Exercise : Self-Taught Learning
First, you will train your sparse autoencoder on an "unlabeled" training dataset of handwritten digits. This produces feature that are penstroke-like. We then extract these learned features from a labeled dataset of handwritten digits. These features will then be used as inputs to the softmax classifier that you wrote in the previous exercise.
Concretely, for each example in the the labeled training dataset 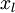 , we forward propagate the example to obtain the activation of the hidden units
, we forward propagate the example to obtain the activation of the hidden units  . We now represent this example using
. We now represent this example using  (the "replacement" representation), and use this to as the new feature representation with which to train the softmax classifier.
(the "replacement" representation), and use this to as the new feature representation with which to train the softmax classifier.
Finally, we also extract the same features from the test data to obtain predictions.
In this exercise, our goal is to distinguish between the digits from 0 to 4. We will use the digits 5 to 9 as our "unlabeled" dataset with which to learn the features; we will then use a labeled dataset with the digits 0 to 4 with which to train the softmax classifier.
Step 1: Generate the input and test data sets
Step 2: Train the sparse autoencoder
use the unlabeled data (the digits from 5 to 9) to train a sparse autoencoder
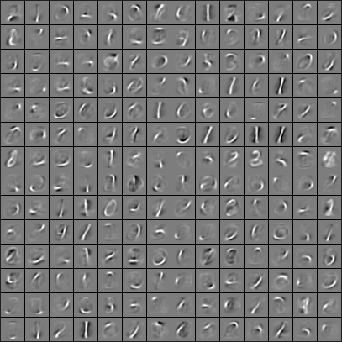
When training is complete, you should get a visualization of pen strokes like the image shown below:
Informally, the features learned by the sparse autoencoder should correspond to penstrokes.
Step 3: Extracting features
After the sparse autoencoder is trained, you will use it to extract features from the handwritten digit images.
Step 4: Training and testing the logistic regression model
Use your code from the softmax exercise (softmaxTrain.m) to train a softmax classifier using the training set features (trainFeatures) and labels (trainLabels).
Step 5: Classifying on the test set
Finally, complete the code to make predictions on the test set (testFeatures) and see how your learned features perform! If you've done all the steps correctly, you should get an accuracy of about 98% percent.
code
%% CS294A/CS294W Self-taught Learning Exercise % Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% self-taught learning. You will need to complete code in feedForwardAutoencoder.m
% You will also need to have implemented sparseAutoencoderCost.m and
% softmaxCost.m from previous exercises.
%
%% ======================================================================
% STEP : Here we provide the relevant parameters values that will
% allow your sparse autoencoder to get good filters; you do not need to
% change the parameters below. inputSize = * ;
numLabels = ;
hiddenSize = ;
sparsityParam = 0.1; % desired average activation of the hidden units.
% (This was denoted by the Greek alphabet rho, which looks like a lower-case "p",
% in the lecture notes).
lambda = 3e-; % weight decay parameter
beta = ; % weight of sparsity penalty term
maxIter = ; %% ======================================================================
% STEP : Load data from the MNIST database
%
% This loads our training and test data from the MNIST database files.
% We have sorted the data for you in this so that you will not have to
% change it. % Load MNIST database files
mnistData = loadMNISTImages('train-images.idx3-ubyte');
mnistLabels = loadMNISTLabels('train-labels.idx1-ubyte'); % Set Unlabeled Set (All Images) % Simulate a Labeled and Unlabeled set
labeledSet = find(mnistLabels >= & mnistLabels <= );
unlabeledSet = find(mnistLabels >= ); %%增加的一行代码
unlabeledSet = unlabeledSet(:end/); numTest = round(numel(labeledSet)/);%拿一半的样本来训练%
numTrain = round(numel(labeledSet)/);
trainSet = labeledSet(:numTrain);
testSet = labeledSet(numTrain+:*numTrain); unlabeledData = mnistData(:, unlabeledSet);%%为什么这两句连在一起都要出错呢?
% pack;
trainData = mnistData(:, trainSet);
trainLabels = mnistLabels(trainSet)' + 1; % Shift Labels to the Range 1-5 % mnistData2 = mnistData;
testData = mnistData(:, testSet);
testLabels = mnistLabels(testSet)' + 1; % Shift Labels to the Range 1-5 % Output Some Statistics
fprintf('# examples in unlabeled set: %d\n', size(unlabeledData, ));
fprintf('# examples in supervised training set: %d\n\n', size(trainData, ));
fprintf('# examples in supervised testing set: %d\n\n', size(testData, )); %% ======================================================================
% STEP : Train the sparse autoencoder
% This trains the sparse autoencoder on the unlabeled training
% images. % Randomly initialize the parameters
theta = initializeParameters(hiddenSize, inputSize); %% ----------------- YOUR CODE HERE ----------------------
% Find opttheta by running the sparse autoencoder on
% unlabeledTrainingImages opttheta = theta;
addpath minFunc/
options.Method = 'lbfgs';
options.maxIter = ;
options.display = 'on';
[opttheta, loss] = minFunc( @(p) sparseAutoencoderLoss(p, ...
inputSize, hiddenSize, ...
lambda, sparsityParam, ...
beta, unlabeledData), ...
theta, options); %% ----------------------------------------------------- % Visualize weights
W1 = reshape(opttheta(:hiddenSize * inputSize), hiddenSize, inputSize);
display_network(W1'); %%======================================================================
%% STEP : Extract Features from the Supervised Dataset
%
% You need to complete the code in feedForwardAutoencoder.m so that the
% following command will extract features from the data. trainFeatures = feedForwardAutoencoder(opttheta, hiddenSize, inputSize, ...
trainData); testFeatures = feedForwardAutoencoder(opttheta, hiddenSize, inputSize, ...
testData); %%======================================================================
%% STEP : Train the softmax classifier softmaxModel = struct;
%% ----------------- YOUR CODE HERE ----------------------
% Use softmaxTrain.m from the previous exercise to train a multi-class
% classifier. % Use lambda = 1e- for the weight regularization for softmax
lambda = 1e-;
inputSize = hiddenSize;
numClasses = numel(unique(trainLabels));%unique为找出向量中的非重复元素并进行排序 % You need to compute softmaxModel using softmaxTrain on trainFeatures and
% trainLabels % You need to compute softmaxModel using softmaxTrain on trainFeatures and
% trainLabels options.maxIter = ;
softmaxModel = softmaxTrain(inputSize, numClasses, lambda, ...
trainFeatures, trainLabels, options); %% ----------------------------------------------------- %%======================================================================
%% STEP : Testing %% ----------------- YOUR CODE HERE ----------------------
% Compute Predictions on the test set (testFeatures) using softmaxPredict
% and softmaxModel [pred] = softmaxPredict(softmaxModel, testFeatures); %% ----------------------------------------------------- % Classification Score
fprintf('Test Accuracy: %f%%\n', *mean(pred(:) == testLabels(:))); % (note that we shift the labels by , so that digit now corresponds to
% label )
%
% Accuracy is the proportion of correctly classified images
% The results for our implementation was:
%
% Accuracy: 98.3%
%
%function [activation] = feedForwardAutoencoder(theta, hiddenSize, visibleSize, data) % theta: trained weights from the autoencoder
% visibleSize: the number of input units (probably )
% hiddenSize: the number of hidden units (probably )
% data: Our matrix containing the training data as columns. So, data(:,i) is the i-th training example. % We first convert theta to the (W1, W2, b1, b2) matrix/vector format, so that this
% follows the notation convention of the lecture notes. W1 = reshape(theta(:hiddenSize*visibleSize), hiddenSize, visibleSize);
b1 = theta(*hiddenSize*visibleSize+:*hiddenSize*visibleSize+hiddenSize); %% ---------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------------------------
% Instructions: Compute the activation of the hidden layer for the Sparse Autoencoder.
activation = sigmoid(W1*data+repmat(b1,[,size(data,)])); %------------------------------------------------------------------- end %-------------------------------------------------------------------
% Here's an implementation of the sigmoid function, which you may find useful
% in your computation of the costs and the gradients. This inputs a (row or
% column) vector (say (z1, z2, z3)) and returns (f(z1), f(z2), f(z3)). function sigm = sigmoid(x)
sigm = ./ ( + exp(-x));
end
Exercise : Self-Taught Learning的更多相关文章
- 一个Self Taught Learning的简单例子
idea: Concretely, for each example in the the labeled training dataset xl, we forward propagate the ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习 四:Neural Networks Learning
背景:跟上一讲一样,识别手写数字,给一组数据集ex4data1.mat,,每个样例都为灰度化为20*20像素,也就是每个样例的维度为400,加载这组数据后,我们会有5000*400的矩阵X(5000个 ...
- Unsupervised Feature Learning and Deep Learning(UFLDL) Exercise 总结
7.27 暑假开始后,稍有时间,“搞完”金融项目,便开始跑跑 Deep Learning的程序 Hinton 在Nature上文章的代码 跑了3天 也没跑完 后来Debug 把batch 从200改到 ...
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:Learning color features with Sparse Autoencoders
Exercise:Learning color features with Sparse Autoencoders 习题链接:Exercise:Learning color features with ...
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:Self-Taught Learning
Exercise:Self-Taught Learning 习题链接:Exercise:Self-Taught Learning feedForwardAutoencoder.m function [ ...
- MachineLearning Exercise 4 :Neural Networks Learning
nnCostFunction 消耗公式: a1 = [ones(m,) X]; z2 = a1*Theta1'; pre = sigmoid(a1*Theta1'); a2 = [ones(m,) p ...
- How do I learn machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-machine-learning-1?redirected_qid=6578644 How Can I Learn X? ...
- A Brief Overview of Deep Learning
A Brief Overview of Deep Learning (This is a guest post by Ilya Sutskever on the intuition behind de ...
- 深度学习Deep learning
In the last chapter we learned that deep neural networks are often much harder to train than shallow ...
随机推荐
- 求推荐go语言开发工具及go语言应该以哪种目录结构组织代码?
go语言的开发工具推荐? go语言开发普通程序及开发web程序的时候,应该以哪种目录结构组织代码? 求推荐go语言开发工具及go语言应该以哪种目录结构组织代码? >> golang这个答案 ...
- PostgreSQL Replication之第二章 理解PostgreSQL的事务日志(4)
2.4 调整检查点和XLOG 目前为止,这一章已经提供深入洞察PostgreSQL如何写入数据,一般来说,XLOG是用来干什么的.考虑到这方面的知识,我们现在可以继续并学习我们能做些什么来使我们的数据 ...
- codeforces 445 B DZY Loves Chemistry【并查集】
题意:给出n种化学物质,其中m对会发生化学反应,每次加入化学物质进去的时候, 如果有能够和它发生反应的,危险值就乘以2,问怎样的放入顺序使得危险值最大 将这m对会反应的用并查集处理,统计每个连通块里面 ...
- BZOJ 3639: Query on a tree VII LCT_set维护子树信息
用 set 维护子树信息,细节较多. Code: #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> ...
- react 中间件相关的一些源码解析
零.随便说说中间件 在react的使用中,我们可以将数据放到redux,甚至将一些数据相关的业务逻辑放到redux,这样可以简化我们组件,也更方便组件抽离.封装.复用,只是redux不能很好的处理异步 ...
- Struts(21)OGNL具体解释
Struts2 中内置了OGNL表达式的支持,使得Struts2的具有比Struts1更为强大的数据訪问的功能.本文主要解说OGNL的用法.并不会去解说一些原理性的东西.想要了解的朋友能够自己去查阅相 ...
- hdu(1069)——Monkey and Banana(LIS变形)
题意: 如今给你n个石块,然后它由坐标来表示(x,y,z).可是它能够有不同的方法,也就是说它的三个坐标能够轮换着来的. 石块的数量不限,可是每次都必须保持上底面的长和宽严格递减,然后问你用这些石块所 ...
- 利用opencv源代码和vs编程序训练分类器haartraining.cpp
如需转载请注明本博网址:http://blog.csdn.net/ding977921830/article/details/47733363. 一 训练框架 训练人脸检測分类器须要三个步骤: (1 ...
- FPGA design flow
FPGA engineering process usually involves the following stages: Architecture design. This stage invo ...
- 【转】Android应用底部导航栏(选项卡)实例
现在很多android的应用都采用底部导航栏的功能,这样可以使得用户在使用过程中随意切换不同的页面,现在我采用TabHost组件来自定义一个底部的导航栏的功能. 我们先看下该demo实例的框架图: 其 ...