Why Deep Learning Works – Key Insights and Saddle Points
Why Deep Learning Works – Key Insights and Saddle Points
A quality discussion on the theoretical motivations for deep learning, including distributed representation, deep architecture, and the easily escapable saddle point.
This post summarizes the key points of a recent blog post by Rinu Boney, based on a lecture by Dr. Yoshua Bengio from this year's Deep Learning Summer School in Montreal, which discusses the theoretical motivations for deep learning.
"To generalize locally, we need representative examples for all relevant variations."
Deep learning is about learning multiple levels of representations, corresponding to multiple levels of abstractions. If we are able to learn these multiple levels of representation, we are able to generalize well.
After setting the general tone of the post with the above (paraphrased) statement, the author presents a number of different artificial intelligence (AI) strategies, from rule-based systems to deep learning, and notes on at which levels of learning their components function. He then states the 3 keys to moving from machine learning (ML) to true artificial intelligence: Lots of data, very flexible models, and powerful priors, and that, since classical ML can handle the first 2, his post deals with the third.
On the path toward AI from today's ML systems, we need learning, generalization, ways to fight the curse of dimensionality, and the ability to disentangle the underlying explanatory factors. Before explaining why non-parametric learning algorithms won't get us to true AI, he gives a nuanced definition of non-parametric. He explains why smoothness, a classical non-parametric approach, won't work on high-dimensionality, and then provides the following insight re: dimensionality:
"If we dig deeper mathematically, it's not the number of dimensions but the number of variations of functions that we learn. In this case, smoothness is about how many ups and downs are present in the curve."
"A line is very smooth. A curve with some ups and downs is less smooth but still smooth."
So, it's clear that smoothness will not beat the curse of dimensionality alone. In fact, smoothness doesn't even apply to modern, complex problems like computer vision or natural language processing. After discussing the downfalls of such competing methods as Gaussian kernels, Boney sets his sights on moving past smoothness, and why that's necessary:
"We want to be non-parametric in the sense that we want the family of functions to grow in flexibility as we get more data. In neural networks, we change the number of hidden units depending on the amount of data."
He notes that in deep learning, 2 priors are used, namely distributed representations and deep architecture.
Why distributed representations?
"With distributed representations, it is possible to represent exponential number of regions with a linear number of parameters. The magic of distributed representation is that it can learn a very complicated function (with many ups and downs) with a low number of examples."
In distributed representations, features are individually and independently meaningful, and they remain so regardless of what the other features are. There maybe some interactions but most features are learned independent of each other. Boney states that neural networks are very good at learning representations capturing the semantic aspects, and that their generalization power is derived from these representations. As a practical exploration of the topic, he recommend's Cristopher Olah's article for some information on distributed representation and Natural Language Processing.
There is a lot of misunderstanding about what depth means.
"Deeper networks does not correspond to a higher capacity. Deeper doesn't mean we can represent more functions. If the function we are trying to learn has a particular characteristic obtained through composition of many operations, then it is much better to approximate these functions with a deep neural network."
Boney then comes full circle. He explains that one of the reasons neural network research was abandon (once again) in the late 90s was because the optimization problem is non-convex. The realization from the work in the 80s and 90s that neural networks have an exponential number of local minima, along with the breakout success of kernel machines, also led to this downfall, as did the fact that networks may get stuck on poor solutions. Recently we have evidence that the issue of non-convexity may be a non-issue, which changes its relationship vis-a-vis neural networks. 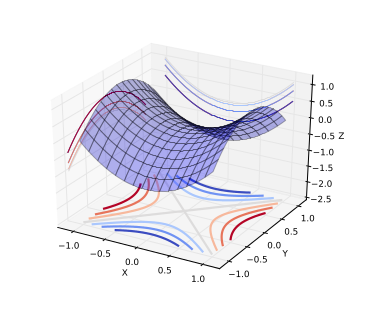
"A saddle point is illustrated in the image above. In a global or local minima, all the directions are going up and in a global or local maxima, all the directions are going down."
Saddle Points.
"Let us consider the optimization problem in low dimensions vs high dimensions. In low dimensions, it is true that there exists lots of local minima. However in high dimensions, local minima are not really the critical points that are the most prevalent in points of interest. When we optimize neural networks or any high dimensional function, for most of the trajectory we optimize, the critical points(the points where the derivative is zero or close to zero) are saddle points. Saddle points, unlike local minima, are easily escapable."
The intuition with the saddle point, is that, for a minima located close to the global minima, all directions should be climbing upward; going further downward is not possible. Local minima exist, but are very close to global minima in terms of objective functions, and theoretical results suggest that some large functions have their probability concentrated between the index (the critical points) and the objective function. The index is the fraction of directions moving downward; for all values of index not 0 or 1 (local minima and maxima, respectively), then it is a saddle point.
Boney goes on to say that there has been empirical validation corroborating this relationship between index and objective function, and that, while there is no proof the results apply to neural network optimization, some evidence suggests that the observed behavior may well correspond to the theoretical results. Stochastic gradient descent, in practice, almost always escapes from surfaces that are not local minima.
This all suggests that local minima may not, in fact, be an issue because of saddle points.
Boney follows his saddle points discussion up by pointing out a few other priors that work with deep distributed representations; human learning, semi-supervised learning, and multi-task learning. He then lists a few related papers on saddle points.
Rinu Boney has written a detailed piece on the motivations for deep learning, including a good discussion on saddle points, all of which is difficult to do justice with a few quotes and some summarization. If you are interested in a deeper discussion of the above points to visit Boney's blog and read the insightful and well-written piece yourself.
Bio: Matthew Mayo is a computer science graduate student currently working on his thesis parallelizing machine learning algorithms. He is also a student of data mining, a data enthusiast, and an aspiring machine learning scientist.
Related:
Most popular last 30 days
Most viewed last 30 days
- Top 5 arXiv Deep Learning Papers, Explained - Oct 1, 2015.
- Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: Key Differences - Sep 29, 2015.
- 60+ Free Books on Big Data, Data Science, Data Mining, Machine Learning, Python, R, and more - Sep 4, 2015.
- R vs Python for Data Science: The Winner is ... - May 26, 2015.
- R vs Python: head to head data analysis - Oct 13, 2015.
- 30 Cant miss Harvard Business Review articles on Data Science, Big Data and Analytics - Sep 30, 2015.
- 9 Must-Have Skills You Need to Become a Data Scientist - Nov 22, 2014.
Most shared last 30 days
- Top 5 arXiv Deep Learning Papers, Explained - Oct 1, 2015.
- 30 Cant miss Harvard Business Review articles on Data Science, Big Data and Analytics - Sep 30, 2015.
- 90+ Active Blogs on Analytics, Big Data, Data Mining, Data Science, Machine Learning - Oct 8, 2015.
- How Big Data Helps Build Smart Cities - Oct 16, 2015.
- Does Deep Learning Come from the Devil? - Oct 9, 2015.
- 5 steps to actually learn data science - Oct 6, 2015.
- R vs Python: head to head data analysis - Oct 13, 2015.
Why Deep Learning Works – Key Insights and Saddle Points的更多相关文章
- why deep learning works
https://medium.com/towards-data-science/deep-learning-for-object-detection-a-comprehensive-review-73 ...
- Growing Pains for Deep Learning
Growing Pains for Deep Learning Advances in theory and computer hardware have allowed neural network ...
- Decision Boundaries for Deep Learning and other Machine Learning classifiers
Decision Boundaries for Deep Learning and other Machine Learning classifiers H2O, one of the leading ...
- Why deep learning?
1. 深度学习中网络越深越好么? 理论上说是这样的,因为网络越深,参数也越多,拟合能力也越强(但实际情况是,网络很深的时候,不容易训练,使得表现能力可能并不好). 2. 那么,不同什么深度的网络,在参 ...
- Use of Deep Learning in Modern Recommendation System: A Summary of Recent Works(笔记)
注意:论文中,很多的地方出现baseline,可以理解为参照物的意思,但是在论文中,我们还是直接将它称之为基线,也 就是对照物,参照物. 这片论文中,作者没有去做实际的实验,但是却做了一件很有意义的事 ...
- (转)WHY DEEP LEARNING IS SUDDENLY CHANGING YOUR LIFE
Main Menu Fortune.com E-mail Tweet Facebook Linkedin Share icons By Roger Parloff Illustration ...
- The Brain vs Deep Learning Part I: Computational Complexity — Or Why the Singularity Is Nowhere Near
The Brain vs Deep Learning Part I: Computational Complexity — Or Why the Singularity Is Nowhere Near ...
- What are some good books/papers for learning deep learning?
What's the most effective way to get started with deep learning? 29 Answers Yoshua Bengio, ...
- (转) Learning Deep Learning with Keras
Learning Deep Learning with Keras Piotr Migdał - blog Projects Articles Publications Resume About Ph ...
随机推荐
- JS实现颜色值的转换
从网上看了个案例,是实现颜色值转换的,就想着自己也写个.网上的案例链接找不到了,这里也就不贴了. JavaScript颜色转换的核心就是进制间的转换. rgba(0,0,0,.4)转换成#000000 ...
- 用python简单处理图片(1):打开\显示\保存图像
一提到数字图像处理,可能大多数人就会想到matlab,但matlab也有自身的缺点: 1.不开源,价格贵 2.软件容量大.一般3G以上,高版本甚至达5G以上. 3.只能做研究,不易转化成软件. 因此, ...
- Matlab中reshape函数的使用
reshape把指定的矩阵改变形状,但是元素个数不变, 例如,行向量: a = [1 2 3 4 5 6] 执行下面语句把它变成3行2列: b = reshape(a,3,2) 执行结果: b = 1 ...
- Python类库下载
https://sourceforge.net/projects/pywin32/files/pywin32/ WMI库的安装 下载 http://timgolden.me.uk/python/wmi ...
- [CareerCup] 3.2 Min Stack 最小栈
3.2 How would you design a stack which, in addition to push and pop, also has a function min which r ...
- LeetCode:Gray Code(格雷码)
题目链接 The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit. Gi ...
- Cordova开发总结(插件篇)
最近刚刚做完一个用Cordova开发了一款电子商务的应用.在选用Cordova前,我有考察过,国内的Appcan, Apicloud等等的解决方案.其实Appcan,ApiCloud的混合方案挺完整的 ...
- 简便的自动布局,对UIStackView的个人理解!
序言: 更新了很久的Linux,我怕朋友们都视觉疲劳了,今天就更新在学ios开发时候,对一些知识点的理解.希望各位会喜欢! 正文: UIStackView 类提供了一个高效的接口用于平铺一行或一列的视 ...
- 获取url据对路径写法
var _absUrl = (function () { var a; return function (url) { if (!a) a = document.createElement('a'); ...
- HTML5+NodeJs实现WebSocket即时通讯
声明:本文为原创文章,如需转载,请注明来源WAxes,谢谢! 最近都在学习HTML5,做canvas游戏之类的,发现HTML5中除了canvas这个强大的工具外,还有WebSocket也很值得注意.可 ...

 Previous post
Previous post