给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(5)-LinkedHashMap源码解析
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
/**
* The head of the doubly linked list.
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> header ; /**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access -order, <tt> false</tt> for insertion -order.
*
* @serial
*/
private final boolean accessOrder;
/**
* LinkedHashMap entry.
*/
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
// 双向链表的上一个节点before和下一个节点after
Entry<K,V> before, after ; // 构造方法直接调用父类HashMap的构造方法(super)
Entry( int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
} /**
* 从链表中删除当前节点的方法
*/
private void remove() {
// 改变当前节点前后两个节点的引用关系,当前节点没有被引用后,gc可以回收
// 将上一个节点的after指向下一个节点
before.after = after;
// 将下一个节点的before指向前一个节点
after.before = before;
} /**
* 在指定的节点前加入一个节点到链表中(也就是加入到链表尾部)
*/
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) {
// 下面改变自己对前后的指向
// 将当前节点的after指向给定的节点(加入到existingEntry前面嘛)
after = existingEntry;
// 将当前节点的before指向给定节点的上一个节点
before = existingEntry.before ; // 下面改变前后最自己的指向
// 上一个节点的after指向自己
before.after = this;
// 下一个几点的before指向自己
after.before = this;
} // 当向Map中获取查询元素或修改元素(put相同key)的时候调用这个方法
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
// 如果accessOrder为true,也就是使用最近较少使用顺序
if (lm.accessOrder ) {
lm. modCount++;
// 先删除,再添加,也就相当于移动了
// 删除当前元素
remove();
// 将当前元素加入到header前(也就是链表尾部)
addBefore(lm. header);
}
} // 当从Map中删除元素的时候调动这个方法
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
remove();
}
}
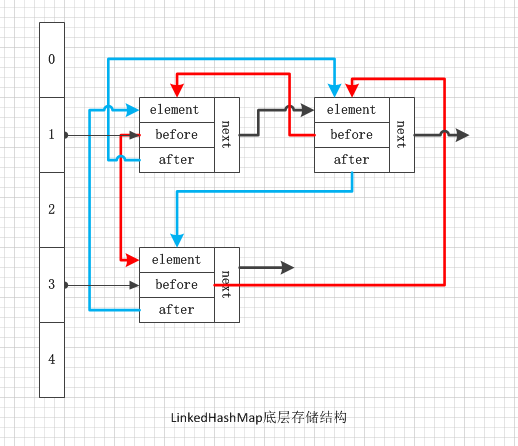
可以看到Entry继承了HashMap中的Entry,但是LinkedHashMap中的Entry多了两个属性指向上一个节点的before和指向下一个节点的after,也正是这两个属性组成了一个双向链表。等等。。。Entry还有一个继承下来的next属性,这个next是单向链表中用来指向下一个节点的,怎么回事嘛,怎么又是单向链表又是双向链表呢,都要晕了对不对,其实想的没错,这里的节点即是Hash表中的单向链表中的一个节点,它又是LinkedHashMap维护的双向链表中的一个节点,是不是瞬间觉得高大上了。图解一下吧(不要告诉我图好乱,我看不懂。。。)
/**
* 构造一个指定初始容量和加载因子的LinkedHashMap,默认accessOrder为false
*/
public LinkedHashMap( int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* 构造一个指定初始容量的LinkedHashMap,默认accessOrder为false
*/
public LinkedHashMap( int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* 构造一个使用默认初始容量(16)和默认加载因子(0.75)的LinkedHashMap,默认accessOrder为false
*/
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* 构造一个指定map的LinkedHashMap,所创建LinkedHashMap使用默认加载因子(0.75)和足以容纳指定map的初始容量,默认accessOrder为false 。
*/
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super(m);
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* 构造一个指定初始容量、加载因子和accessOrder的LinkedHashMap
*/
public LinkedHashMap( int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap( int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor); // Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1; this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);
table = new Entry[capacity];
init();
} /**
* Initialization hook for subclasses. This method is called
* in all constructors and pseudo -constructors (clone, readObject)
* after HashMap has been initialized but before any entries have
* been inserted. (In the absence of this method, readObject would
* require explicit knowledge of subclasses.)
*/
void init() {
哦,明白了,init()在HashMap中是一个空方法,也就是给子类留的一个回调函数,ok,我们来看下LinkedHashMap对init()方法的实现吧。
/**
* Called by superclass constructors and pseudoconstructors (clone,
* readObject) before any entries are inserted into the map. Initializes
* the chain.
*/
void init() {
// 初始化话header,将hash设置为-1,key、value、next设置为null
header = new Entry<K,V>(-1, null, null, null);
// header的before和after都指向header自身
header.before = header. after = header ;
/**
* This override alters behavior of superclass put method. It causes newly
* allocated entry to get inserted at the end of the linked list and
* removes the eldest entry if appropriate.
*/
void addEntry( int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 调用createEntry方法创建一个新的节点
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); // Remove eldest entry if instructed, else grow capacity if appropriate
// 取出header后的第一个节点(因为header不保存数据,所以取header后的第一个节点)
Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after ;
// 判断是容量不够了是要删除第一个节点还是需要扩容
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
// 删除第一个节点(可实现FIFO、LRU策略的Cache)
removeEntryForKey(eldest. key);
} else {
// 和HashMap一样进行扩容
if (size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length );
}
} /**
* This override differs from addEntry in that it doesn't resize the
* table or remove the eldest entry.
*/
void createEntry( int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 下面三行代码的逻辑是,创建一个新节点放到单向链表的头部
// 取出数组bucketIndex位置的旧节点
HashMap.Entry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex];
// 创建一个新的节点,并将next指向旧节点
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, old);
// 将新创建的节点放到数组的bucketIndex位置
table[bucketIndex] = e; // 维护双向链表,将新节点添加在双向链表header前面(链表尾部)
e.addBefore( header);
// 计数器size加1
size++;
} /**
* 默认返回false,也就是不会进行元素删除了。如果想实现cache功能,只需重写该方法
*/
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)getEntry(key);
if (e == null)
return null;
e.recordAccess( this);
return e.value ;
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value.
*
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt> true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
// Overridden to take advantage of faster iterator
// 遍历双向链表,查找指定的value
if (value==null) {
for (Entry e = header .after; e != header; e = e.after )
if (e.value ==null)
return true;
} else {
for (Entry e = header .after; e != header; e = e.after )
if (value.equals(e.value ))
return true;
}
return false;
}
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map; public class MyLocalCache extends LinkedHashMap<String, Object> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7182816356402068265L; private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_CAPACITY = 1024; private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; private int maxCapacity; public enum Policy {
FIFO, LRU
} public MyLocalCache(Policy policy) {
super(DEFAULT_MAX_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, Policy.LRU .equals(policy));
this.maxCapacity = DEFAULT_MAX_CAPACITY;
} public MyLocalCache(int capacity, Policy policy) {
super(capacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, Policy. LRU.equals(policy));
this.maxCapacity = capacity;
} @Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<String, Object> eldest) {
return this.size() > maxCapacity;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLocalCache cache = new MyLocalCache(5, Policy.LRU);
cache.put( "k1", "v1" );
cache.put( "k2", "v2" );
cache.put( "k3", "v3" );
cache.put( "k4", "v4" );
cache.put( "k5", "v5" );
cache.put( "k6", "v6" ); System. out.println("size=" + cache.size()); System. out.println("----------------------" );
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : cache.entrySet()) {
System. out.println(entry.getValue());
} System. out.println("----------------------" ); System. out.println("k3=" + cache.get("k3")); System. out.println("----------------------" );
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : cache.entrySet()) {
System. out.println(entry.getValue());
}
} }
参见:
给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(5)-LinkedHashMap源码解析的更多相关文章
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(7)-TreeMap源码解析
TreeMap是基于红黑树结构实现的一种Map,要分析TreeMap的实现首先就要对红黑树有所了解. 要了解什么是红黑树,就要了解它的存在主要是为了解决什么问题,对比其他数据结构比如数组,链 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(6)-HashSet源码解析&Map迭代器
今天的主角是HashSet,Set是什么东东,当然也是一种java容器了. 现在再看到Hash心底里有没有会心一笑呢,这里不再赘述hash的概念原理等一大堆东西了(不懂得需要先回去看下Has ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(4)-HashMap源码解析
前面了解了jdk容器中的两种List,回忆一下怎么从list中取值(也就是做查询),是通过index索引位置对不对,由于存入list的元素时安装插入顺序存储的,所以index索引也就是插入的次序. M ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(12)-PriorityQueue源码解析
PriorityQueue是一种什么样的容器呢?看过前面的几个jdk容器分析的话,看到Queue这个单词你一定会,哦~这是一种队列.是的,PriorityQueue是一种队列,但是它又是一种什么样的队 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(2)-LinkedList源码解析
LinkedList是基于链表结构的一种List,在分析LinkedList源码前有必要对链表结构进行说明. 1.链表的概念 链表是由一系列非连续的节点组成的存储结构,简单分下类的话,链 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(1)-ArrayList源码解析
工作中经常听到别人讲“容器”,各种各样的容器,话说到底什么是容器,通俗的讲“容器就是用来装东西的器皿,比如:水桶就是用来盛水的,水桶就是一个容器.” ok,在我们写程序的时候常常要对大量的对象进行管理 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(13)-总结篇之Java集合与数据结构
是的,这篇blogs是一个总结篇,最开始的时候我提到过,对于java容器或集合的学习也可以看做是对数据结构的学习与应用.在前面我们分析了很多的java容器,也接触了好多种常用的数据结构,今天 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(11)-Queue之ArrayDeque源码解析
前面讲了Stack是一种先进后出的数据结构:栈,那么对应的Queue是一种先进先出(First In First Out)的数据结构:队列. 对比一下Stack,Queue是一种先进先出的容 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(10)-Stack&Vector源码解析
前面我们已经接触过几种数据结构了,有数组.链表.Hash表.红黑树(二叉查询树),今天再来看另外一种数据结构:栈. 什么是栈呢,我就不找它具体的定义了,直接举个例子,栈就相当于一个很窄的木桶 ...
随机推荐
- Dapper基础用法
假如你喜欢原生的Sql语句,又喜欢ORM的简单,那你一定会喜欢上Dapper这款ROM.点击下载Dapper的优势:1,Dapper是一个轻型的ORM类.代码就一个SqlMapper.cs文件,编译后 ...
- HDU 4891 The Great Pan (模拟)
The Great Pan 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/123554#problem/D Description As a programm ...
- Spring Filter components in auto scanning
In this Spring auto component scanning tutorial, you learn about how to make Spring auto scan your c ...
- CentOS查看系统信息-CentOS查看命令
一:查看cpu more /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" grep "model name" /proc/cpuinfo 如 ...
- HDU 1068 Girls and Boys (二分图最大独立集)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1068 有n个同学,格式ni:(m) n1 n2 n3表示同学ni有缘与n1,n2,n3成为情侣,求集合 ...
- Java学习笔记(六):面向对象、接口和抽象类
类和对象 Java是一门面向对象的语言,下面我们来了解一下Java中的面向对象. 方法和重载 Java中的方法格式如下: 访问修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数){ 方法主体 } Java的方法支持重载 ...
- poj 1191 棋盘分割 动态规划
棋盘分割 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 11457 Accepted: 4032 Description ...
- .Net 揭密--JIT怎样运行你的代码
方法调用: 第一部分 (普通调用) 译者:我们都知道.NET托管代码如C#.VB.NET写成的代码,都是先被编译成中间语言(IL,Intermediate Language,在运行时,再由即时编译器( ...
- 存储过程[st_MES_RptInspectShipment]
USE [ChangHong_612]GO/****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[st_MES_RptInspectShipment] Script Date: ...
- FOR XML PATH的用法
USE [ChangHongWMS612]GO/****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[st_WMS_SelStockInBillList] Script Date ...
