CS61B sp2018笔记 | Lists
Lists
1. IntLists
下面我们来一步一步的实现List类,首先你可以实现一个最简单的版本:
public class IntList {
public int first;
public IntList rest;
public IntList(int f, IntList r) {
first = f;
rest = r;
}
}
这样一个链表看起来特别丑陋,比如,我们要生成一个拥有5,10,15三个整数的链表,不得不这么做:
IntList L = new IntList(5, null);
L.rest = new IntList(10, null);
L.rest.rest = new IntList(15, null);
或者时这样:
IntList L = new IntList(15, null);
L = new IntList(10, L);
L = new IntList(5, L);
尽管看起来丑陋,使用起来也十分困难,不过我们还是要为它添加几个方法,首先是size方法:
/** Return the size of the list using... recursion! */
public int size() {
if (rest == null) {
return 1;
}
return 1 + this.rest.size();
}
/** Return the size of the list using no recursion! */
public int iterativeSize() {
IntList p = this;
int totalSize = 0;
while (p != null) {
totalSize += 1;
p = p.rest;
}
return totalSize;
}
随后的几个方法在Lab 2(Lab 2同时教了debug)中呈现,先是讲解方法分为Destructive和Non-Destructive,也就是是否改变参数的值。然后讲义部分给出了将一个链表所有数值平方的三种实现,分别使用了Destructive版本、Non-Destructive迭代版本和Non-Destructive递归版本(实现代码),然后让学生自己实现链表拼接的Destructive版本和Non-Destructive版本,下面是我的实现:
/**
* Returns a list consisting of the elements of A followed by the
* * elements of B. May modify items of A. Don't use 'new'.
*/
public static IntList dcatenate(IntList A, IntList B) {
//TODO: fill in method
IntList res = A;
while (A.rest != null) {
A = A.rest;
}
A.rest = B;
return res;
}
/**
* Returns a list consisting of the elements of A followed by the
* * elements of B. May NOT modify items of A. Use 'new'.
*/
public static IntList catenate(IntList A, IntList B) {
//TODO: fill in method
IntList res = new IntList(A.first, null);
IntList ptr = res;
A = A.rest;
while (A != null) {
ptr.rest = new IntList(A.first, null);
ptr = ptr.rest;
A = A.rest;
}
ptr.rest = B;
return res;
}
2. SLLists
理论上讲,IntList可以实现一个链表能够做的所有事,不过它难以使用,代码难以理解。最主要的是,如果一个程序员想使用它,就必须了解它复杂的递归思想,要手动写出next的指向,这会大大降低这种数据结构的使用率。
所以,在原有IntList的基础上,我们设计一种新的类SLLists(Single Linked Lists),并为它提供一系列的方法。
首先我们创建一个新的类IntNode:
public class IntNode {
public int item;
public IntNode next;
public IntNode(int i, IntNode n) {
item = i;
next = n;
}
}
除了名字不同以外,它好像和IntList没有任何区别,没错,我们还需要创建另外一个类SLList:
public class SLList {
public IntNode first;
public SLList(int x) {
first = new IntNode(x, null);
}
}
它将IntNode进行了封装,会使用者提供了更简洁的使用方法,当使用IntList和SLList时,你可以清楚的看出SLList优秀的地方:
IntList L1 = new IntList(5, null);
SLList L2 = new SLList(5);
SLList隐藏了IntNode中靠next取得的联系,使用者不必关心SLList内部如何实现,只知道如何用它来存储数据就足够了。我们再为SLList添加几个方法:
public class SLList {
public IntNode first;
public SLList(int x) {
first = new IntNode(x, null);
}
/** Adds an item to the front of the list. */
public void addFirst(int x) {
first = new IntNode(x, first);
}
/** Retrieves the front item from the list. */
public int getFirst() {
return first.item;
}
}
通过比较,你会发现SLList使用起来更简单了:
SLList L = new SLList(15);
L.addFirst(10);
L.addFirst(5);
int x = L.getFirst();
IntList L = new IntList(15, null);
L = new IntList(10, L);
L = new IntList(5, L);
int x = L.first;
再来比较一下它们的内部实现:
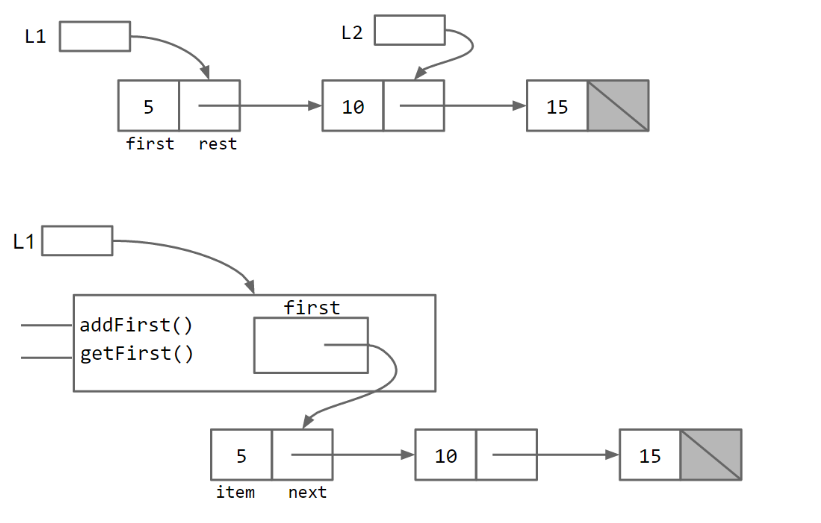
不过,如果使用者这样使用呢?
SLList L = new SLList(15);
L.addFirst(10);
L.first.next.next = L.first.next;

这将会导致死循环,所以我们要把first声明为私有变量,禁止使用者调用它,这样,上面的操作将会报错。不过这时,我们有两个.java文件,使用者每次使用都要导入这两个文件,所以,我们可以将IntNode写入SLList类中,这也称为Nested Classes。并且IntNode不会调用它以外的SLList中的值,所以我们把它声明为static类型,实现如下:
public class SLList {
public static class IntNode {
public int item;
public IntNode next;
public IntNode(int i, IntNode n) {
item = i;
next = n;
}
}
private IntNode first;
...
我们再为它添加size方法:
/** Returns the size of the list starting at IntNode p. */
private static int size(IntNode p) {
if (p.next == null) {
return 1;
}
return 1 + size(p.next);
}
public int size() {
return size(first);
}
然而,size方法内部使用了递归或者迭代,如果长度为1000的链表的size需要耗时2秒,那么计算长度为1,000,000的链表的size就可能会耗时2000秒。所以我们要将size方法的时间复杂度设计为常数,这里用到了储存(caching)的思想,我们添加一个size变量,并时刻跟踪改变它的值:
public class SLList {
... /* IntNode declaration omitted. */
private IntNode first;
private int size;
public SLList(int x) {
first = new IntNode(x, null);
size = 1;
}
public void addFirst(int x) {
first = new IntNode(x, first);
size += 1;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
...
}
这样,无论链表多么长,size方法都会很快的返回它的值。下面我们再仔细思考,如果一个链表为空,我们如何表示它?一种方法是为它设计空参构造函数:
public SLList() {
first = null;
size = 0;
}
不过它的addLst方法将变得很庞大,而且之后每添加一个类似的方法,我们都需要考虑链表为空的情况。
public void addLast(int x) {
size += 1;
if (first == null) {
first = new IntNode(x, null);
return;
}
IntNode p = first;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = new IntNode(x, null);
}
所以,在设计伊始,我们设计的模型要在根本上解决这个问题。这里的设计思想一开始可能会难以接受,不过渐渐你会发现它的优秀之处。我们采取的手段是添加一个空的node节点,称之为sentinel node。
于是,当我们通过SLList L = new SLList()实例化一个SLList对象时,它的内部将会变成这样:
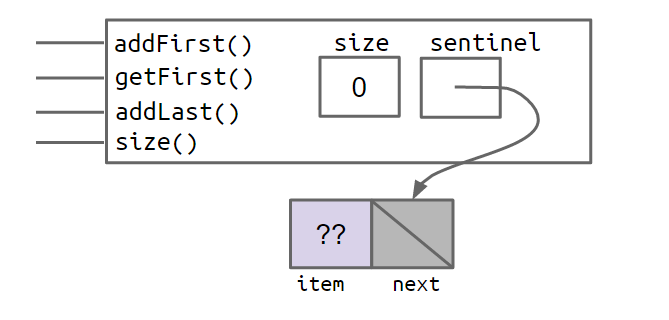
当为链表添加5,10,15三个元素时,它将变成这样:

这样,addLast方法就变得简洁易读多了。
public void addLast(int x) {
size += 1;
IntNode p = sentinel;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = new IntNode(x, null);
}
但是,addLst方法同样存在一个问题,就是链表的长度越长,它的执行时间也就越长。为了解决这一问题,我们同样可以使用储存的思想,为它添加一个last变量,时刻记录尾节点的位置。
public class SLList {
private IntNode sentinel;
private IntNode last;
private int size;
public void addLast(int x) {
last.next = new IntNode(x, null);
last = last.next;
size += 1;
}
...
}
它的内部就变成了下面这样:
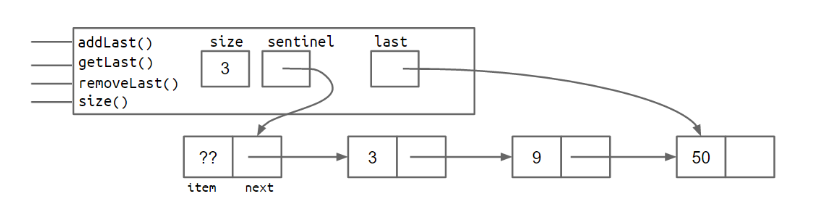
再考虑,如果我们要添加一个移除最后一个元素的removeLast方法,该如何实现?大致的思路就是获取到倒数第二个节点,然后将倒数第二个节点的next设为null,可是,如何获取到倒数第二个节点呢?
从sentinel向后遍历是不可能的了,那将使方法具有线性复杂度,其实,在现有的模型结构下很难实现,所以,我们不得在现有模型的基础上再次设计一种新的数据结构,也就是下面的DLList。
3. DLLists
这一次的改造更加彻底,我们在每一个IntNode中添加一个prev变量,也就是为整个链表添加了Back pointers :
public class IntNode {
public IntNode prev;
public int item;
public IntNode next;
}
之所以称之为DLList,其实是Doubly linked list,也就是双向链表,空链表和非空链表的内部结构如下所示:

目前,我们设计的DLList已经可以在头部和尾部进行快速的添加、获取和删除操作,唯一不足的地方就是last指针有时指向带有数据的节点,有时指向sentinel这种特殊的空接点,在以后的实现中可能会造成混乱。
所以,我们可以用以下两种方法来避免:
一种是在尾部增加一个sentinel空结点。
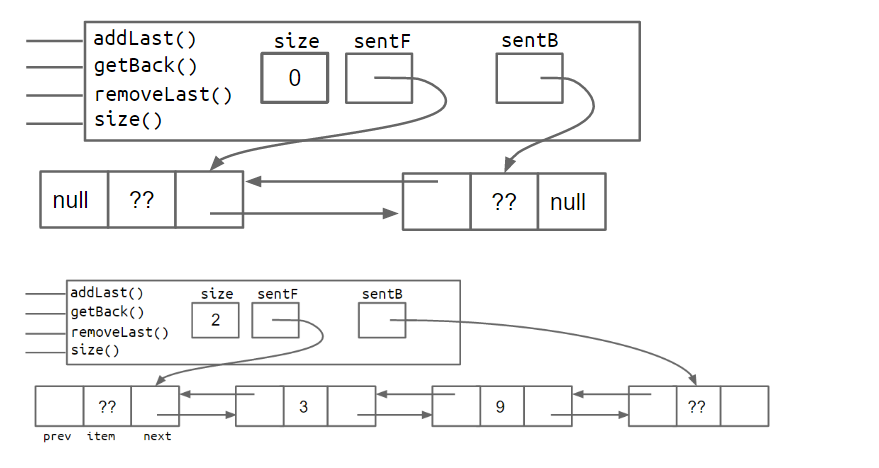
一种是采用
circle的的思想,让首尾指针指向同一个sentinel空结点。

这两种设计思想都很完美,在这里,cs61b让学生自己实现这种数据结构,并添加一定的方法,而且需要设计成泛型,也就是Project 1A的第一部分。
我采取的第二种实现版本,这里是我的实现,上一个目录有说明文件。
至此,我们已经设计并实现了一种健壮实用易扩展的数据结构,更重要的是在设计过程中发现问题、解决问题的设计思想。底层实现过程和设计思想,这也是cs61b最重视的部分。
CS61B sp2018笔记 | Lists的更多相关文章
- CSS 笔记二(Text/Fonts/Links/Lists)
CSS Text 1> Text Color used to set the color of the text 2> Text Alignment used to set the hor ...
- Python笔记 #02# Inner workings of lists
源:DataCamp datacamp 的 DAILY PRACTICE + 日常收集. List of lists Subset and conquer Slicing and dicing Li ...
- erlang的lists笔记
一般循环用在遍历列表的时候,erlang有lists模块直接支持遍历,不需要自己写尾递归遍历list lists:foreach 用来遍历列表,不保存结果,最后一次返回ok lists:map 遍历列 ...
- [笔记] Access Control Lists (ACL) 学习笔记汇总
一直不太明白Windows的ACL是怎么回事,还是静下心来看一手的MSDN吧. [翻译] Access Control Lists [翻译] How Access Check Works Modify ...
- 【leetcode刷题笔记】Merge k Sorted Lists
Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity. 题 ...
- Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees 阅读笔记
论文地址:https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2018/papers/08-oltpindexes1/pugh-skiplists-cacm1990.pdf ...
- java collections读书笔记(11) Lists
继续这个系列,好久没学习了,懒惰呀. Set接口,实际上是collection 类别中最简单的一个接口,因为它并没有比Collection 接口增加任何的内容,相对而言,大家可能更喜欢List接口和它 ...
- Numbers、Strings、Lists 笔记<一>
下一篇:流程控制<二> 阅读链接:官方Python3.7教程 废话:最近开始阅读python3.7文档,希望把容易混淆的知识记下来. 除法总是返回一个浮点数 >>> 8/ ...
- Leetcode 笔记 113 - Path Sum II
题目链接:Path Sum II | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each ...
随机推荐
- oracle_How to Recover Data (Without a Backup!)
How to Recover Data (Without a Backup!) It's the classic career-limiting maneuver(职业限制机动): accidenta ...
- MovieReview—The Foreigner (英伦对决)
The Foreigner's theme is revenge.The whole story is carried out in two dimensions:political struggle ...
- Let’s Encrypt 最近很火的免费SSL 使用教程
2015年10月份,微博上偶然看到Let's Encrypt 推出了beta版,作为一个曾经被https虐出血的码农来说,这无疑是一个重磅消息.并且在全站Https的大趋势下,Let's Encryp ...
- 树的直径的求法即相关证明【树形DP || DFS】
学习大佬:树的直径求法及证明 树的直径 定义: 一棵树的直径就是这棵树上存在的最长路径. 给定一棵树,树中每条边都有一个权值,树中两点之间的距离定义为连接两点的路径边权之和.树中最远的两个节点之间的距 ...
- Spring 声明式事务管理方式
声明式事务管理,基于AOP对目标代理,添加环绕通知,比编码方案优势,不具有侵入式,不需要修改原来的代码. 1.基于XML配置的声明式事务管理方案(案例) 接口Service public i ...
- Yii 判断是不是post方式提交的数据
一.在controller里判断提交是不是通过post方式: if(Yii::$app->request->isPost){ return true; }else{ return fals ...
- 九、IntelliJ IDEA 编译方式介绍及编译器的设置和选择
相对于 Eclipse 的实时自动编译,IntelliJ IDEA 的编译更加手动化,虽然 IntelliJ IDEA 也可以通过设置开启实时编译,但是太浪费资源了,因此不建议这样做.IntelliJ ...
- 远程桌面连接(连接服务器)报错Oracle修正
解决方案: 开始——运行——gpedit.msc——计算机配置——管理模版——系统——凭据分配——加密oracle修正——易受攻击 ok
- 【洛谷P3807】(模板)卢卡斯定理
卢卡斯定理 把n写成p进制a[n]a[n-1][n-2]…a[0],把m写成p进制b[n]b[n-1][n-2]…b[0],则C(n,m)与C(a[n],b[n])*C(a[n-1],b[n-1])* ...
- c#正则表达式最简demo
各个语言的正则表达式规则略有不同 项目中用到,所以将这个最简单的demo记录 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System. ...
