HDFS 读写流程-英
HDFS 文件读取流程
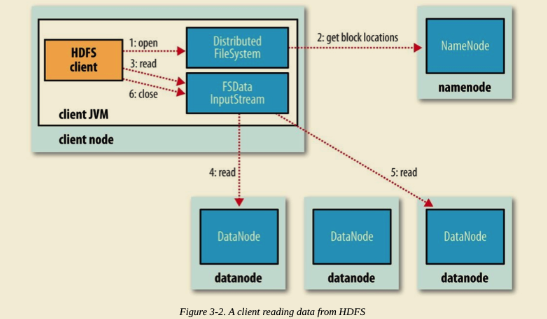
The client opens the file it wishes to read by calling open() on the FileSystem object, which for HDFS is an instance of DistributedFileSystem (step 1 in Figure 3-2).
DistributedFileSystem calls the namenode, using remote procedure calls (RPCs), to determine the locations of the first few blocks in the file (step 2). For each block, the namenode returns the addresses of the datanodes that have a copy of that block.
Furthermore, the datanodes are sorted according to their proximity to the client (according to the topology of the cluster’s network;). If the client is itself a datanode (in the case of a MapReduce task, for instance), the client will read from the local datanode if that datanode hosts a copy of the block.
The DistributedFileSystem returns an FSDataInputStream (an input stream that supports file seeks) to the client for it to read data from. FSDataInputStream in turn wraps a DFSInputStream, which manages the datanode and namenode I/O.
The client then calls read() on the stream (step 3). DFSInputStream, which has stored the datanode addresses for the first few blocks in the file, then connects to the first (closest) datanode for the first block in the file. Data is streamed from the datanode back to the client, which calls read() repeatedly on the stream (step 4). When the end of the block is reached, DFSInputStream will close the connection to the datanode, then find the best datanode for the next block (step 5). This happens transparently to the client, which from its point of view is just reading a continuous stream.
Blocks are read in order, with the DFSInputStream opening new connections to datanodes as the client reads through the stream. It will also call the namenode to retrieve the datanode locations for the next batch of blocks as needed. When the client has finished reading, it calls close() on the FSDataInputStream (step 6).
During reading, if the DFSInputStream encounters an error while communicating with a datanode, it will try the next closest one for that block. It will also remember datanodes that have failed so that it doesn’t needlessly retry them for later blocks. The DFSInputStream also verifies checksums for the data transferred to it from the datanode.
If a corrupted block is found, the DFSInputStream attempts to read a replica of the block from another datanode; it also reports the corrupted block to the namenode.
One important aspect of this design is that the client contacts datanodes directly to retrieve data and is guided by the namenode to the best datanode for each block. This design allows HDFS to scale to a large number of concurrent clients because the data traffic is spread across all the datanodes in the cluster. Meanwhile, the namenode merely has to service block location requests (which it stores in memory, making them very efficient) and does not, for example, serve data, which would quickly become a bottleneck as the number of clients grew.
HDFS 文件写入流程
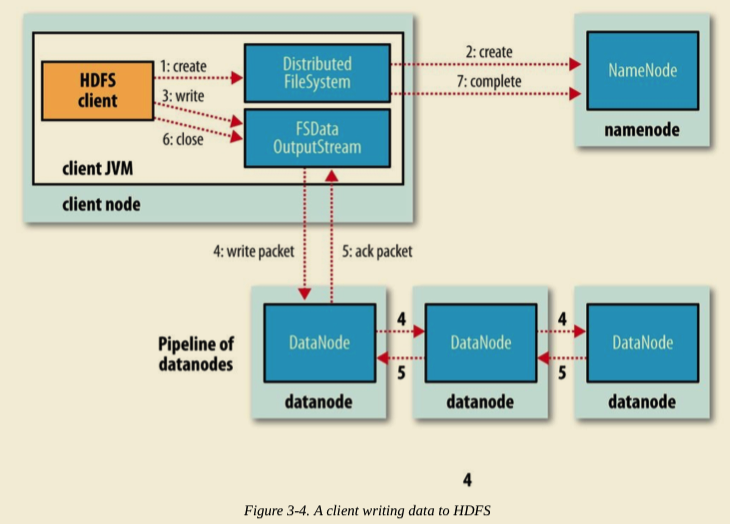
The client creates the file by calling create() on DistributedFileSystem (step 1 in Figure 3-4).
DistributedFileSystem makes an RPC call to the namenode to create a new file in the filesystem’s namespace, with no blocks associated with it (step 2). The namenode performs various checks to make sure the file doesn’t already exist and that the client has the right permissions to create the file. If these checks pass, the namenode makes a record of the new file; otherwise, file creation fails and the client is thrown an IOException. The DistributedFileSystem returns an FSDataOutputStream for the client to start writing data to. Just as in the read case, FSDataOutputStream wraps a DFSOutputStream, which handles communication with the datanodes and namenode.
As the client writes data (step 3), the DFSOutputStream splits it into packets, which it writes to an internal queue called the data queue. The data queue is consumed by the DataStreamer, which is responsible for asking the namenode to allocate new blocks by picking a list of suitable datanodes to store the replicas. The list of datanodes forms a pipeline, and here we’ll assume the replication level is three, so there are three nodes in the pipeline. The DataStreamer streams the packets to the first datanode in the pipeline, which stores each packet and forwards it to the second datanode in the pipeline. Similarly, the second datanode stores the packet and forwards it to the third (and last) datanode in the pipeline (step 4).
The DFSOutputStream also maintains an internal queue of packets that are waiting to be acknowledged by datanodes, called the ack queue. A packet is removed from the ack queue only when it has been acknowledged by all the datanodes in the pipeline (step 5).
If any datanode fails while data is being written to it, then the following actions are taken, which are transparent to the client writing the data. First, the pipeline is closed, and any packets in the ack queue are added to the front of the data queue so that datanodes that are downstream from the failed node will not miss any packets. The current block on the good datanodes is given a new identity, which is communicated to the namenode, so that the partial block on the failed datanode will be deleted if the failed datanode recovers later on.
The failed datanode is removed from the pipeline, and a new pipeline is constructed from the two good datanodes. The remainder of the block’s data is written to the good datanodes in the pipeline. The namenode notices that the block is under-replicated, and it arranges for a further replica to be created on another node. Subsequent blocks are then treated as normal.
When the client has finished writing data, it calls close() on the stream (step 6). This action flushes all the remaining packets to the datanode pipeline and waits for acknowledgments before contacting the namenode to signal that the file is complete (step 7). The namenode already knows which blocks the file is made up of (because DataStreamer asks for block allocations), so it only has to wait for blocks to be minimally replicated before returning successfully.
欢迎关注我的公众号

HDFS 读写流程-英的更多相关文章
- 大数据系列文章-Hadoop的HDFS读写流程(二)
在介绍HDFS读写流程时,先介绍下Block副本放置策略. Block副本放置策略 第一个副本:放置在上传文件的DataNode:如果是集群外提交,则随机挑选一台磁盘不太满,CPU不太忙的节点. 第二 ...
- 【转】HDFS读写流程
概述开始之前先看看其基本属性,HDFS(Hadoop Distributed File System)是GFS的开源实现. 特点如下: 能够运行在廉价机器上,硬件出错常态,需要具备高容错性流式数据访问 ...
- HDFS读写流程(转载)
概述开始之前先看看其基本属性,HDFS(Hadoop Distributed File System)是GFS的开源实现.特点如下: 能够运行在廉价机器上,硬件出错常态,需要具备高容错性 ...
- 超详细的HDFS读写流程详解(最容易理解的方式)
HDFS采用的是master/slaves这种主从的结构模型管理数据,这种结构模型主要由四个部分组成,分别是Client(客户端).Namenode(名称节点).Datanode(数据节点)和Seco ...
- Hadoop之HDFS读写流程
hadoophdfs 1. HDFS写流程 2. HDFS写流程 1. HDFS写流程 HDFS写流程 副本存放策略: 上传的数据块后,触发一个新的线程,进行存放. 第一个副本:与client最近的机 ...
- HDFS 读写流程-译
HDFS 文件读取流程 Client 端调用 DistributedFileSystem 对象的 open() 方法. 由 DistributedFileSystem 通过 RPC 向 NameNod ...
- HDFS读写流程(重点)
@ 目录 一.写数据流程 举例: 二.异常写流程 读数据流程 一.写数据流程 ①服务端启动HDFS中的NN和DN进程 ②客户端创建一个分布式文件系统客户端,由客户端向NN发送请求,请求上传文件 ③NN ...
- HDFS读写流程learning
有许多对流程进行描述的博客,但是感觉还是应当学习一遍代码,不然总感觉怪怪的,https://blog.csdn.net/popsuper1982/article/details/51615285,首先 ...
- HDFS读写流程
01.并行读取 02.逐个节点写入
随机推荐
- Kafka学习(四)-------- Kafka核心之Producer
通过https://www.cnblogs.com/tree1123/p/11243668.html 已经对consumer有了一定的了解.producer比consumer要简单一些. 一.旧版本p ...
- scrapyd schedule.json setting 传入多个值
使用案例: import requests adder='http://127.0.0.1:6800' data = { 'project':'v1', 'version':'12379', 'set ...
- Danjgo学习笔记(一)
## 创建项目: 1. 通过命令行的方式:首先要进入到安装了django的虚拟环境中.然后执行命令: ``` django-admin startproject [项目的名称] ``` 这样就可以在当 ...
- win10和浏览器快捷键
1. Win10快捷键[Win+↑/↓/←/→] 将当前窗口按比例固定到屏幕的四个边角,如左上.右上.左下.右下.[Win+1/2/3…] 按顺序打开任务栏上的已固定程序(不包括第一个“任务视图”按钮 ...
- 利用DoHome APP和音箱控制LED灯实验参考步骤
准备材料: Arduino Uno 一块 Arduino 扩展板 购买链接 DT-06模块一个 购买链接 安卓手机一个 小度音箱一个 小灯珠一个 杜邦线若干 1.DT-06固 ...
- JVM 内存模型概述
我们都知道,Java程序在执行前首先会被编译成字节码文件,然后再由Java虚拟机执行这些字节码文件从而使得Java程序得以执行.事实上,在程序执行过程中,内存的使用和管理一直是值得关注的问题.Java ...
- 重学计算机组成原理(五)- "旋转跳跃"的指令实现
CPU执行的也不只是一条指令,一般一个程序包含很多条指令 因为有if-else.for这样的条件和循环存在,这些指令也不会一路平直执行下去. 一个计算机程序是怎么被分解成一条条指令来执行的呢 1 CP ...
- Java学习|Exception和Error有什么区别?
典型回答: Exception和Error都继承了Throwable类,java中只有Throwable类型的实例才能被Throw(抛出)或者catch(捕获). Exceptio ...
- lxml解析网页
目录 1. 什么是lxml 2. 初次使用 3. xpath 3.2 标签定位 3.3 序列定位 3.4 轴定位 4. 实例 1. 什么是lxml lxml是干什么的?简单的说来,lxml是帮助我们解 ...
- C#_会员管理系统
https://www.cnblogs.com/start-from-scratch/p/5420588.html
