Core Java Volume I — 3.3. Data Types
3.3. Data Types
Java is a strongly typed language(强类型语音). This means that every variable must have a declared type(每个变量都必须声明类型). There are eight primitive types in Java(Java有8种原始类型). Four of them are integer types; two are floatingpoint number types; one is the character type char, used for code units in the Unicode encoding scheme; and one is a boolean type for truth values.
3.3.1. Integer Types
The integer types are for numbers without fractional parts(小数部分). Negative values are allowed. Java provides the four integer types shown in Table 3.1.

In most situations, the int type is the most practical. If you want to represent the number of inhabitants of our planet, you’ll need to resort to a long. The byte and short types are mainly intended for specialized applications, such as low-level file handling, or for large arrays when storage space is at a premium.
Under Java, the ranges of the integer types do not depend on the machine on which you will be running the Java code(整型的取值范围与机器无关). This alleviates a major pain for the programmer who wants to move software from one platform to another, or even between operating systems on the same platform. In contrast, C and C++ programs use the most efficient integer type for each processor. As a result, a C program that runs well on a 32-bit processor may exhibit integer overflow on a 16-bit system. Since Java programs must run with the same results on all machines, the ranges for the various types are fixed.
Long integer numbers have a suffix L(长整型以L后缀表示) (for example, 4000000000L). Hexadecimal numbers have a prefix 0x (for example, 0xCAFE). Octal numbers have a prefix 0. For example, 010 is 8. Naturally, this can be confusing, so we recommend against the use of octal constants.
Starting with Java 7, you can write numbers in binary, with a prefix 0b(从Java7开始可以以0b前缀表示二进制). For example, 0b1001 is 9. Also starting with Java 7, you can add underscores to number literals(从Java7开始可以在数字之间加上下划线), such as 1_000_000 (or 0b1111_0100_0010_0100_0000) to denote one million. The underscores are for human eyes only. The Java compiler simply removes them.
3.3.2. Floating-Point Types
The floating-point types denote numbers with fractional parts. The two floating-point types are shown in Table 3.2.
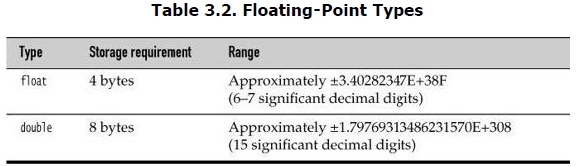
The name double refers to the fact that these numbers have twice the precision(double的精度是float的两倍) of the float type. (Some people call these double-precision numbers.) Here, the type to choose in most applications is double. The limited precision of float is simply not sufficient for many situations. Seven significant (decimal) digits may be enough to precisely express your annual salary in dollars and cents, but it won’t be enough for your company president’s salary. It only makes sense to use float in the rare situations where the slightly faster processing of singleprecision numbers is important, or when you need to store a large number of them.
Numbers of type float have a suffix F(float类型以F为后缀) (for example, 3.14F). Floating-point numbers without an F suffix (such as 3.14) are always considered to be of type double(没有F后缀则默认为double类型,D后缀为可选的). You can optionally supply the D suffix (for example, 3.14D).
All floating-point computations follow the IEEE 754 specification. In particular, there are three special floating-point values to denote overflows and errors:
- Positive infinity
- Negative infinity
- NaN (not a number)
For example, the result of dividing a positive number by 0 is positive infinity. Computing 0/0 or the square root of a negative number yields NaN.
3.3.3. The char Type
The char type is used to describe individual characters(char类型用于描述单个字符). Most commonly, these will be character constants. For example, 'A' is a character constant with value 65. It is different from "A", a string containing a single character. Unicode code units can be expressed as hexadecimal values that run from \u0000 to \uFFFF. For example, \u2122 is the trademark symbol and \u03C0 is the Greek letter pi.
Besides the \u escape sequences(转义符) that indicate the encoding of Unicode code units, there are several escape sequences for special characters, as shown in Table 3.3. You can use these escape sequences inside quoted character constants and strings, such as '\u2122' or "Hello\n". The \u escape sequence (but none of the other escape sequences) can even be used outside quoted character constants and strings. For example,
public static void main(String\u005B\u005D args)
is perfectly legal—\u005B and \u005D are the encodings for [ and ].

To fully understand the char type, you have to know about the Unicode encoding scheme. Unicode was invented to overcome the limitations of traditional character encoding schemes. Before Unicode, there were many different standards: ASCII in the United States, ISO 8859-1
for Western European languages, KOI-8 for Russian, GB18030 and BIG-5 for Chinese, and so on. This causes two problems. A particular code value corresponds to different letters in the different encoding schemes. Moreover, the encodings for languages with large character sets have variable length: Some common characters are encoded as single bytes, others require two or more bytes.
Unicode was designed to solve these problems. When the unification effort started in the 1980s, a fixed 2-byte code was more than sufficient to encode all characters used in all languages in the world, with room to spare for future expansion—or so everyone thought at the time. In 1991, Unicode 1.0 was released, using slightly less than half of the available 65,536 code values. Java was designed from the ground up to use 16-bit Unicode characters, which was a major advance over other programming languages that used 8-bit characters.
Unfortunately, over time, the inevitable happened. Unicode grew beyond 65,536 characters, primarily due to the addition of a very large set of ideographs used for Chinese, Japanese, and Korean. Now, the 16-bit char type is insufficient to describe all Unicode characters.
We need a bit of terminology to explain how this problem is resolved in Java, beginning with Java SE 5.0. A code point is a code value that is associated with a character in an encoding scheme. In the Unicode standard, code points are written in hexadecimal and prefixed with U+, such as U+0041 for the code point of the Latin letter A. Unicode has code points that are grouped into 17 code planes. The first code plane, called the basic multilingual plane, consists of the “classic” Unicode characters with code points U+0000 to U+FFFF. Sixteen additional planes, with code points U+10000 to U+10FFFF, hold the supplementary characters.
The UTF-16 encoding represents all Unicode code points in a variable-length code. The characters in the basic multilingual plane are represented as 16-bit values, called code units. The supplementary characters are encoded as consecutive pairs of code units. Each of the values in such an encoding pair falls into a range of 2048 unused values of the basic multilingual plane, called the surrogates area (U+D800 to U+DBFF for the first code unit, U+DC00 to U+DFFF for the second code unit). This is rather clever, because you can immediately tell whether a code unit encodes a single character or it is the first or second part of a supplementary character. For example, the mathematical symbol for the set of integers ZZ has code point U+1D56B and is encoded by the two code units U+D835 and U+DD6B. (See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UTF-16 for a description of the encoding algorithm.)
In Java, the char type describes a code unit in the UTF-16 encoding.
Our strong recommendation is not to use the char type in your programs unless you are actually manipulating UTF-16 code units. You are almost always better off treating strings as abstract data types.
3.3.4. The boolean Type
The boolean type has two values, false and true(boolean类型有两个值分别为false和true). It is used for evaluating logical conditions. You cannot convert between integers and boolean values.
Core Java Volume I — 3.3. Data Types的更多相关文章
- Core Java Volume I — 1.2. The Java "White Paper" Buzzwords
1.2. The Java "White Paper" BuzzwordsThe authors of Java have written an influential White ...
- Core Java Volume I — 4.7. Packages
4.7. PackagesJava allows you to group classes in a collection called a package. Packages are conveni ...
- Core Java Volume I — 5.1. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses
5.1. Classes, Superclasses, and SubclassesLet's return to the Employee class that we discussed in th ...
- Core Java Volume I — 4.10. Class Design Hints
4.10. Class Design HintsWithout trying to be comprehensive or tedious, we want to end this chapter w ...
- Core Java Volume I — 4.6. Object Construction
4.6. Object ConstructionYou have seen how to write simple constructors that define the initial state ...
- Core Java Volume I — 3.10. Arrays
3.10. ArraysAn array is a data structure that stores a collection of values of the same type. You ac ...
- Core Java Volume I — 4.5. Method Parameters
4.5. Method ParametersLet us review the computer science terms that describe how parameters can be p ...
- Core Java Volume I — 4.1. Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
4.1. Introduction to Object-Oriented ProgrammingObject-oriented programming, or OOP for short, is th ...
- Core Java Volume I — 3.8. Control Flow
3.8. Control FlowJava, like any programming language, supports both conditional statements and loops ...
随机推荐
- spring mvc读取url变量
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}/{name}", method=RequestMethod.GET) public ModelAndView getUrl ...
- 互斥锁pthread_mutex_t的使用(转载)
1. 互斥锁创建 有两种方法创建互斥锁,静态方式和动态方式.POSIX定义了一个宏PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER来静态初始化互斥锁,方法如下: pthread_mut ...
- 使用ASP.Net WebAPI构建REST服务(六)——Self-Host
Asp.Net WebAPI生成的是一个程序集,并不是独立的进程,因此,要运行的时候必须将其承载在相应的宿主上,一般比较常见的是IIS承载.很多时候,我们为了简化部署或者功能集成,需要将其承载到独立的 ...
- 在phpmyadmin中执行sql语句出现的错误:Unknown storage engine 'InnoDB'
在phpmyadmin中执行sql语句出现的错误:Unknown storage engine 'InnoDB' 解决方法:解决方法: 1.关闭MySQL数据库 2 ...
- redis OK
http://redis.readthedocs.org/en/2.4/set.html1, client.end();redis.expire(key,10) ,lsize,llen APPEND ...
- [转载]android的消息处理机制(图+源码分析)——Looper,Handler,Message
2013-12-18 14:17:33 转载自: http://www.cnblogs.com/codingmyworld/archive/2011/09/14/2174255.html 请跳转到转载 ...
- SO从 \u 这样的字符串 构建对象
ShowMessage(SO('\u4F18\u8D28\u670D\u52A112').AsString); 正确 得到 优质服务12 ShowMessage(so( 个数字,后面的中文未能解析出.
- RPI学习--webcam_用fswebcam抓取图片
若 ls /dev 下没有video0,可以参考http://www.cnblogs.com/skynext/p/3644873.html,更新firmware 1,安装fswebcam: sudo ...
- 在shell脚本中进行条件控制以及使用循环
转载请标明:http://www.cnblogs.com/winifred-tang94/ if条件语句语法: if [ 条件表达式 ] then 代码 else 代码 fi 注意:在上面的if条件语 ...
- 关于Xcode调试的帖子,感觉不错,转来看看
http://www.raywenderlich.com/10209/my-app-crashed-now-what-part-1 http://www.raywenderlich.com/10505 ...
