[C++]Linux之网络实时检测功能
声明:如需引用或者摘抄本博文源码或者其文章的,请在显著处注明,来源于本博文/作者,以示尊重劳动成果,助力开源精神。也欢迎大家一起探讨,交流,以共同进步,乃至成为朋友~ 0.0
由于学习操作系统实验课程的缘故,这几日都在捣鼓底层,也发现底层确实蛮有意思的。其中,有一个实验要求实时检测网络速率嘛,今晚终于搞定了~
大致思路如下:
1.读取linux文件系统下的/proc/net/dev目录,读取其网络配置信息
温馨提示:除了第一/二行外,剩余各行分别是计算机主机的【各网卡(有线网卡*/本机回环*/无线网卡*等)】的网络收发信息(字节/包/帧等)

2.使用相关函数读取其网络信息(关键信息如下:接收的总字节数和发送的总字节数)
3.网速的计算:(需要间隔一段(一般为1秒),然后再次执行步骤2)
(net_current_receive_total - net_previous_receive_total) + (net_current_transmit_total - net_previous_transmit_total) / 2
注意事项:
一般使用C库函数的文件操作(常用API:fopen;fseek;fclose;fget(按行读取);sscanf等),但我并不想说这些。
我想提俩很小的细节,但确实是坑了我好久好久的:
坑1:数据是需要先读两行无关的信息后,才开始读我们需要的网络配置信息的
坑2:获取并重置游标位置为文件开头处(注意:此处是大坑 原因:每次更新计算机的网络的信息时,必须重新读入,或者重置游标的默认位置为文件流开始位置处)
net_off = fseek(net_stream, 0, SEEK_SET);
程序共有如下函数:
//注意:所有的log相关的执行程序,仅仅是打印日志,方便读者查看监测细节,如需实用时,除去log/lineLog相关代码即可,不会影响程序正常执行
void net_update(bool log);//初始化【必选】
void net_init(bool log, bool lineLog);//更新网络各参数信息【必选】
float net_usage(char * TYPE, bool log, bool lineLog);//通过TYPE值,获取网络信息的指定参数【必选】
void net_close();//关闭网络监测【必选】 //测试用例执行函数
void calculate(bool initLog, bool usageLog, bool lineLog)
void execute(bool initLog, bool usageLog, bool lineLog)
int main()
源码如下:(可以根据每个用户的需要,一般地,更改define部分和去除掉log相关形参即可,实现实时网络检测)
/*
@url:http://www.cnblogs.com/johnnyzen/p/8009053.html
@author:Johnny Zen
@school:XiHua University
@contact:johnnyztsd@gmail.com or 1125418540@qq.com
@date:2017-12-10 01:33
@description:实现网络检测功能(也提供实时)
@environment:Linux For Ubuntu 16.04/64
*/
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h> //为了兼容C++
#undef bool
#undef true
#undef false
#define bool int
#define true 1
#define false 0 #define NET_INFO_PATH "/proc/net/dev" #define NET_DIFF_TIME 1 //时间差阈值(单位:秒) //全局参数:以供随时调用函数,随时返回值(存在延时1s以内)
static time_t net_previous_timeStamp;//记录上一次系统时间戳 时间单位:秒
static time_t net_current_timeStamp;//记录当前系统时间戳 时间单位:秒
static double net_dif_time;//记录时间差 时间单位:秒 static char net_file[64] = {NET_INFO_PATH};//要读取的目标文件名
static int net_off;//记录文件游标当前偏移位置
static int line_num;//记录行数
static FILE *net_stream; //访问虚拟文件系统的文件流
static char net_buffer[256];//行缓冲区
static char *net_line_return;//记录读取每行的时候的返回结果(NULL或者返回 net_buffer)
static char net_tmp_itemName[32];//临时存放文件中的每行的项目名称 static int net_itemReceive;//存放每一个网卡的接受到的字节总数(单位:Byte)
static int net_itemTransmit;//存放每一个网卡的已发送的字节总数(单位:Byte) static int net_current_receive_total;//存放【当前】收到的网络包字节总数(单位:Byte)
static int net_previous_receive_total;//存放【上一次】收到的网络包字节总数(单位:Byte)
static int net_receive_speed;//平均接受网络字节速度 static int net_current_transmit_total; //存放【当前】已发送的网络包字节总数(单位:Byte)
static int net_previous_transmit_total;//存放【上一次】已发送的网络包字节总数(单位:Byte)
static int net_transmit_speed;//平均发送网络字节速度 static float net_averageLoad_speed; //网络负载情况(单位:Bytes/s)
//(net_current_receive_total - net_previous_receive_total) + (net_current_transmit_total - net_previous_transmit_total) / 2
static float net_result; //函数返回值 //声明所有函数体
//注意:所有的log相关的执行程序,仅仅是打印日志,方便读者查看监测细节,如需实用时,除去log/lineLog相关代码即可,不会影响程序正常执行
void net_update(bool log);//初始化【必选】
void net_init(bool log, bool lineLog);//更新网络各参数信息【必选】
float net_usage(char * TYPE, bool log, bool lineLog);//通过TYPE值,获取网络信息的指定参数【必选】
void net_close();//关闭网络监测【必选】 //更新网络各信息
void net_update(bool log){// log:是否按行打印日志
net_previous_receive_total = net_current_receive_total;//初始化上一次接收总数据
net_previous_transmit_total = net_current_transmit_total;//初始化上一次发送总数据
net_current_receive_total = 0; //对当前网络接收数据总数清零,重新计算
net_current_transmit_total = 0;//对当前网络发送数据总数清零,重新计算 //获取网络的初始化数据
/*step1: 获取并重置游标位置为文件开头处(注意:此处是大坑 原因:每次更新计算机的网络的信息时,必须重新读入,或者重置游标的默认位置)*/
net_off = fseek(net_stream, 0, SEEK_SET);//获取并重置游标位置为文件流开头处,SEEK_CUR当前读写位置后增加net_off个位移量,重置游标位置比重新打开并获取文件流的资源要低的道理,应该都懂吧 0.0 line_num = 1;//重置行数
net_line_return = fgets (net_buffer, sizeof(net_buffer), net_stream);//读取第一行
//printf("[net_update] line %d: %s\n", line_num, net_line_return);
line_num++;
net_line_return = fgets (net_buffer, sizeof(net_buffer), net_stream);//读取第二行
//printf("[net_update] line %d: %s\n", line_num, net_line_return); net_itemReceive = 0;
net_itemTransmit = 0;
int flag = 1;
while(flag == 1){
line_num++;
net_line_return = fgets (net_buffer, sizeof(net_buffer), net_stream);
net_itemReceive = 0;
net_itemTransmit = 0;
if(net_line_return != NULL){
sscanf( net_buffer,
"%s%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d",
net_tmp_itemName,
&net_itemReceive,
&net_itemTransmit,
&net_itemTransmit,
&net_itemTransmit,
&net_itemTransmit,
&net_itemTransmit,
&net_itemTransmit,
&net_itemTransmit,
&net_itemTransmit);
net_current_receive_total += net_itemReceive;//初始化接收字节总数
net_current_transmit_total += net_itemTransmit;//初始化发送字节总数
} else {
flag = -1;
} if(log == true){
if(flag != -1)//如果当前行不是末尾行时,不添加换行符
printf("[net_update] line %d: %s", line_num, net_line_return);
else //反之,添加换行符
printf("[net_update] line %d: %s\n", line_num, net_line_return);
printf("[net_update] line %d:net_itemReceive: %d\n", line_num, net_itemReceive);
printf("[net_update] line %d:net_itemTransmit: %d\n", line_num, net_itemTransmit);
printf("[net_update] line %d:net_current_receive_total: %d\n", line_num, net_current_receive_total);
printf("[net_update] line %d:net_current_transmit_total: %d\n\n", line_num, net_current_transmit_total);
}
}
} //初始化
void net_init(bool log, bool lineLog){//log:打印更新的【网络各参数信息】,以便检测细节; lineLog:按行打印网络文件信息细节
//读取数据
net_line_return = "INIT"; //设置初始值,只要不为空字符串即可
/*step1: 打开文件 (注意:此处是大坑 原因:每次更新计算机的网络的信息时,必须重新读入,或者重置游标的默认位置)*/
net_stream = fopen (net_file, "r"); //以R读的方式打开文件再赋给指针fd
net_off = fseek(net_stream, 0, SEEK_SET);//获取并重置游标位置为文件流开头处,SEEK_CUR当前读写位置后增加net_off个位移量 net_update(lineLog);//更新计算机的网络的信息 net_previous_receive_total = net_current_receive_total;//初始化上一次接收总数据
net_previous_transmit_total = net_current_transmit_total;//初始化上一次发送总数据 net_receive_speed = 0;//初始化接收网速为:0
net_transmit_speed = 0;//初始化发送网速为:0
net_averageLoad_speed = 0.0; //初始化网络负载速度为:0
net_previous_timeStamp = net_current_timeStamp = time(NULL);//开始获取初始化的时间戳
net_dif_time = 0;//初始化时间差 if(log == true){
printf("\n[INIT NET] net_current_timeStamp: %f\n", (double)net_current_timeStamp);
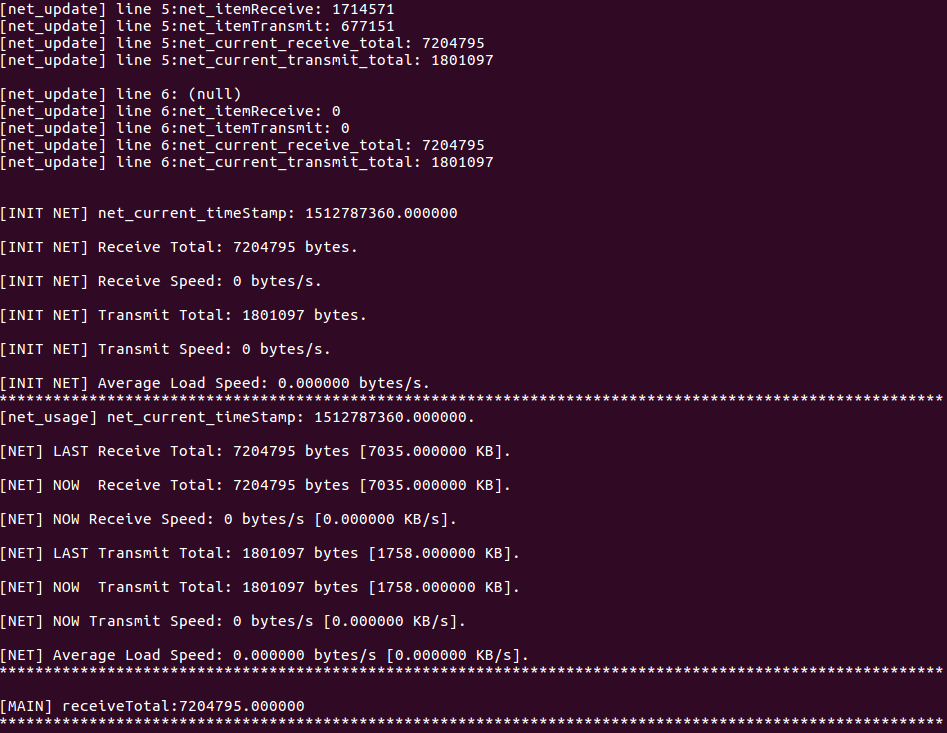
printf("\n[INIT NET] Receive Total: %d bytes.\n", net_current_receive_total);
printf("\n[INIT NET] Receive Speed: %d bytes/s.\n", net_receive_speed);
printf("\n[INIT NET] Transmit Total: %d bytes.\n", net_current_transmit_total);
printf("\n[INIT NET] Transmit Speed: %d bytes/s.\n", net_transmit_speed);
printf("\n[INIT NET] Average Load Speed: %f bytes/s.\n", net_averageLoad_speed);
printf("*********************************************************************************************************\n");
}
} //参数:TYPE:["receiveTotal/receiveSpeed/transmitTotal/transmitSpeed/averageLoadSpeed"]
float net_usage(char * TYPE, bool log, bool lineLog){//log:打印更新的【网络各参数信息】,以便检测细节; lineLog:按行打印网络文件信息细节
net_current_timeStamp = time(NULL);//time() 单位:秒
printf("[net_usage] net_current_timeStamp: %f.\n", (double)net_current_timeStamp);//time_t[long int]必须转型,否则无法正常(输出显示:0.000)
net_dif_time = (double)(net_current_timeStamp - net_previous_timeStamp);//计算时间差(单位:秒)
if( (net_dif_time) >= NET_DIFF_TIME ){//只有满足达到时间戳以后,才更新接收与发送的网络字节数据信息
net_update(lineLog);//是否按行打印更新的网络参数信息
net_receive_speed = (net_current_receive_total - net_previous_receive_total) / NET_DIFF_TIME;//更新接收网速(单位:字节/秒)
net_transmit_speed = (net_current_transmit_total - net_previous_transmit_total) / NET_DIFF_TIME;//更新发送网速(单位:字节/秒)
net_averageLoad_speed = (net_receive_speed + net_transmit_speed) / 2; //更新平均网络负载情况
//更新时间戳
net_previous_timeStamp = net_current_timeStamp;
} if(log == true){
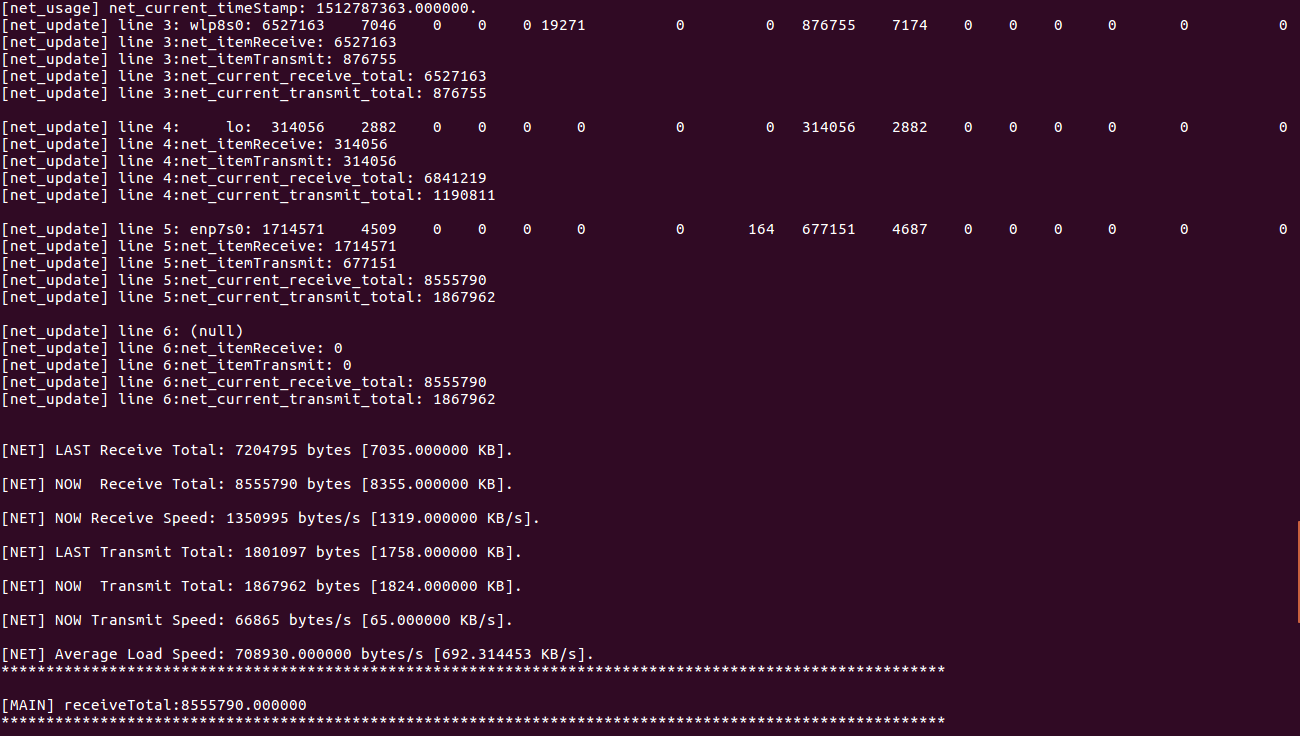
printf("\n[NET] LAST Receive Total: %d bytes [%f KB].\n", net_previous_receive_total, (double)(net_previous_receive_total / 1024));
printf("\n[NET] NOW Receive Total: %d bytes [%f KB].\n", net_current_receive_total, (double)(net_current_receive_total / 1024));
printf("\n[NET] NOW Receive Speed: %d bytes/s [%f KB/s].\n", net_receive_speed, (double)(net_receive_speed / 1024)); printf("\n[NET] LAST Transmit Total: %d bytes [%f KB].\n", net_previous_transmit_total, (double)(net_previous_transmit_total / 1024));
printf("\n[NET] NOW Transmit Total: %d bytes [%f KB].\n", net_current_transmit_total, (double)(net_current_transmit_total / 1024));
printf("\n[NET] NOW Transmit Speed: %d bytes/s [%f KB/s].\n", net_transmit_speed, (double)(net_transmit_speed / 1024));
printf("\n[NET] Average Load Speed: %f bytes/s [%f KB/s].\n", net_averageLoad_speed, (double)(net_averageLoad_speed / 1024));
printf("*********************************************************************************************************\n");
} if(TYPE == "receiveTotal"){
net_result = (float)net_current_receive_total;
} else if(TYPE == "receiveSpeed"){
net_result = (float)net_receive_speed;
} else if(TYPE == "transmitTotal"){
net_result = (float)net_current_transmit_total;
} else if(TYPE == "transmitSpeed"){
net_result = (float)net_transmit_speed;
} else if(TYPE == "averageLoadSpeed"){
net_result = net_averageLoad_speed;
} else {// TYPE 不存在时,抛出异常值 -1
net_result = -1;
} return net_result;
} //关闭网络监控
void net_close(){
fclose(net_stream); //关闭文件net_stream
} ///////////////////////////////////
// ↓demo↓ //
/////////////////////////////////// /*
initLog:是否打印【初始化后的网络各参数】日志;
usageLog:是否打印更新的当前的【网络各参数信息】,以便检测细节;
lineLog:是否【按行】打印【网络当前状态信息细节】
*/
/* void calculate(bool initLog, bool usageLog, bool lineLog){
printf("\n[MAIN] receiveTotal:%f\n", net_usage("receiveTotal", usageLog, lineLog));//log:打印日志在屏幕上:以便检测细节
printf("*********************************************************************************************************\n");
sleep(3);
printf("\n[MAIN] receiveTotal:%f\n", net_usage("receiveTotal", usageLog, lineLog));//log:打印日志在屏幕上:以便检测细节
printf("*********************************************************************************************************\n");
} void execute(bool initLog, bool usageLog, bool lineLog){//
system("cat /proc/net/dev");
printf("*********************************************************************************************************\n");
net_init(initLog, lineLog);
calculate(initLog, usageLog, lineLog);
net_close();
} int main(){
execute(true, true, true);//测试用例1
printf("########################################################################################################\n");
execute(false, true, false);//测试用例2
return 0;
} */
运行效果:
测试用例2:

测试用例1:

参考文献:
原创。
[C++]Linux之网络实时检测功能的更多相关文章
- Linux下网络流量实时监控工具
Linux下网络流量实时监控工具大全 在工作中发现,经常因为业务的原因,需要即时了解某台服务器网卡的流量,虽然公司也部署了cacti软件,但cacti是五分钟统计的,没有即时性,并且有时候打开监控页面 ...
- 网络实时流量监控工具iftop---转
网络实时流量监控工具iftop 分类: LINUX 1.安装依赖软件库 [root@localhost ~]# yum install libpcap libpcap-devel ncurses nc ...
- 安全运维之:网络实时流量监测工具iftop
网络管理是基础运维中一个很重要的工作,在看似平静的网络运行中,其实暗流汹涌,要保证业务系统稳定运行,网络运维者必须要了解网络的流量状态.各个网段的使用情形,带宽的利用率.网络是否存在瓶颈等,同时,当网 ...
- Linux基本命令 网络命令
概述 网络和监控命令类似于这些: hostname, ping, ifconfig, iwconfig, netstat, nslookup, traceroute, finger, telnet, ...
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(二)--数据包的传递过程--转
转载地址http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7492423 作者:闫明 本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13 注:标题中的”(上 ...
- 嵌入式linux的网络编程(1)--TCP/IP协议概述
嵌入式linux的网络编程(1)--TCP/IP协议概述 1.OSI参考模型及TCP/IP参考模型 通信协议用于协调不同网络设备之间的信息交换,它们建立了设备之间互相识别的信息机制.大家一定都听说过著 ...
- Atitit.linux 内核 新特性 新功能
Atitit.linux 内核 新特性 新功能 1. Linux 3.2内核新特性 2012-02-12 22:41:471 1.1. EXT4:支持更大的块2 1.2. BTRFS:更快的数据清理 ...
- 网络入侵检测规避工具fragrouter
网络入侵检测规避工具fragrouter 网络入侵检测系统可以通过拦截数据包,获取内容进而判断是否为恶意数据包.对于传输较大的数据包,通常会采用分片的方式,将大数据包拆分为小数据包进行传输.如果入 ...
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十一)--驱动程序层(下)
本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13 原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7555870 更多请查看专栏,地 ...
随机推荐
- mybatis 二级缓存
Mybatis读取缓存次序: 先从二级缓存中获取数据,如果有直接获取,如果没有进行下一步: 从一级缓存中取数据,有直接获取,如果没有进行下一步: 到数据库中进行查询,并保存到一级缓存中: 当sqlSe ...
- 为什么分布式一定要有redis?
为什么分布式一定要有redis? 孤独烟 架构师小秘圈 昨天 作者:孤独烟 来自:http://rjzheng.cnblogs.com/ 1.为什么使用redis 分析:博主觉得在项目中使用red ...
- P1024 一道naive的二分
好吧,这道题思路还是比较简单的.整个程序大体上很快就打出来了,然后修改了解为整数的情况. 但是交上去一直是50分,最后我很无耻的看了题解,然后抄了一个玄学if回来,瞬间AC,不知道为什么... 这句就 ...
- vue2.0项目实战(1)基础入门
最近公司的H5项目准备重构,部门老大说前端使用vue2.0来开发,所以就准备把整个项目的开发过程记录下来,一方面是为了记录开发过程中遇到的坑,另一方面也加强自己写作的能力. 什么是 Vue? 简要介绍 ...
- [luogu1552][派遣]
题目链接 思路 首先肯定要树形dp,一直没想到怎么用左偏树.如果不断弹出又不断地合并复杂度不就太高了.瞄了眼题解才知道可以直接用大根树.然后记录出当前这棵左偏树的大小(树里面所有点的薪水之和)以及点的 ...
- 关于 HDC 的释放
GetDC和ReleaseDC的调用配对,CreateDC和DeleteDC的调用配对. GetDC是从窗口获取现有的DC,而CreateDC是创建DC,所以ReleaseDC和DeleteDC的作用 ...
- 关于Java中扫描仪next()与nextLine()的区别
首先,next()一定要读取到有效字符后才可以结束输入,对输入有效字符之前遇到的空格键.Tab键或Enter键等结束符,next()方法会自动将其去掉,只有在输入有效字符之后,next()方法才将其后 ...
- 跨域技术(JSONP与CROS)
JSONP 我们发现,Web页面上调用js文件时不受是否跨域的影响,凡是拥有"src"这个属性的标签都拥有跨域的能力,比如<script>.<img>.&l ...
- Mac下如何生成SSH Key-使用GitLab
步骤1.检查是否已经存在SSH Key 打开电脑终端,输入以下命令: ls -al ~/.ssh 会出现两种情况 步骤2. 生成/设置SSH Key 继续上一步可能出现的情况 (1)情况一:终端出现文 ...
- JDBC批处理(Batch)MySQL中的表
在数据库test里先创建表school,内容如下 向school表中一次增加多行.addBatch,executeBatch import java.sql.Connection; import ja ...
