后端框架学习1-----Spring
Spring学习笔记
spring全家桶:https://www.springcloud.cc/spring-reference.html
spring中文文档:http://c.biancheng.net/spring/
spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IOC)和面向切面编程(AOP)的容器框架。
IOC本质:实质上是一种设计思想,DI(依赖注入)是实现ioc的一种方法。。没有ioc的程序中,使用面向对象编程,对象的创建于对象间的依赖关系完全硬编码在程序中,对象的创建由程序自己控制,控制反转后将对象的创建转移给第三方
注意:使用xml配置的Bean,Bean的定义信息是和实现分离的,采用注解的方式可以把二者合为一体。
定义:控制反转是一种通过描述(XML或注解)并通过第三方生产获取特定对象的方式,在spring中实现控制反转的是ioc容器,实现方法是依赖注入
1、由 Spring IoC 容器管理的对象称为 Bean,Bean 根据 Spring 配置文件中的信息创建。
Properties 配置文件主要以 key-value 键值对的形式存在,只能赋值,不能进行其他操作,适用于简单的属性配置。
2、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 该类从类路径 ClassPath 中寻找指定的 XML 配置文件,并完成 ApplicationContext 的实例化工作
3、
通过set注入
导入pom依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.8</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2、学生信息
package com.zheng.pojo;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
3、xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="student" class="com.zheng.pojo.Student">
<property name="name" value="小红"></property>
<property name="age" value="12"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
4、测试
package com.zheng.pojo;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Student st1 = (Student) context.getBean("student");
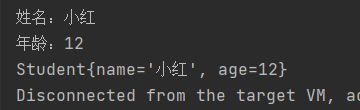
System.out.println("姓名:" + st1.getName());
System.out.println("年龄:" + st1.getAge());
System.out.println(st1.toString());
}
}
通过构造函数注入
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
xml文件
<bean id="student1" class="com.zheng.pojo.Student">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="小黑"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
测试
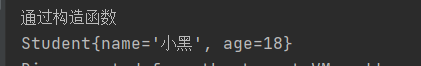
System.out.println("通过构造函数");
Student st2 = (Student) context.getBean("student1");
System.out.println(st2.toString());
结果
注意:
在application中导入其他配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<import resource="beans.xml"/>
<import resource="beans1.xml"/>
</beans>
获得容器方法
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
依赖注入
构造函数注入
setter注入
复杂类型依赖注入
student
package com.zheng.dao;
import java.util.*;
public class Student {
private String name;
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String, String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private String wife;
private Properties info;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String[] getBooks() {
return books;
}
public void setBooks(String[] books) {
this.books = books;
}
public List<String> getHobbys() {
return hobbys;
}
public void setHobbys(List<String> hobbys) {
this.hobbys = hobbys;
}
public Map<String, String> getCard() {
return card;
}
public void setCard(Map<String, String> card) {
this.card = card;
}
public Set<String> getGames() {
return games;
}
public void setGames(Set<String> games) {
this.games = games;
}
public String getWife() {
return wife;
}
public void setWife(String wife) {
this.wife = wife;
}
public Properties getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(Properties info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
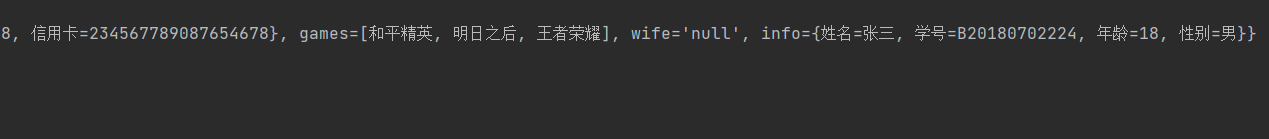
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
", books=" + Arrays.toString(books) +
", hobbys=" + hobbys +
", card=" + card +
", games=" + games +
", wife='" + wife + '\'' +
", info=" + info +
'}';
}
}
address
package com.zheng.dao;
public class Address {
private String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="com.zheng.dao.Address">
<property name="address" value="上海"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.zheng.dao.Student">
<property name="name" value="小红"></property>
<property name="address" ref="address"></property>
<!--为数组注入值-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>JAVA</value>
<value>PHP</value>
<value>C++</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--为list集合注入值-->
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>足球</value>
<value>篮球</value>
<value>乒乓球</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--map集合注入值-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="身份证" value="234567655678987678"></entry>
<entry key="信用卡" value="234567789087654678"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--set注入-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>和平精英</value>
<value>明日之后</value>
<value>王者荣耀</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--注入空值-->
<property name="wife">
<null/>
</property>
<!--注入properties-->
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="学号">B20180702224</prop>
<prop key="姓名">张三</prop>
<prop key="性别">男</prop>
<prop key="年龄">18</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试
import com.zheng.dao.Student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}

Bean的作用域
1)singleton
默认值,单例模式,表示在 Spring 容器中只有一个 Bean 实例,Bean 以单例的方式存在。
2)prototype
原型模式,表示每次通过 Spring 容器获取 Bean 时,容器都会创建一个 Bean 实例。
Bean的自动装配
- byName自动装配
<bean id="cat" class="com.zheng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.zheng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<!--
byName:会自动在容器上下文中查找,和自己对象set方法后面的值对应的beanid
-->
<bean id="user" class="com.zheng.pojo.User" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="小红"></property>
</bean>
- byType自动装配
<bean class="com.zheng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean class="com.zheng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<!--
byName:会自动在容器上下文中查找,和自己对象属性类型相同的bean
-->
<bean id="user" class="com.zheng.pojo.User" autowire="byType">
<property name="name" value="小红"></property>
</bean>
注解自动装配
1、导入约束context约束
2、配置注解支持 <context:annotation-config/>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--开启注解的支持-->
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>
举例
- @Autowired
可以应用到 Bean 的属性变量、属性的 setter 方法、非 setter 方法及构造函数等,配合对应的注解处理器完成 Bean 的自动配置工作。默认按照 Bean 的类型进行装配。
@Qualifier
与 @Autowired 注解配合使用,会将默认的按 Bean 类型装配修改为按 Bean 的实例名称装配,Bean 的实例名称由 @Qualifier 注解的参数指定。
package com.zheng.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class User {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
private Cat cat;
private String name;
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--开启注解的支持-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="cat" class="com.zheng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.zheng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="user" class="com.zheng.pojo.User"/>
</beans>
两者配合使用
@Autowired
@Qualifier("dog")
private Dog dog;
<bean class="com.zheng.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.zheng.pojo.Dog"></bean>
二、spring注解开发
xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--指定扫描下的包,这个包下的注解就会自动生效-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zheng.pojo"/>
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>
实体类
package com.zheng.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Component //相当于== <bean id="student" class="com.zheng.pojo.Student"/>
public class Student {
@Value("小红") //相当于== <property name="name" value="小红"/>
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试
import com.zheng.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml");
Student st1 = context.getBean("student", Student.class);//默认的实例名是类的小写
System.out.println(st1.getName());
}
}
衍生的注解(重点理解)
@Component有几个衍生注解,在web开发中,按照mvc三层架构
- dao【@Repository】
- service【@Service】
- controller【@Controller】
四个注解的功能一样,都是代表将某个类注册到spring中,装配Bean
后端框架学习1-----Spring的更多相关文章
- 第65节:Java后端的学习之Spring基础
Java后端的学习之Spring基础 如果要学习spring,那么什么是框架,spring又是什么呢?学习spring中的ioc和bean,以及aop,IOC,Bean,AOP,(配置,注解,api) ...
- Spring框架学习03——Spring Bean 的详解
1.Bean 的配置 Spring可以看做一个大型工厂,用于生产和管理Spring容器中的Bean,Spring框架支持XML和Properties两种格式的配置文件,在实际开发中常用XML格式的配置 ...
- Spring 框架学习(1)--Spring、Spring MVC扫盲
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行 文章大纲 什么是spring 传统Java web应用架构 更强的Java Web应用架构--MVC框架 Spring--粘合式框架 spring的内涵 spring核 ...
- 后端框架学习3------SpringMVC
springMVC学习笔记 官方文档地址:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html# ...
- 框架学习之Spring(一IOC)----HelloWrod
一.概述 Spring是一个开源框架,它的核心是控制反转(IOC)和面向切面(AOP).简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EEfull-stack(一站式)轻量级开源框架. EE 开发分 ...
- Spring框架学习02——Spring IOC 详解
1.Spring IOC的基本概念 IOC(Inverse of Control)反转控制的概念,就是将原本在程序中手动创建对象的控制权,交由Spring框架管理.当某个Java对象(调用者)需要调用 ...
- 后端框架学习-----mybatis(使用mybatis框架遇到的问题)
1.配置文件没有注册(解决:在核心配置文件中注册mapper,注册有三种形式.资源路径用斜杆,包和类用点) <mappers> <!--每一个mapper.xml文件都需要在myba ...
- 后端框架学习-----mybatis(4)
文章目录 4.解决属性名和字段名不一致的问题 4.解决属性名和字段名不一致的问题 1.问题.数据库字段名和属性名不一致,导致查出的数据部分为空 2.resultMap(用于解决数据库表中的字段和属性) ...
- Springboot 框架学习
Springboot 框架学习 前言 Spring Boot是Spring 官方的顶级项目之一,她的其他小伙伴还有Spring Cloud.Spring Framework.Spring Data等等 ...
随机推荐
- 【原创】Asp.NET Core Web API与Vue 3.0搭建前后分离项目
特地记录一下,网上的教程写的稀里糊涂的,整得我都心塞塞的,其实实现的过程蛮简单的 问题是这样的:我将Vue构建生成好的文件,放在后端wwwroot文件里面,并开启静态文件访问功能,结果总是无法显示相应 ...
- 结束语句之 break
C 语言自学之 break Dome1: 找出0-50之间的所有素数,所谓素数就是只能被1和它本身整除的数字,比如:7,13,23等. 运行结果: 2 3 5 7 ...
- Spring源码 13 IOC refresh方法8
本文章基于 Spring 5.3.15 Spring IOC 的核心是 AbstractApplicationContext 的 refresh 方法. 其中一共有 13 个主要方法,这里分析第 8 ...
- Vmware 虚拟机连接外网和设置固定IP
NAT 模式(地址转换模式) 在NAT模式中,主机网卡直接与虚拟NAT设备相连,然后虚拟NAT设备与虚拟DHCP服务器一起连接在虚拟交换机VMnet8上,虚拟机借助NAT功能,通过宿主机器所在的网络来 ...
- Canvas 线性图形(一):路径
路径的概念 路径是从起始点到结束点之间的连线.个人认为,二维画布中分为线性图形和非线性图形,线性图形包括矩形.直线.曲线.圆形等各种几何图形:非线性图形包括图象.文本.像素.线性图形中又分为路径和非路 ...
- 洛谷P4135 作诗(不一样的分块)
题面 给定一个长度为 n n n 的整数序列 A A A ,序列中每个数在 [ 1 , c ] [1,c] [1,c] 范围内.有 m m m 次询问,每次询问查询一个区间 [ l , r ] [l, ...
- python必备基础
1. 基础函数 序号 函数 说明 1 print() 打印 2 input() 输入 3 int() 转化为整形 4 float() 转化为浮点型 5 str() ...
- 【Java】学习路径59-多个连接的服务器端
ServerSocket可以对接多个Socket对象,利用这点,就可以实现:一台服务器对多个客户端. import java.io.IOException; import java.net.*; pu ...
- Rust 从入门到精通06-语句和表达式
1.语句和表达式 语句和表达式是 Rust 语言实现逻辑控制的基本单元. 在 Rust 程序里面,语句(Statement)是执行一些操作但不返回的指令,表达式(Expressions)计算并产生一个 ...
- win10电脑自动连接蓝牙设备攻略
每次在电脑上想连接蓝牙耳机,但不想手动去连接怎么办呢? 自动连接! 其实微软已经解决了这个问题,只要打开蓝牙,他就会自动匹配上次连接的设备 打开设置--->设备勾选 "显示使用&quo ...
