFactory
- EnvironmentAware's setEnvironment
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware's setEmbeddedValueResolver
- ResourceLoaderAware's setResourceLoader (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware's setApplicationEventPublisher (only applicable when running in an application context)
- MessageSourceAware's setMessageSource (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ApplicationContextAware's setApplicationContext (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ServletContextAware's setServletContext (only applicable when running in a web application context)
- postProcessBeforeInitialization methods of BeanPostProcessors
- InitializingBean's afterPropertiesSet
- a custom init-method definition
- postProcessAfterInitialization methods of BeanPostProcessors
- postProcessBeforeDestruction methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
- DisposableBean's destroy
- a custom destroy-method definition
## 示例代码分析
Spring IOC 源码简单分析 04 - bean的初始化的更多相关文章
- Spring IOC 源码简单分析 02 - Bean Reference
### 准备 ## 目标 了解 bean reference 装配的流程 ##测试代码 gordon.study.spring.ioc.IOC02_BeanReference.java ioc02 ...
- Spring IOC 源码简单分析 03 - 循环引用
### 准备 ## 目标 了解 Spring 如何处理循环引用 ##测试代码 gordon.study.spring.ioc.IOC03_CircularReference.java ioc03. ...
- Spring IOC 源码简单分析 01 - BeanFactory
### 准备 ## 目标 了解 Spring IOC 的基础流程 ## 相关资源 Offical Doc:http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/4.3.9.RELEASE ...
- Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(一)
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(一) 前言 上一篇文章Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Ioc容器注册BeanPostProcessor后置处理器以及事件消息处理已经完成了对 ...
- Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(二)
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(二) 前言 上篇文章Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(一)简单分析了getBean()方法,还记得分析了什么吗?不记得了才 ...
- Spring Ioc源码分析系列--容器实例化Bean的四种方法
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--实例化Bean的几种方法 前言 前面的文章Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(二)在讲解到bean真正通过那些方式实例化出来的时候,并没有继续分 ...
- Spring IOC 源码分析
Spring 最重要的概念是 IOC 和 AOP,本篇文章其实就是要带领大家来分析下 Spring 的 IOC 容器.既然大家平时都要用到 Spring,怎么可以不好好了解 Spring 呢?阅读本文 ...
- spring IoC源码分析 (3)Resource解析
引自 spring IoC源码分析 (3)Resource解析 定义好了Resource之后,看到XmlFactoryBean的构造函数 public XmlBeanFactory(Resource ...
- Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Ioc的基础知识准备
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Ioc的基础知识准备 本系列文章代码基于Spring Framework 5.2.x Ioc的概念 在Spring里,Ioc的定义为The IoC Containe ...
随机推荐
- web站点检查简易shell脚本
1.web样式 <h4>THE STATUS OF RS:</h4> <meta http-equiv="> <table border=" ...
- 二维坐标系极角排序的应用(POJ1696)
Space Ant Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 3170 Accepted: 2029 Descrip ...
- mysql数据库新插入数据,需要立即获取最新插入的id
在MySQL中,使用auto_increment类型的id字段作为表的主键.通常的做法,是通过“select max(id) from tablename”的做法,但是显然这种做法需要考虑并发的情况, ...
- java 常见几种发送http请求案例
import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java ...
- Windows上的巧克力味Chocolatey详解
Chocolatey是什么?很简单,Chocolatey就是Windows系统的yum或apt-get. 一.Chocolatey介绍 Chocolatey是一款专为Windows系统开发的.基于Nu ...
- WebDriver API 实例详解(二)
十一.双击某个元素 被测试网页的html源码: <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> </head&g ...
- loadrunner11的移动端性能测试之脚本优化
测试步骤之脚本优化(Script) 看到这里,是不是疑惑录制好的脚本还需要优化吗,答案是肯定的. 优化概要 脚本优化包括插入注释(Comment),插入事务(Transaction),插入检查点(Ch ...
- PAT 1128 N Queens Puzzle[对角线判断]
1128 N Queens Puzzle(20 分) The "eight queens puzzle" is the problem of placing eight chess ...
- 创建工具条ToolBar
/***ToolBar***/ QToolBar * tlb_ImageOpen; QToolBar * tlb_VideoOpen; QToolBar * tlb_AudioOpen; void M ...
- 制造抽象基类--《C++必知必会》 条款33
抽象类,含有纯虚函数的类,不可以创建对象. 然而,有时我们并不需要某个函数定义为纯虚函数,但是任然希望此类像抽象类一样,不可以创建对象. 方法1:通过确保类中不存在共有构造函数来模拟抽象基类的性质.意 ...
