Square Destroyer-POJ 1084 (IDA*)
Description
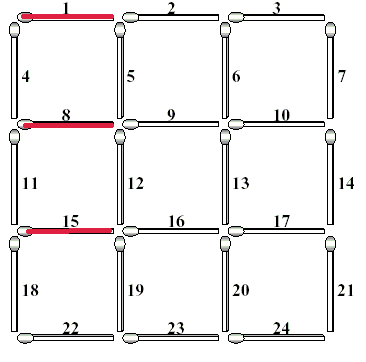
Each matchstick of the complete grid is identified with a unique number which is assigned from left to right and from top to bottom as shown in the left figure. If you take some matchsticks out from the complete grid, then some squares in the grid will be destroyed, which results in an incomplete 3*3 grid. The right figure illustrates an incomplete 3*3 grid after removing three matchsticks numbered with 12, 17 and 23. This removal destroys 5 squares of size one, 3 squares of size two, and 1 square of size three. Consequently, the incomplete grid does not have squares of size three, but still has 4 squares of size one and 1 square of size two.

As input, you are given a (complete or incomplete) n*n grid made with no more than 2n(n+1) matchsticks for a natural number 5 <= n . Your task is to compute the minimum number of matchsticks taken
out to destroy all the squares existing in the input n*n grid.
Input
Each test case consists of two lines: The first line contains a natural number n , not greater than 5, which implies you are given a (complete or incomplete) n*n grid as input, and the second line begins with a nonnegative integer k , the number of matchsticks that are missing from the complete n*n grid, followed by
k numbers specifying the matchsticks. Note that if k is equal to zero, then the input grid is a complete n*n grid; otherwise, the input grid is an incomplete n*n grid such that the specified k matchsticks are missing from the complete n*n grid.
Output
Sample Input
2
2
0
3
3 12 17 23
Sample Output
3
3
题意:t组数据,给出n代表n*n的网格,给一个值k,然后k个值,表示去掉k所代表的边,问还需要最少去掉几条边可以使得网格中没有正方形。
思路:
评估函数:每出现一个正方形,就删去其含有的边,然后继续扫描正方形,这样计数出来的次数比实际需要次数小(因为一次删去了多条边)
对于网格中正方形的枚举:
①先枚举正方形大小,1 <= size <= n;
②枚举网格每行最左边的火柴
③对于每个行位置,枚举该行可以成为该size大小正方形的最左边火柴
④标记该正方形的所有上边界和下边界(知道size和上边界最左火柴很容易求得)
标记该正方形的所有左边界和有边界
(代码借鉴网上,侵删)
stick【i】表示含有i火柴的正方形编号
square【i】表示i正方形所含火柴编号
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std; int t;
int totsquare,totstick,base;
vector<int>stick[],square[];
int n,k;
int ans;
int exi[],tmp[]; int cal()
{
int res = ;
for(int i=;i<=totsquare;i++)tmp[i] = exi[i];
for(int i=;i<=totsquare;i++)if(!tmp[i])
{
res++;
for(int j=;j<square[i].size();j++)
{
for(int l=;l<stick[square[i][j]].size();l++)
{
tmp[stick[square[i][j]][l]]--;
}
}
}
return res;
} bool dfs(int sum,int lim)
{
if(sum + cal() > lim)return ;
int tmp = ;
while(exi[tmp] < && tmp <= totsquare)tmp++;
if(tmp > totsquare)
{
ans = min(ans,sum);
return ;
}
for(int i=;i<square[tmp].size();i++)
{
int sti = square[tmp][i];
for(int j=;j<stick[sti].size();j++)
{
exi[stick[sti][j]]--;
}
if(dfs(sum+,lim))return ;
for(int j=;j<stick[sti].size();j++)
{
exi[stick[sti][j]]++;
}
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
totsquare = ,totstick = *n*(n+),base = *n+;
for(int i=; i<; i++)
{
stick[i].clear();
square[i].clear();
}
for(int sz=; sz<=n; sz++)
{
for(int i=; (i-)/base+sz<=n; i+=base)
{
for(int j=i; j-i+sz<=n; j++)
{
totsquare++;
for(int l=j; l-j<sz; l++) // 正方形上下边界标记
{
square[totsquare].push_back(l);
square[totsquare].push_back(l+sz*base);
stick[l].push_back(totsquare);
stick[l+sz*base].push_back(totsquare);
}
for(int l=j+n; (l-j-sz)/base<sz; l+=base) //正方形左右边界标记
{
square[totsquare].push_back(l);
square[totsquare].push_back(l+sz);
stick[l].push_back(totsquare);
stick[l+sz].push_back(totsquare);
}
}
}
}
memset(exi,,sizeof(exi));
for(int i=; i<=k; i++)
{
int t_st;
scanf("%d",&t_st);
for(int j=; j<stick[t_st].size(); j++)
{
exi[stick[t_st][j]]--;
}
totstick--;
}
ans = totstick;
for(int maxd=;; maxd++)
{
if(dfs(,maxd))
{
printf("%d\n",ans);
break;
}
}
}
}
Square Destroyer-POJ 1084 (IDA*)的更多相关文章
- Booksort POJ - 3460 (IDA*)
Description The Leiden University Library has millions of books. When a student wants to borrow a ce ...
- POJ题目(转)
http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/07/29/2120667.html 初期:一.基本算法: (1)枚举. (poj1753,poj29 ...
- Repeater POJ - 3768 (分形)
Repeater POJ - 3768 Harmony is indispensible in our daily life and no one can live without it----may ...
- UVA - 10384 The Wall Pusher(推门游戏)(IDA*)
题意:从起点出发,可向东南西北4个方向走,如果前面没有墙则可走:如果前面只有一堵墙,则可将墙向前推一格,其余情况不可推动,且不能推动游戏区域边界上的墙.问走出迷宫的最少步数,输出任意一个移动序列. 分 ...
- Radar Installation POJ - 1328(贪心)
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. ...
- Best Cow Fences POJ - 2018 (二分)
Farmer John's farm consists of a long row of N (1 <= N <= 100,000)fields. Each field contains ...
- E - The Balance POJ - 2142 (欧几里德)
题意:有两种砝码m1, m2和一个物体G,m1的个数x1, m2的个数为x2, 问令x1+x2最小,并且将天平保持平衡 !输出 x1 和 x2 题解:这是欧几里德拓展的一个应用,欧几里德求不定方程 ...
- 人类即将进入互联网梦境时代(IDA)
在电影<盗梦空间>中,男主角科布和妻子在梦境中生活了50年,从楼宇.商铺.到河流浅滩.一草一木.这两位造梦师用意念建造了属于自己的梦境空间.你或许并不会想到,在不久未来,这看似科幻的情节将 ...
- POJ 2286 The Rotation Game(IDA*)
The Rotation Game Time Limit: 15000MS Memory Limit: 150000K Total Submissions: 6396 Accepted: 21 ...
随机推荐
- swift 学习- 15 -- 构造过程 01
// 构造过程 是使用类,结构体 或 枚举类型的实例之前的准备过程, // 在新实例可用前必须执行这个过程, 具体操作包括 设置实例中每个存储型属性的初始值 和 执行其他必须的设置 或 初始化工作 / ...
- Confluence 6 允许其他用户编辑站点欢迎消息
你可以通过使用 Include Page 宏从你站点其他页面中包含内容,而允许其他不是 Confluence 管理员的用户编辑站点欢迎消息.使用这种方式能够避免直接对模板文件中的内容进行编辑. 从站点 ...
- Swift中 @objc 使用介绍
在swift 中 如果一个按钮添加点击方法 如果定义为Private 或者 定义为 FilePrivate 那么会在Addtaget方法中找不到私有方法 但是又不想把方法暴露出来,避免外界访问 ,那 ...
- sublime c++
install: sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/sublime-text-3 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get i ...
- 最短路径之Bellman-Ford算法
第一行为源点个数,边的个数m 接下来m行为a->b和权值 5 52 3 21 2 -31 5 54 5 23 4 3 Bellman-Ford算法(1): #include<iostrea ...
- 剑指offer 二叉树中和为某一个值的路径
剑指offer 牛客网 二叉树中和为某一个值的路径 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Tue Apr 9 15:53:58 2 ...
- 安装AngularJS Batarang遇到的问题
AngularJS Batarang是AngularJS在谷歌浏览器上的一个调试工具,因为国内目前无法访问谷歌浏览器应用商店,所以Batarang只能离线安装.不过在安装这个插件的过程中遇到了一些麻烦 ...
- 古代猪文:数论大集合:欧拉定理,exgcd,china,逆元,Lucas定理应用
/* 古代猪文:Lucas定理+中国剩余定理 999911658=2*3*4679*35617 Lucas定理:(m,n)=(sp,tp)(r,q) %p 中国剩余定理:x=sum{si*Mi*ti} ...
- Nginx详解三:Nginx基础篇之yum安装
Nginx快速搭建 Mainline version ----开发版:具有最新功能的版本,用于测试.研究.学习,不用于企业生成环境 Stable version----稳定版:官方认可,且通过测试的 ...
- 官方版sublime Text3汉化和激活注册码
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/chaonuanxi/p/9371837.html sublimeText3 很不错,前面几天下了vscore学习Node.js,感觉有点懵,今天 ...
