Show All Running Processes in Linux
ps由于历史的原因,所以很奇特,有些命令必须加"-",比如:
ps A
上面的写法是错误的
********* simple selection ********* ********* selection by list *********
-A all processes -C by command name
-N negate selection -G by real group ID (supports names)
-a all w/ tty except session leaders -U by real user ID (supports names)
-d all except session leaders -g by session OR by effective group name
-e all processes -p by process ID
T all processes on this terminal -s processes in the sessions given
a all w/ tty, including other users -t by tty
g OBSOLETE -- DO NOT USE -u by effective user ID (supports names)
r only running processes U processes for specified users
x processes w/o controlling ttys t by tty
*********** output format ********** *********** long options ***********
-o,o user-defined -f full --Group --User --pid --cols --ppid
-j,j job control s signal --group --user --sid --rows --info
-O,O preloaded -o v virtual memory --cumulative --format --deselect
-l,l long u user-oriented --sort --tty --forest --version
-F extra full X registers --heading --no-heading --context
********* misc options *********
-V,V show version L list format codes f ASCII art forest
-m,m,-L,-T,H threads S children in sum -y change -l format
-M,Z security data c true command name -c scheduling class
-w,w wide output n numeric WCHAN,UID -H process hierarchy
[test@localhost smplayer]$ ps A
ERROR: Unsupported option (BSD syntax)
********* simple selection ********* ********* selection by list *********
-A all processes -C by command name
-N negate selection -G by real group ID (supports names)
-a all w/ tty except session leaders -U by real user ID (supports names)
-d all except session leaders -g by session OR by effective group name
-e all processes -p by process ID
T all processes on this terminal -s processes in the sessions given
a all w/ tty, including other users -t by tty
g OBSOLETE -- DO NOT USE -u by effective user ID (supports names)
r only running processes U processes for specified users
x processes w/o controlling ttys t by tty
*********** output format ********** *********** long options ***********
-o,o user-defined -f full --Group --User --pid --cols --ppid
-j,j job control s signal --group --user --sid --rows --info
-O,O preloaded -o v virtual memory --cumulative --format --deselect
-l,l long u user-oriented --sort --tty --forest --version
-F extra full X registers --heading --no-heading --context
********* misc options *********
-V,V show version L list format codes f ASCII art forest
-m,m,-L,-T,H threads S children in sum -y change -l format
-M,Z security data c true command name -c scheduling class
-w,w wide output n numeric WCHAN,UID -H process hierarchy
How do I see all running process in Linux operating systems using command line or GUI options?
You need to use the ps
command. It provide information about the currently running processes,
including their process identification numbers (PIDs). Both Linux and
UNIX support the ps command to display information about all
running process. The ps command gives a snapshot of the current
processes. If you want a repetitive update of this status, use top,
atop, and/or htop command as described below.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Easy (rss) |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | ps/top/htop |
| Estimated completion time | 5 minutes |
Apart from ps command, you can also use the following commands to display info about processes on Linux:
- top command : Display and update sorted information about processes.
- atop : Advanced System & Process Monitor.
- htop : Interactive process viewer.
The ps command
Type the following ps command to display all running process:
# ps aux | less
Where,
- -A: select all processes
- a: select all processes on a terminal, including those of other users
- x: select processes without controlling ttys
Task: see every process on the system
# ps -A
# ps -e
上面两条命令是一样的
Task: See every process except those running as root
# ps -U root -u root -N
[test@localhost Documents]$ ps -U test|grep su
pts/ :: su
pts/ :: su
[test@localhost Documents]$ ps -u test|grep su
Task: See process run by user vivek
# ps -u vivek
Task: top command
The top program provides a dynamic real-time view of a running system. Type the top at command prompt:
# top
Output:
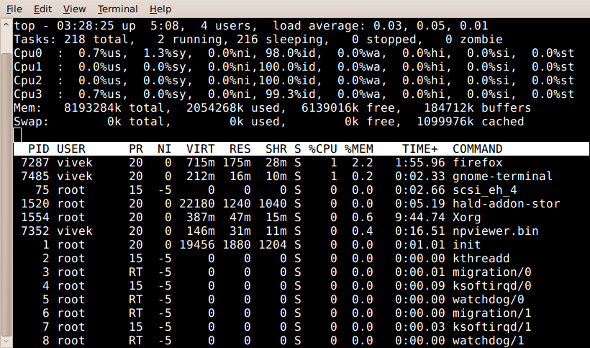
Fig.01: top command: Display Linux Tasks
To quit press q, for help press h.
Task: display a tree of processes
pstree shows running processes as a tree. The tree is rooted at either pid or init if pid is omitted. If a user name is specified, all process trees rooted at processes owned by that user are shown.
$ pstree
Sample outputs:
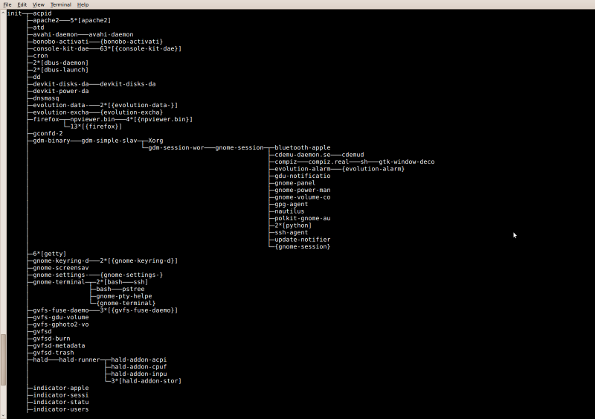
Fig.02: pstree - Display a tree of processes
Task: Print a process tree using ps
# ps -ejH
# ps axjf
Task: Get info about threads
Type the following command:
# ps -ejH
# ps axjf
Task: Get info about threads
Type the following command:
Show All Running Processes in Linux的更多相关文章
- Show tree of processes in linux
pstree(1): tree of processes - Linux man pagehttps://linux.die.net/man/1/pstree How to view process ...
- What are long running processes?
转自:https://blog.bernd-ruecker.com/what-are-long-running-processes-b3ee769f0a27 Some communities have ...
- 路由器逆向分析------Running Debian MIPS Linux in QEMU
本文博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qq1084283172/article/details/70176583 下面的文章内容主要参考英文博客<Running Debian ...
- [原]Threads vs Processes in Linux 分析
Linux中thread (light-weighted process) 跟process在實作上幾乎一樣. 最大的差異來自於,thread 會分享 virtual memory address s ...
- check running processes in Ubuntu
Check processes If you want to see what processes are running use the command ps -ef If you want to ...
- Kill Processes in Linux
Step 1: find processes to kill ps -ef | grep java Step 2: Kill the process based on process id kill ...
- How do I Find Out Linux CPU Utilization?
From:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/how-do-i-find-out-linux-cpu-utilization.html Whenever a Linux sys ...
- linux processes
So that Linux can manage the processes in the system, each process is represented by a task_struct ...
- Beginning Linux Programming 学习--chapter 11 Processes and Signals
What's process--什么是进程? The UNIX standards, specifically IEEE Std 1003.1, 2004 Edition, defines a pr ...
随机推荐
- 《Velocity java开发指南》中文版(下)转载
文章出自:http://sakyone.iteye.com/blog/524292 8.Application Attributes Application Attributes (应用程序属性)是和 ...
- jquery data方法取值与js attr取值的区别
<a data-v="3"></a> jquery data方法的运行机制: 第一次查找dom,使用attributes获取到dom节点值,并将其值存到缓存 ...
- Javascript 中 call 的两种用法
用法一(常见用法): 表现形式为:一个对象.方法.call(另一个对象),意义是用另一个对象代替当前对象,执行当前对象的方法.先看示例: function Class1(){ this.name = ...
- JavaScript学习总结【6】、JS BOM
1.BOM 简介 所谓的 BOM 即浏览器对象模型(Browser Object Model).BOM 赋予了 JS 操作浏览器的能力,即 window 操作.DOM 则用于创建删除节点,操作 HTM ...
- HTML5-javascript屏幕旋转事件:onorientationchange
屏幕旋转事件:onorientationchange 添加屏幕旋转事件侦听,可随时发现屏幕旋转状态(左旋.右旋还是没旋) 判断屏幕是否旋转 function orientationChange() { ...
- AlertDialog中EditText不能获取焦点以及不宽度不能自动铺满的完美解决方案
问题分析: 因为 dialog的Attributes使用的默认的,其中一个属性就是:flags ,就是这个属性导致不能获取焦点,默认的是FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE,故名思义不能获取输入焦点, ...
- ServletContext与application的关系
ServletContext 就是application 生命周期是从servletContext创建到服务器关闭 其实servletContext和application 是一样的,就相当于一个类创 ...
- sql server 查询表某个字段不重复数据
SELECT TOP (500) ID, Personname, Personcode, Telphone, Fraction into temp3 FROM Records AS a WHERE ( ...
- BenchmarkDotNet
.NET Core性能测试组件BenchmarkDotNet 支持.NET Framework Mono .NET Core 超强性能测试组件BenchmarkDotNet 支持Full .NET F ...
- (转载)Convolutional Neural Networks卷积神经网络
Convolutional Neural Networks卷积神经网络 Contents 一:前导 Back Propagation反向传播算法 网络结构 学习算法 二:Convolutional N ...
