机器学习(四) 分类算法--K近邻算法 KNN (上)
一、K近邻算法基础
KNN------- K近邻算法--------K-Nearest Neighbors
思想极度简单
应用数学知识少 (近乎为零)
效果好(缺点?)
可以解释机器学习算法使用过程中很多细节问题
更完整的刻画机器学习应用的流程
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 实现我们自己的 kNN
创建简单测试用例
raw_data_X = [[3.393533211, 2.331273381],
[3.110073483, 1.781539638],
[1.343808831, 3.368360954],
[3.582294042, 4.679179110],
[2.280362439, 2.866990263],
[7.423436942, 4.696522875],
[5.745051997, 3.533989803],
[9.172168622, 2.511101045],
[7.792783481, 3.424088941],
[7.939820817, 0.791637231]
]
raw_data_y = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
X_train = np.array(raw_data_X)
y_train = np.array(raw_data_y)
X_train
array([[ 3.39353321, 2.33127338],
[ 3.11007348, 1.78153964],
[ 1.34380883, 3.36836095],
[ 3.58229404, 4.67917911],
[ 2.28036244, 2.86699026],
[ 7.42343694, 4.69652288],
[ 5.745052 , 3.5339898 ],
[ 9.17216862, 2.51110105],
[ 7.79278348, 3.42408894],
[ 7.93982082, 0.79163723]])
y_train
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])

kNN的过程
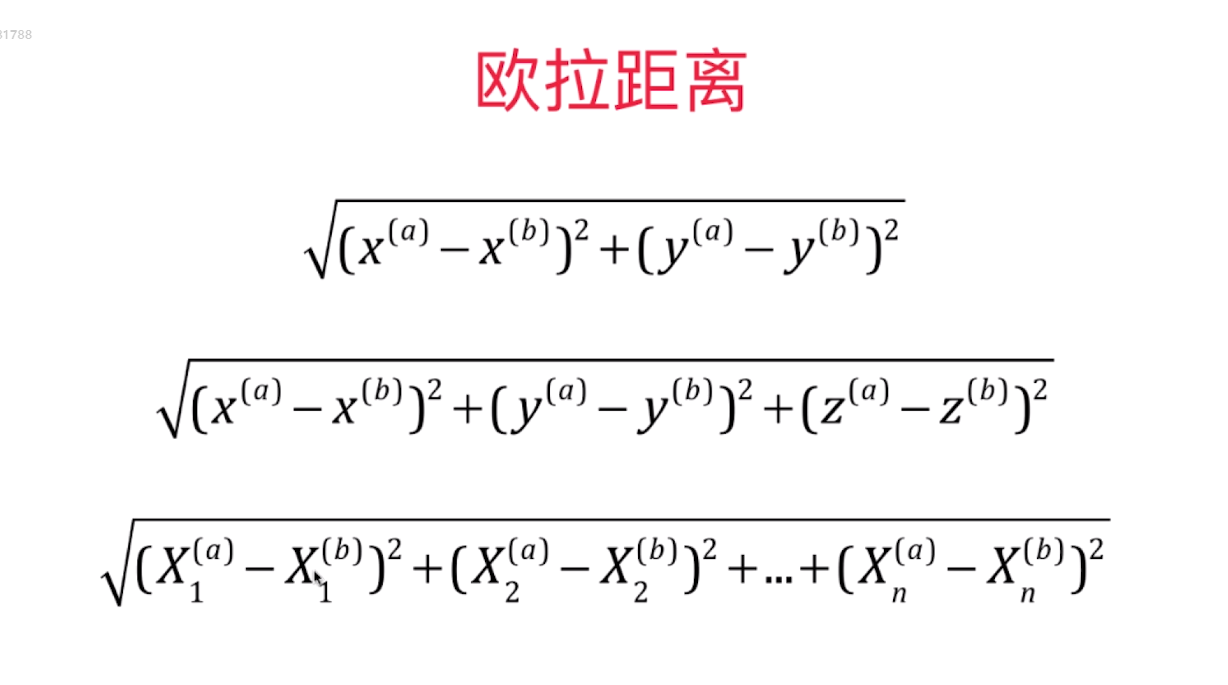
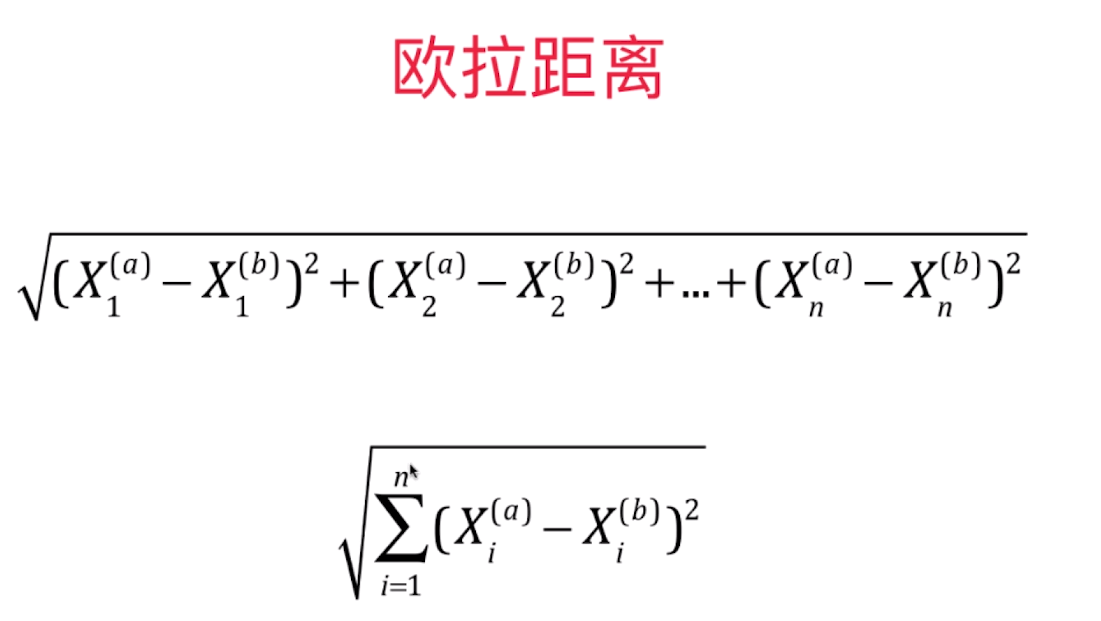
from math import sqrt
distances = []
for x_train in X_train:
d = sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2))
distances.append(d)
distances
[4.812566907609877,
5.229270827235305,
6.749798999160064,
4.6986266144110695,
5.83460014556857,
1.4900114024329525,
2.354574897431513,
1.3761132675144652,
0.3064319992975,
2.5786840957478887]
distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2))
for x_train in X_train]
distances
[4.812566907609877,
5.229270827235305,
6.749798999160064,
4.6986266144110695,
5.83460014556857,
1.4900114024329525,
2.354574897431513,
1.3761132675144652,
0.3064319992975,
2.5786840957478887]
np.argsort(distances)
array([8, 7, 5, 6, 9, 3, 0, 1, 4, 2])
nearest = np.argsort(distances)
k = 6
topK_y = [y_train[neighbor] for neighbor in nearest[:k]]
topK_y
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
from collections import Counter
votes = Counter(topK_y)
votes
Counter({0: 1, 1: 5})
votes.most_common(1)
[(1, 5)]
predict_y = votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
predict_y
1
二、scikit-learn 中的机器学习算法封装
KNN/KNNN.py
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
from collections import Counter class KNNClassifier: def __init__(self, k):
"""初始化kNN分类器"""
assert k >= 1, "k must be valid"
self.k = k
self._X_train = None
self._y_train = None def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
"""根据训练数据集X_train和y_train训练kNN分类器"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be at least k." self._X_train = X_train
self._y_train = y_train
return self def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self._X_train is not None and self._y_train is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1], \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train" y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict]
return np.array(y_predict) def _predict(self, x):
"""给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值"""
assert x.shape[0] == self._X_train.shape[1], \
"the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2))
for x_train in self._X_train]
nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]]
votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0] def __repr__(self):
return "KNN(k=%d)" % self.k
kNN_function/KNN.py
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
from collections import Counter def kNN_classify(k, X_train, y_train, x): assert 1 <= k <= X_train.shape[0], "k must be valid"
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must equal to the size of y_train"
assert X_train.shape[1] == x.shape[0], \
"the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2)) for x_train in X_train]
nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [y_train[i] for i in nearest[:k]]
votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0]

三、训练数据集、测试数据集
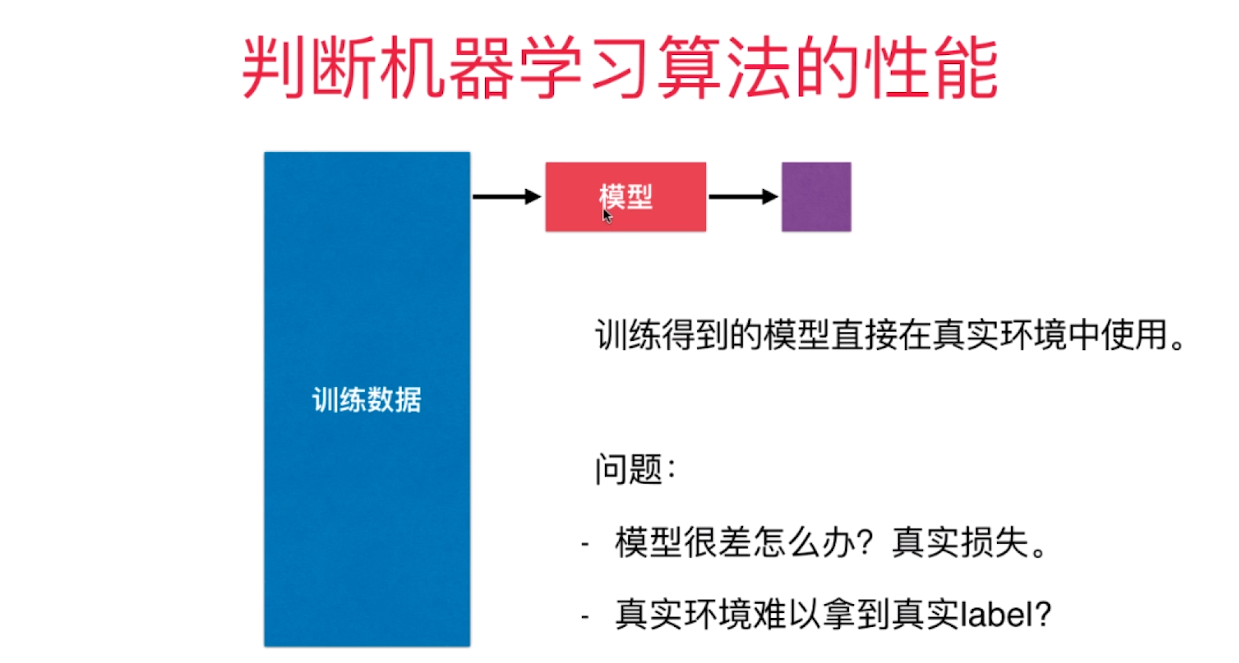
判断机器学习算法的性能
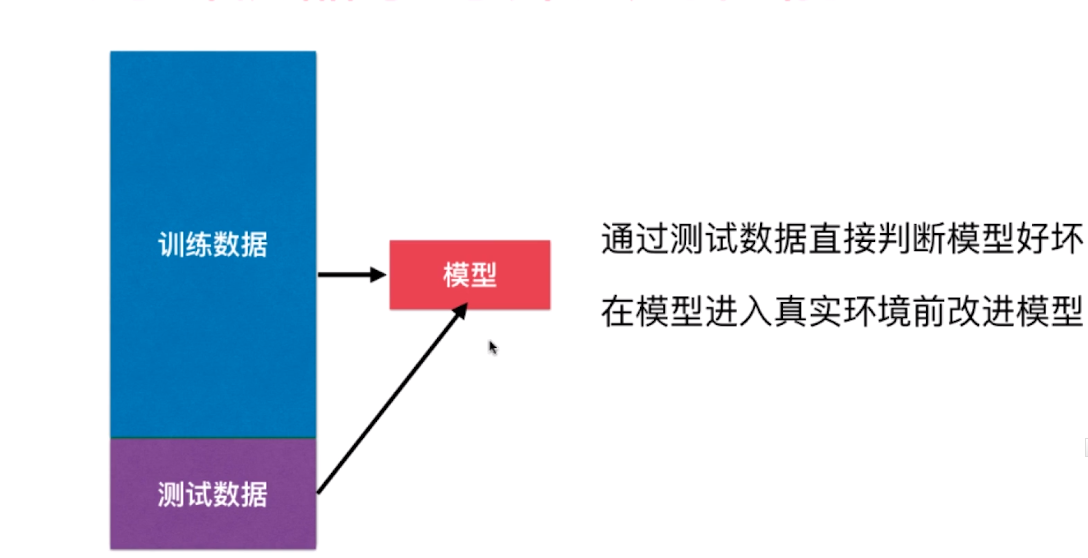
playML/KNN.py
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
from collections import Counter class KNNClassifier: def __init__(self, k):
"""初始化kNN分类器"""
assert k >= 1, "k must be valid"
self.k = k
self._X_train = None
self._y_train = None def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
"""根据训练数据集X_train和y_train训练kNN分类器"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be at least k." self._X_train = X_train
self._y_train = y_train
return self def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self._X_train is not None and self._y_train is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1], \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train" y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict]
return np.array(y_predict) def _predict(self, x):
"""给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值"""
assert x.shape[0] == self._X_train.shape[1], \
"the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2))
for x_train in self._X_train]
nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]]
votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0] def __repr__(self):
return "KNN(k=%d)" % self.k
playML/model_selection.py
import numpy as np def train_test_split(X, y, test_ratio=0.2, seed=None):
"""将数据 X 和 y 按照test_ratio分割成X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test"""
assert X.shape[0] == y.shape[0], \
"the size of X must be equal to the size of y"
assert 0.0 <= test_ratio <= 1.0, \
"test_ration must be valid" if seed:
np.random.seed(seed) shuffled_indexes = np.random.permutation(len(X)) test_size = int(len(X) * test_ratio)
test_indexes = shuffled_indexes[:test_size]
train_indexes = shuffled_indexes[test_size:] X_train = X[train_indexes]
y_train = y[train_indexes] X_test = X[test_indexes]
y_test = y[test_indexes] return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
playML/__init__.py



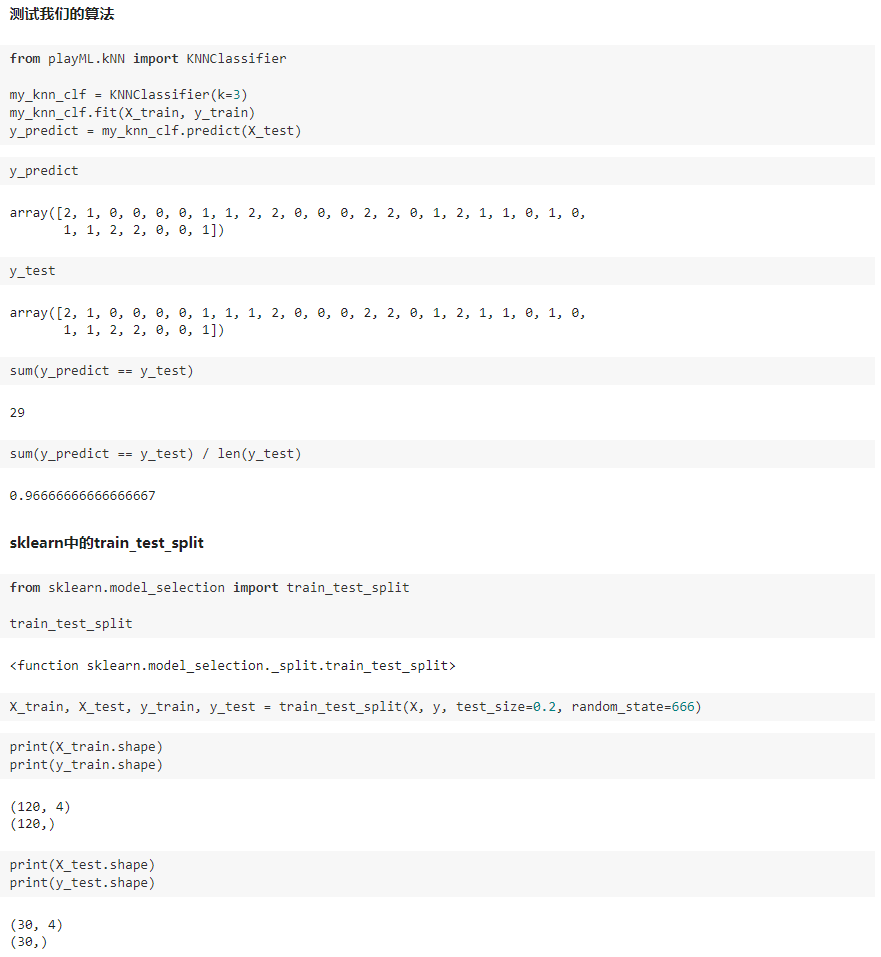
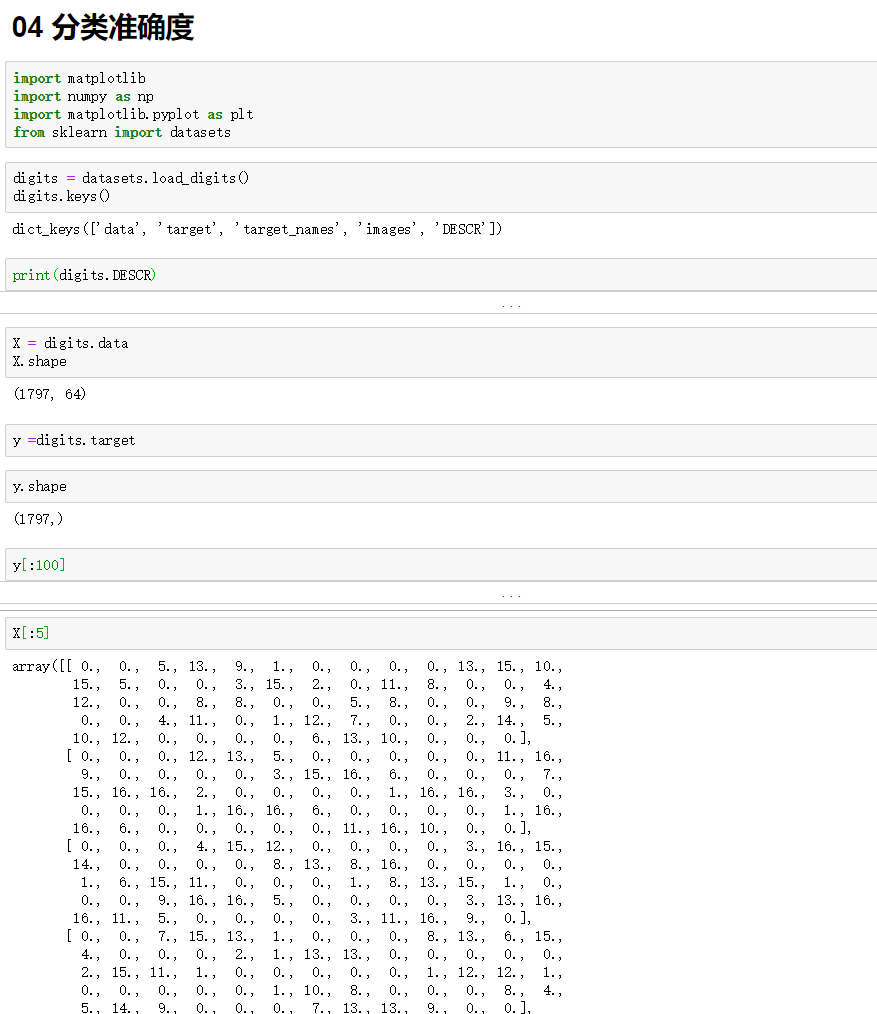
四、分类的准确度
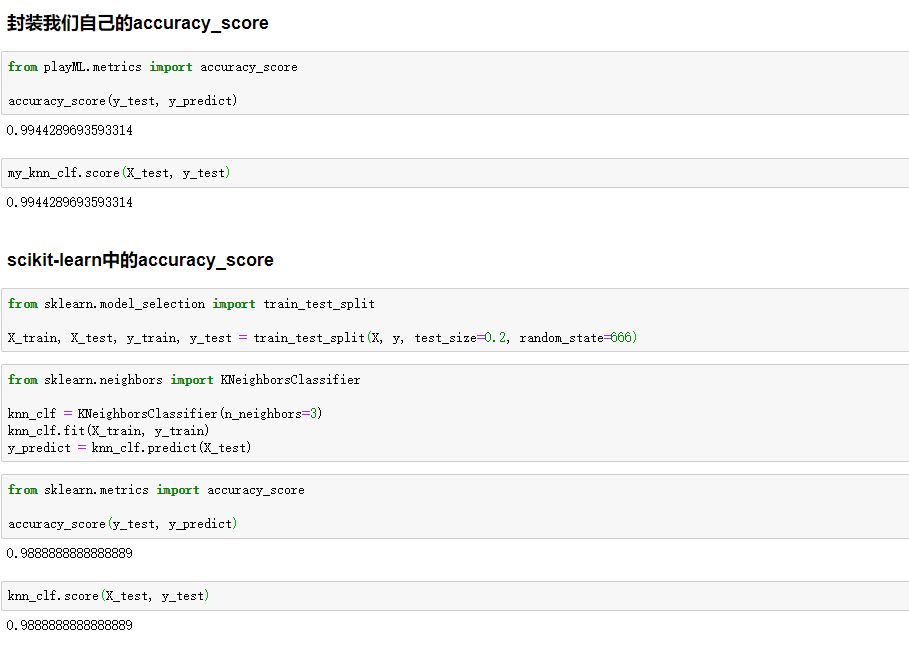
playML/metrics.py
import numpy as np def accuracy_score(y_true, y_predict):
'''计算y_true和y_predict之间的准确率'''
assert y_true.shape[0] == y_predict.shape[0], \
"the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict" return sum(y_true == y_predict) / len(y_true)
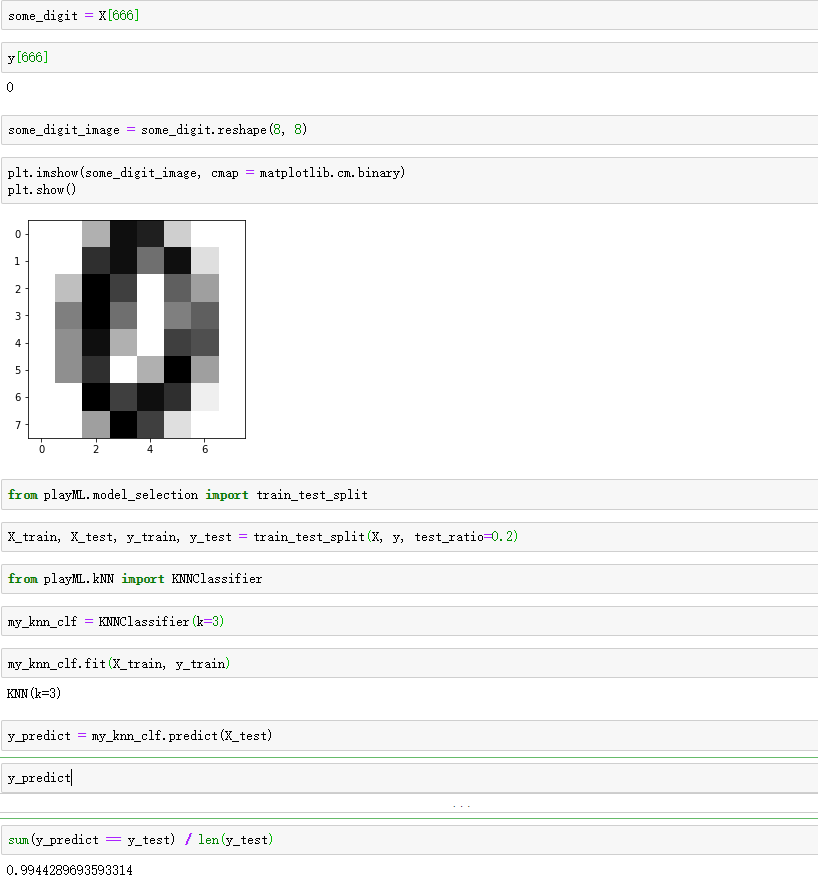
model_selection.py-->KNNClassifier 类 里面添加 这样一个方法
from .metrics import accuracy_score
def score(self, X_test, y_test):
"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict = self.predict(X_test)
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
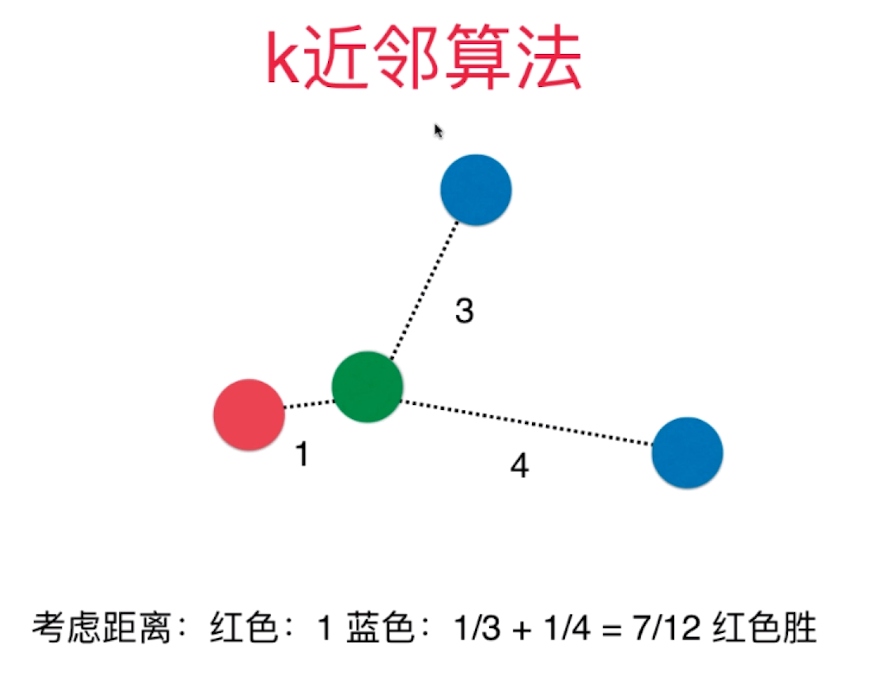
五、超参数
超参数:在算法运行前需要决定的参数
模型参数:算法过程中学习的参数
KNN算法没有模型参数
KNN算法中的 K 是 典型的 超参数
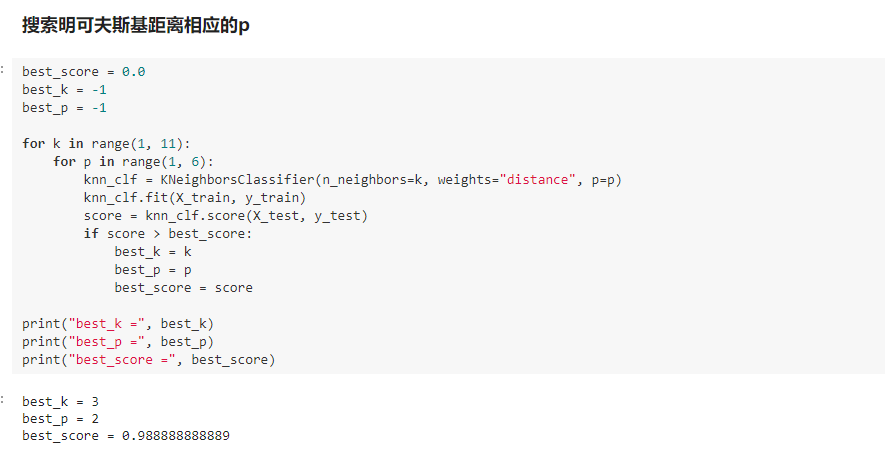
寻找好的超参数:
领域知识、经验数值、实验搜索





我写的文章只是我自己对bobo老师讲课内容的理解和整理,也只是我自己的弊见。bobo老师的课 是慕课网出品的。欢迎大家一起学习。
机器学习(四) 分类算法--K近邻算法 KNN (上)的更多相关文章
- 第4章 最基础的分类算法-k近邻算法
思想极度简单 应用数学知识少 效果好(缺点?) 可以解释机器学习算法使用过程中的很多细节问题 更完整的刻画机器学习应用的流程 distances = [] for x_train in X_train ...
- 机器学习(四) 机器学习(四) 分类算法--K近邻算法 KNN (下)
六.网格搜索与 K 邻近算法中更多的超参数 七.数据归一化 Feature Scaling 解决方案:将所有的数据映射到同一尺度 八.scikit-learn 中的 Scaler preprocess ...
- python 机器学习(二)分类算法-k近邻算法
一.什么是K近邻算法? 定义: 如果一个样本在特征空间中的k个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的样本中的大多数属于某一个类别,则该样本也属于这个类别. 来源: KNN算法最早是由Cover和Hart提 ...
- 分类算法----k近邻算法
K最近邻(k-Nearest Neighbor,KNN)分类算法,是一个理论上比较成熟的方法,也是最简单的机器学习算法之一.该方法的思路是:如果一个样本在特征空间中的k个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的 ...
- 机器学习(1)——K近邻算法
KNN的函数写法 import numpy as np from math import sqrt from collections import Counter def KNN_classify(k ...
- SIGAI机器学习第七集 k近邻算法
讲授K近邻思想,kNN的预测算法,距离函数,距离度量学习,kNN算法的实际应用. KNN是有监督机器学习算法,K-means是一个聚类算法,都依赖于距离函数.没有训练过程,只有预测过程. 大纲: k近 ...
- 最基础的分类算法-k近邻算法 kNN简介及Jupyter基础实现及Python实现
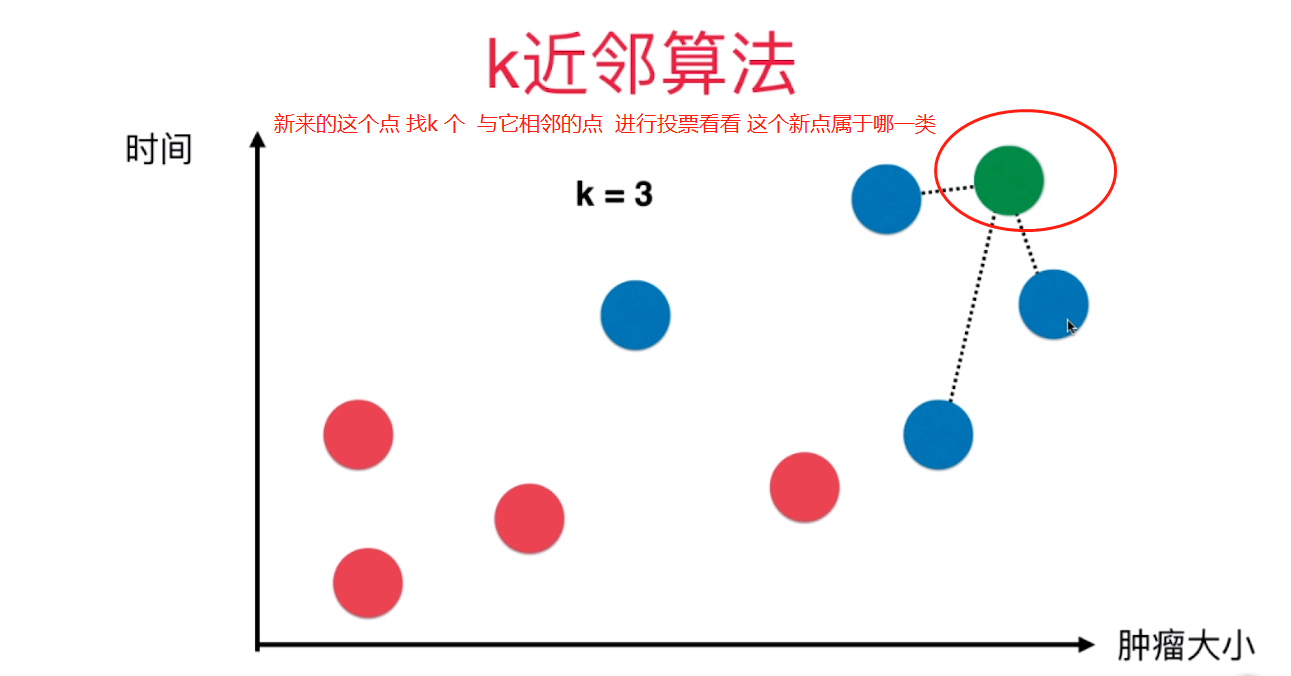
k-Nearest Neighbors简介 对于该图来说,x轴对应的是肿瘤的大小,y轴对应的是时间,蓝色样本表示恶性肿瘤,红色样本表示良性肿瘤,我们先假设k=3,这个k先不考虑怎么得到,先假设这个k是 ...
- 【学习笔记】分类算法-k近邻算法
k-近邻算法采用测量不同特征值之间的距离来进行分类. 优点:精度高.对异常值不敏感.无数据输入假定 缺点:计算复杂度高.空间复杂度高 使用数据范围:数值型和标称型 用例子来理解k-近邻算法 电影可以按 ...
- 机器学习03:K近邻算法
本文来自同步博客. P.S. 不知道怎么显示数学公式以及排版文章.所以如果觉得文章下面格式乱的话请自行跳转到上述链接.后续我将不再对数学公式进行截图,毕竟行内公式截图的话排版会很乱.看原博客地址会有更 ...
随机推荐
- Vue组件开发 -- Markdown
利用marked 和 highlight.js开发markdown组件 实现效果图如下: markdown组件已这种形式<Markdown v-model="markdown" ...
- [luogu] P2787 语文1(chin1)- 理理思维(分块)
P2787 语文1(chin1)- 理理思维 题目背景 蒟蒻HansBug在语文考场上,挠了无数次的头,可脑子里还是一片空白. 题目描述 考试开始了,可是蒟蒻HansBug脑中还是一片空白.哦不!准确 ...
- linux的一页是多大
命令 getconf PAGESIZE 结果为4096,即一页=4096字节=4KB(注意是Byte,1B=8bit) 在使用mmap映射函数时,它的实际映射单位也是以页为单位的,即不过我们把MAP_ ...
- 优秀Swift开源项目推荐
工具类 SwiftyJSON:GitHub上最为开发者认可的JSON解析类 Safe.ijaimi:源码漏洞分析检测工具,一键完成 Dollar.swift:Swift版Lo-Dash(或unders ...
- Linux下查询CPU 缓存的工具
在Linux下能够使用例如以下工具查询CPU缓存: 方式1: $ lscpu L1d cache: 32K <span style="white-space:pre"> ...
- mysql-数据库维护
一.备份数据 1.使用mysqldump命令备份:前提:musql的版本必须一致. mysqldump -u username -p --default -character-set=gbk dbn ...
- Django Admin site 显示问题
Django Admin site 显示问题 今天配置了一下Django admin site,可是admin site的显示有一些问题,当我打开源码.訪问里面的admin 的css 文件时候,htt ...
- 状态压缩dp初学__$Corn Fields$
明天计划上是要刷状压,但是作为现在还不会状压的\(ruoruo\)来说是一件非常苦逼的事情,所以提前学了一下状压\(dp\). 鸣谢\(hmq\ juju\)的友情帮助 状态压缩动态规划 本博文的大体 ...
- Android 如何打造Android自定义的下拉列表框控件
一.概述 Android中的有个原生的下拉列表控件Spinner,但是这个控件有时候不符合我们自己的要求, 比如有时候我们需要类似windows 或者web网页中常见的那种下拉列表控件,类似下图这样的 ...
- codeforces 400 C Inna and Huge Candy Matrix【模拟】
题意:给出一个矩形的三种操作,顺时针旋转,逆时针旋转,对称,给出原始坐标,再给出操作数,问最后得到的坐标 画一下模拟一下操作就可以找到规律了 #include<iostream> #inc ...
