C lang:character input and output (I/O)
Xx_Introduction
- Character input and output is by more line character conpose of the text flow
- Define name common use capital letter,easy read.
- The Standard C Library ----->provide I/O model ------>use character flow way.
Ax_Application
- file copy,charater count,line count,word count
Bx_Method
- I/O model common use getchar and putchar,interactive use of putchar and printf.
1 getchar() //read next character
2 putcahr() //print next character
3 printf() //print next(bunch) character - File Copy
- file copy version 1
1 #include<stdio.h>
2
3 int main()
4 {
5 int c;
6
7 c = getchar();
8 while(c != EOF){
9 putchar(c);
10 c = getchar();
11 }
12 } - file copy version 2
1 #include<stdio.h>
2
3 int main()
4 {
5 int c;
6
7 while((c = getchar())!= EOF){
8 putchar(c);
9 }
10 }!= : unequal to. priority overtop assignment(=) EOF:end of file
- Conclusion:computer use bit storage of character and any data type.
- Assignment can portion of expression.
- Complex statement simple easy read,but so hard understand.
- Due to unequal to relational operator(!=) priority not overtop assignment(=),so c expression use bracket.
1 #include <stdio.h>
2
3 int main()
4 {
5 int c;
6
7 while (c = getchar() != EOF){
8 printf("%d\n",c);
9 }
10 printf("%d - at EOF\n",c);
11 return 0;
12 }if not use bracket,will priority operation EOF,value by 1,if input end or else print "c - at EOF".
- Print EOF value programming
1 #include <stdio.h>
2
3 int main()
4 {
5 printf("EOF is %d\n",EOF);
6 return 0;
7 }character constant EOF is in <stdio.h> file definition,value by -1
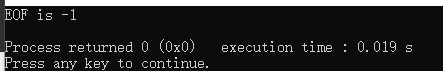
- In other system can by definition other value.
- file copy version 1
- Charater Count(2019-10-8 update)
- Character count version 1
#include <stdio.h> int main()
{
// version 1
long nc; nc = ;
while (getchar() != EOF)
++nc;
printf("%ld\n",nc-);
return ;
}++(--) is operater, be euivalent to eg(nc = nc + 1);impression add one.
- ++(--) use a prefix effect in variable before add.in suffix it's first call variable before use progressive increase.
- Long than int more big,long support 32bit int support 16bit,but different system imparity,long in printf use %ld.
- Character version 2
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double nc;
for (nc = ; getchar() != EOF;++nc)
;
printf("%.0f\n", nc-);
return ;
}double and float use %f format output.double more than float.
- For circulation a circulation body must exsit,null statement for alone semicolon(;).
- Important is circulation in execute programs before must judge test condition whether it meets.
- Character count version 1
- Line Count
- mind:line equal to line break number.
- Line count program
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c,nl; nl = ;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF)
if (c == '\n')
++nl;
printf("%d\n",nl);
return ;
}==:mean equal. 'A':mean character constant.corresponding ASCII number.

- Count blanks,tabs,and newlines.
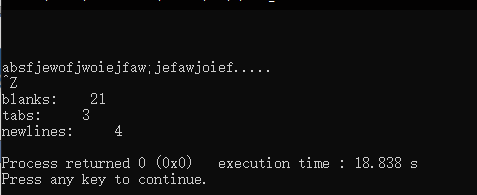
version 1
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c, nb, nt, nl; nb = ; /* number of blanks */
nt = ; /* number of tabs */
nl = ; /* number of newlines */
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF){
if ( c == ' ')
++nb;
if ( c == '\t')
++nt;
if ( c == '\n')
++nl;
}
printf("blanks:%6d\ntabs:%6d\nnewlines:%6d\n", nb, nt, nl);
return ;
}....>>>
- version 2
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c, nb, nt, nl; nb = ; /* number of blanks */
nt = ; /* number of tabs */
nl = ; /* number of newlines */
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF)
if ( c == ' ')
++nb;
else ( c == '\t')
++nt;
else ( c == '\n')
++nl; printf("blanks:%6d\ntabs:%6d\nnewlines:%6d\n", nb, nt, nl);
return ;
}but I not successful execute.
- Replace string of blanks with a single blank
- version 1
#include <stdio.h>
#define NONBLANK 'a'
int main()
{
int c, lastc; lastc = NONBLANK;
while (( c = getchar()) != EOF){
if (c != ' ')
putchar(c);
if (c == ' ')
if (lastc != ' ')
putchar(c);
lastc = c;
}
return ;
}one if statement control nonblank output.tow if statement deal with blank.three blank check blank is one or more blank.last print c.
version 2
#include<stdio.h>
#define NONBLANK 'a'
int main()
{
int c, lastc; lastc = NONBLANK;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF ){
if (c != ' ')
putchar(c);
else if (lastc != ' ')
putchar(c);
lastc = c;
}
return ;
}ok,success!
- version 3
#include <stdio.h> #define NONBLANK 'a'
int main()
{
int c, lastc; lastc = NONBLANK;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF){
if (c != ' ' || lastc != ' ')
putchar(c);
lastc = c;
}
return ;
}this method use logic simbol (OR) || realize.

ok,this aim at blank deal wilth three method.
- version 1
- Replace tabs and backspaces with visible characters.
- Realize
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c; while ((c = getchar())!= EOF){
if (c == '\t')
printf("\\t");
if (c == '\b')
printf("\\b");
if (c == '\\')
printf("\\\\");
if (c != '\b')
if (c != '\t')
if (c != '\\')
putchar(c);
}
return ;
}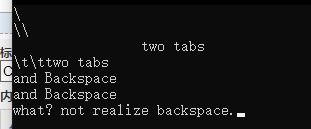
why?//??????????????????????------------------------------program bug.......I brain in the blue screen.so,go to www.baidu.com to find out.
- Truth to version 2
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c; while ((c = getch())!= EOF){ /*getchar not identify keyboard backspace.*/
if (c == '\t')
printf("\\t");
if (c == '\b')
printf("\\b");
if (c == '\\')
printf("\\\\");
if (c != '\b')
if (c != '\t')
if (c != '\\')
putchar(c);
}
return ;
}getchar not catch backspace so,will getchar replace getch. getch() can catch any print behavior.

oh,yes!
- It can also be used if-else. to version 3
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c; while((c = getch())!= EOF)
if (c == '\t')
printf("\\t");
else if (c == '\b')
printf("\\b");
else if (c == '\\')
printf("\\\\");
else
putchar(c);
return ;
}ok.next is a word count.
- Realize
- word count
- count input lines,words and strings number.
#include <stdio.h>
#define IN 1
#define OUT 0 int main()
{
int c, nl, nw, nc, state; state = OUT;
nl = nw = nc = ;
while ((c = getchar())!= EOF){
++nc;
if (c == '\n')
++nl;
if (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t')
state = OUT;
else if (state == OUT){
state = IN;
++nw;
}
}
printf("lines:%9d\nword:%9d\nstring:%9d\n",nl,nw,nc);
return ;
}&&:AND ||: OR , AND higher priority OR. expression from left to right. a = b = c = 0 if meanwhile include value and assignment two type,order from right to left.

- IF statement
if(expression)
statement1 /* true */
else
statement2 /* false */
else if (expression){
statement1 /* true*/
...
}true or false.
- count input lines,words and strings number.
- Print input one word per line.
- last practical program.very basis.very important.
#include<stdio.h> #define IN 1
#define OUT 0 int main()
{
int c, state; state = OUT;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF){
if (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t'){
if (state == IN){
putchar('\n');
state = OUT;
}
} else if (state == OUT){
state = IN;
putchar(c);
} else
putchar(c);
}
return ;
}state is a BOOL value.
- last practical program.very basis.very important.
Cx_Conclusion
- I/O model common use getchar and putchar,interactive use of putchar and printf.
- File Copy
- Charater Count
- Line Count
- Count blanks,tabs,and newlines.
- Replace string of blanks with a single blank
- Replace tabs and backspaces with visible characters.
- word count
- Print input one word per line.
- getchar and putchar printf().and putch()
- != and ==\=
- ++ / --
- EOF
- LONG and DOUBLE
- while and if else
- ASCII 'A'
- || OR ; && AND
C lang:character input and output (I/O)的更多相关文章
- Python - 3. Input and Output
from:http://interactivepython.org/courselib/static/pythonds/Introduction/InputandOutput.html Input a ...
- 7. Input and Output
7. Input and Output There are several ways to present the output of a program; data can be printed i ...
- [20160704]Addition program that use JOptionPane for input and output
//Addition program that use JOptionPane for input and output. import javax.swing.JOptionPane; public ...
- Python Tutorial 学习(七)--Input and Output
7. Input and Output Python里面有多种方式展示程序的输出.或是用便于人阅读的方式打印出来,或是存储到文件中以便将来使用.... 本章将对这些方法予以讨论. 两种将其他类型的值转 ...
- [Python] Print input and output in table
Print the input and output in a table using prettyTable. from prettytable import PrettyTable import ...
- Input and Output File
Notes from C++ Primer File State Condition state is used to manage stream state, which indicates if ...
- [20171128]rman Input or output Memory Buffers.txt
[20171128]rman Input or output Memory Buffers.txt --//做一个简单测试rman 的Input or output Memory Buffers. 1 ...
- Angular4学习笔记(六)- Input和Output
概述 Angular中的输入输出是通过注解@Input和@Output来标识,它位于组件控制器的属性上方. 输入输出针对的对象是父子组件. 演示 Input 新建项目connInComponents: ...
- Java中的IO流,Input和Output的用法,字节流和字符流的区别
Java中的IO流:就是内存与设备之间的输入和输出操作就成为IO操作,也就是IO流.内存中的数据持久化到设备上-------->输出(Output).把 硬盘上的数据读取到内存中,这种操作 成为 ...
随机推荐
- luogu P3807 【模板】卢卡斯定理
求 C(n,n+m)%p C(m,n)%p=C(m%p,n%p)*C(m/p,n/p) #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include& ...
- 最新28道java基础面试题-上
28道java基础面试题 1.面向对象的特征有哪些方面? 答:面向对象的特征主要有以下几个方面: 抽象:抽象是将一类对象的共同特征总结出来构造类的过程,包括数据抽象和行为抽象两方面.抽象只关注对象有哪 ...
- nitacm第十六届浙江大学宁波理工学院程序设计大赛总结
校赛时间:2019.11.30周六下午12:00-16:00 重现赛链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/2995#question 体验: 11点多到达石鳞大 ...
- ARTS-S 最难的事情
小朋友不舒服,看了医生也开了药吃了.但还是一直闹,不睡觉,弄的我和我爱人精疲力尽. 现在看来,技术上的难题真不算什么.照顾小朋友才是这个世界上最难的事情.
- ARTS-S anaconda常用命令
建新的环境 conda create --name py36 python=3.6 显示所有环境 conda info --envs 一键安装 wget https://repo.anaconda.c ...
- Orleans的生产环境部署
这一章非常简单 只要照着官方文档做就行了 文档地址 打好NUGET包后 Sql脚本是在项目下的OrleansAdoNetContent
- iSensor APP 之 摄像头调试 OV5642 续集2
参考上一篇博客 作为续集,主要测试 RAW格式下的 不同分辨率效果 iSensor APP 之 摄像头调试 OV5642 直接上图吧 720p 拍照效果
- Altium PCB二维码Logo设计(转 crazybingo)
Altium PCB二维码Logo设计 每次设计PCB的时候,都会在空白部分放Logo上去,一来板卡显得更充实,二来更有成就感一些... 今天突然想着...这两年二维码越来越火,火到快爆发,不如在板卡 ...
- RT-Thread的位图调度算法分析(最新版)
RT-Thread的内核调度算法 rt-thread的调度算法为基于优先级调度和基于时间片轮转调度共存的策略.rt-thread内核中存在多个线程优先级,并且支持多个线程具有同样的线程优先级.线程级别 ...
- 【搞定Jvm面试】 JVM 垃圾回收揭秘附常见面试题解析
JVM 垃圾回收 写在前面 本节常见面试题 问题答案在文中都有提到 如何判断对象是否死亡(两种方法). 简单的介绍一下强引用.软引用.弱引用.虚引用(虚引用与软引用和弱引用的区别.使用软引用能带来的好 ...

