Kilani and the Game CodeForces - 1105D (bfs)
Kilani is playing a game with his friends. This game can be represented as a grid of size n×mn×m, where each cell is either empty or blocked, and every player has one or more castles in some cells (there are no two castles in one cell).
The game is played in rounds. In each round players expand turn by turn: firstly, the first player expands, then the second player expands and so on. The expansion happens as follows: for each castle the player owns now, he tries to expand into the empty cells nearby. The player ii can expand from a cell with his castle to the empty cell if it's possible to reach it in at most sisi (where sisi is player's expansion speed) moves to the left, up, right or down without going through blocked cells or cells occupied by some other player's castle. The player examines the set of cells he can expand to and builds a castle in each of them at once. The turned is passed to the next player after that.
The game ends when no player can make a move. You are given the game field and speed of the expansion for each player. Kilani wants to know for each player how many cells he will control (have a castle their) after the game ends.
Input
The first line contains three integers nn, mm and pp (1≤n,m≤10001≤n,m≤1000, 1≤p≤91≤p≤9) — the size of the grid and the number of players.
The second line contains pp integers sisi (1≤s≤1091≤s≤109) — the speed of the expansion for every player.
The following nn lines describe the game grid. Each of them consists of mm symbols, where '.' denotes an empty cell, '#' denotes a blocked cell and digit xx (1≤x≤p1≤x≤p) denotes the castle owned by player xx.
It is guaranteed, that each player has at least one castle on the grid.
Output
Print pp integers — the number of cells controlled by each player after the game ends.
Examples
3 3 2
1 1
1..
...
..2
6 3
3 4 4
1 1 1 1
....
#...
1234
1 4 3 3
Note
The picture below show the game before it started, the game after the first round and game after the second round in the first example:
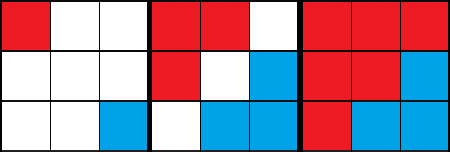
In the second example, the first player is "blocked" so he will not capture new cells for the entire game. All other player will expand up during the first two rounds and in the third round only the second player will move to the left.
题意:棋盘上有障碍物‘#’和‘.’和数字,每个数字有一个可以扩张的速度,数字一次扩张( 上下左右,可以转弯),一个'.'被占领了就不可以被占了,问最后的棋盘上的最终的数字的个数是多少
题解:差不多就是暴力bfs就可以了,记录一下什么先跑什么后跑就好了,一开始题意理解错了以为不可以转弯。
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdlib>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1e3+; int n,m,t;
struct node{
int x,y,t;
};
int dx[]={,-,,};
int dy[]={,,,-};
int s[];
queue<node>q1[];
queue<node>q2[];
char map[maxn][maxn];
int vis[maxn][maxn]; int expand(int p)
{
int newx = ;
while(!q2[p].empty())
{
node x = q2[p].front();
q2[p].pop();
x.t = ; //此句话要与后面有句话连起来看,就是每次放进 q2[i] 队列的都要将步数为0
q1[p].push(x);
}
while(!q1[p].empty())
{
node x = q1[p].front();
q1[p].pop();
if (x.t == s[p])
{
q2[p].push(x); //如果已经满 s[p] 步,就将它重新放进 q1 的队列,并将步数归0
continue;
} for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
int xx = x.x + dx[i];
int yy = x.y + dy[i];
if(xx< || yy< || xx>n || yy>m || map[xx][yy]=='#' || vis[xx][yy] != || x.t+>s[p])
continue;
newx++;
q1[p].push(node{xx,yy,x.t+}); //步数+1
vis[xx][yy] = p; //记录棋盘
}
}
if(newx >= )
return ;
else
return ;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&t);
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
scanf("%d",&s[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j = ; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] >= '' && map[i][j] <= '')
{
vis[i][j] = map[i][j] - '';
q2[vis[i][j]].push(node{i,j,});
}
}
} while(true)
{
int flag = ;
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
flag += expand(i);
if(flag == )
break;
}
int count[];
memset(count,,sizeof count);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
count[vis[i][j]]++;
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
printf("%d ",count[i]);
}
/*
Input
3 3 2
1 1
1..
...
..2
Output
6 3
Input
3 4 4
1 1 1 1
....
#...
1234
Output
1 4 3 3
*/
Kilani and the Game CodeForces - 1105D (bfs)的更多相关文章
- Amr and Chemistry CodeForces 558C(BFS)
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/558/C 分析:将每一个数在给定范围内(10^5)可变成的数(*2或者/2)都按照广搜的方式生成访问一遍,标记上访问 ...
- codeforces #Round354-div2-D(BFS)
题目链接:题目链接 题意:一个n*m的区域,每个格子都有上下左右四个门,相邻的两个格子A可以通向B当且仅当A对B的门和B对A的门都打开,问从起点S到终点T需要的最短时间 #include<bit ...
- Fire Again CodeForces - 35C (BFS)
After a terrifying forest fire in Berland a forest rebirth program was carried out. Due to it N rows ...
- Statues CodeForces - 129C(bfs)
In this task Anna and Maria play a game with a very unpleasant rival. Anna and Maria are in the oppo ...
- 深搜(DFS)广搜(BFS)详解
图的深搜与广搜 一.介绍: p { margin-bottom: 0.25cm; direction: ltr; line-height: 120%; text-align: justify; orp ...
- 【算法导论】图的广度优先搜索遍历(BFS)
图的存储方法:邻接矩阵.邻接表 例如:有一个图如下所示(该图也作为程序的实例): 则上图用邻接矩阵可以表示为: 用邻接表可以表示如下: 邻接矩阵可以很容易的用二维数组表示,下面主要看看怎样构成邻接表: ...
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)与广度优先搜索(BFS)的Java实现
1.基础部分 在图中实现最基本的操作之一就是搜索从一个指定顶点可以到达哪些顶点,比如从武汉出发的高铁可以到达哪些城市,一些城市可以直达,一些城市不能直达.现在有一份全国高铁模拟图,要从某个城市(顶点) ...
- 【BZOJ5492】[HNOI2019]校园旅行(bfs)
[HNOI2019]校园旅行(bfs) 题面 洛谷 题解 首先考虑暴力做法怎么做. 把所有可行的二元组全部丢进队列里,每次两个点分别向两侧拓展一个同色点,然后更新可行的情况. 这样子的复杂度是\(O( ...
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)
深度优先搜索(DFS) 广度优先搜索(BFS) 1.介绍 广度优先搜索(BFS)是图的另一种遍历方式,与DFS相对,是以广度优先进行搜索.简言之就是先访问图的顶点,然后广度优先访问其邻接点,然后再依次 ...
随机推荐
- C#常用控件的属性以及方法(转载)
-----以前看别人的,保存了下来,但是忘了源处,望见谅. C#常用控件属性及方法介绍 目录 1.窗体(Form) 2.Label (标签)控件 3.TextBox(文本框)控件 4.RichText ...
- asp.net MVC 4.0 Model元数据回顾——HtmlHelper的ModelMetadata
模板方法包括Display/DisplayFor.Editor/EditorFor.DisplayForModel/EditForModel提供辅助生成Html的模型元数据信息 public stat ...
- 关于Arduino项目的构建思想-转自openbook开源杂志
- RING0到RING3
在前一篇文章里面,我们将了CPU保护模式中的几种特权RING0,RING1,RING2,RING3!操作系统通常运行在RING0,应用程序通常运行在RING3. CPU如何从RING0到RING3 先 ...
- fish 与oh-my-fish 的安装
fish 相对于 自带的shell优势很大,最近在研究使用中. 安装教程如下: sudo apt-get install fish oh-my-fish是github上开源项目,使得fish的使用更加 ...
- sql2012,返回数据多时不走索引
当数据达到一定值时,都会走表扫描旧版如SQL2005时就有计算选择性的比例为 满足条件的行数/总行数<=0.7181,会走索引,其它会走表扫描有兴趣可以自己去不同版本中去测试 Roy Wu(吴熹 ...
- mybatis-映射器的CRUD
设计步骤:model.mapper.dao.service.junit单元测试.log4j日志 项目和之前的一样在此只是创建了test和修改了mapper 1.修改映射 1.1修改接口 package ...
- Head First HTML与CSS阅读笔记(二)
上一篇Head First HTML与CSS阅读笔记(一)中总结了<Head First HTML与CSS>前9章的知识点,本篇则会将剩下的10~15章内容进行总结,具体如下所示. div ...
- 远程链接mongoDB robomongo
墙裂推荐一个软件robomongo 下载地址:https://robomongo.org/download 最初不用这个软件的时候需要shell链接mongoDB,折腾了半天结果版本不匹配 用robo ...
- An incomplete guide to LaTex
LATEX入门与提高.陈志杰数理学院喜闻乐见的电子书.这本电子书由于是图片版本,所以无法使用搜索功能,幸亏目录详细. LaTeX Beginner's Guide.latex使用者都是从模版开始学习, ...
