Springboot源码分析之TargetSource
摘要:
其实我第一次看见这个东西的时候也是不解,代理目标源不就是一个class嘛还需要封装干嘛。。。
其实proxy代理的不是target,而是TargetSource,这点非常重要,一定要分清楚!!!
通常情况下,一个代理对象只能代理一个target,每次方法调用的目标也是唯一固定的target。但是,如果让proxy代理TargetSource,可以使得每次方法调用的target实例都不同(当然也可以相同,这取决于TargetSource实现)。这种机制使得方法调用变得灵活,可以扩展出很多高级功能,如:单利,原型,本地线程,目标对象池、运行时目标对象热替换目标源等等。
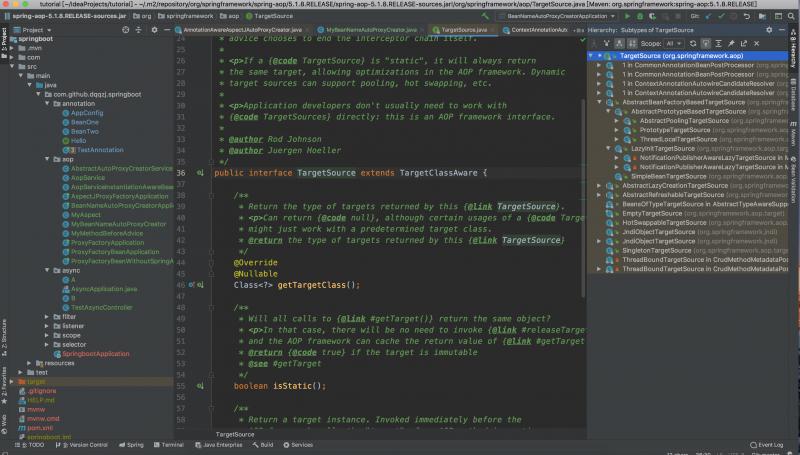
Spring内置的TargetSource
SingletonTargetSource
public class SingletonTargetSource implements TargetSource, Serializable {
/** Target cached and invoked using reflection. */
private final Object target;
//省略无关代码......
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
return this.target;
}
//省略无关代码......
}
从这个目标源取得的目标对象是单例的,成员变量target缓存了目标对象,每次getTarget()都是返回这个对象。
PrototypeTargetSource
public class PrototypeTargetSource extends AbstractPrototypeBasedTargetSource {
/**
* Obtain a new prototype instance for every call.
* @see #newPrototypeInstance()
*/
@Override
public Object getTarget() throws BeansException {
return newPrototypeInstance();
}
/**
* Destroy the given independent instance.
* @see #destroyPrototypeInstance
*/
@Override
public void releaseTarget(Object target) {
destroyPrototypeInstance(target);
}
//省略无关代码......
}
每次getTarget()将生成prototype类型的bean,即其生成的bean并不是单例的,因而使用这个类型的TargetSource时需要注意,封装的目标bean必须是prototype类型的。PrototypeTargetSource继承了AbstractBeanFactoryBasedTargetSource拥有了创建bean的能力。
public abstract class AbstractPrototypeBasedTargetSource extends AbstractBeanFactoryBasedTargetSource {
//省略无关代码......
/**
* Subclasses should call this method to create a new prototype instance.
* @throws BeansException if bean creation failed
*/
protected Object newPrototypeInstance() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating new instance of bean '" + getTargetBeanName() + "'");
}
return getBeanFactory().getBean(getTargetBeanName());
}
/**
* Subclasses should call this method to destroy an obsolete prototype instance.
* @param target the bean instance to destroy
*/
protected void destroyPrototypeInstance(Object target) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Destroying instance of bean '" + getTargetBeanName() + "'");
}
if (getBeanFactory() instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
((ConfigurableBeanFactory) getBeanFactory()).destroyBean(getTargetBeanName(), target);
}
else if (target instanceof DisposableBean) {
try {
((DisposableBean) target).destroy();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Destroy method on bean with name '" + getTargetBeanName() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
}
//省略无关代码......
}
可以看到,PrototypeTargetSource的生成prototype类型bean的方式主要是委托给BeanFactory进行的,因为BeanFactory自有一套生成prototype类型的bean的逻辑,因而PrototypeTargetSource也就具有生成prototype类型bean的能力,这也就是我们要生成的目标bean必须声明为prototype类型的原因。
ThreadLocalTargetSource
public class ThreadLocalTargetSource extends AbstractPrototypeBasedTargetSource
implements ThreadLocalTargetSourceStats, DisposableBean {
/**
* ThreadLocal holding the target associated with the current
* thread. Unlike most ThreadLocals, which are static, this variable
* is meant to be per thread per instance of the ThreadLocalTargetSource class.
*/
private final ThreadLocal<Object> targetInThread =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Thread-local instance of bean '" + getTargetBeanName() + "'");
/**
* Set of managed targets, enabling us to keep track of the targets we've created.
*/
private final Set<Object> targetSet = new HashSet<>();
//省略无关代码......
/**
* Implementation of abstract getTarget() method.
* We look for a target held in a ThreadLocal. If we don't find one,
* we create one and bind it to the thread. No synchronization is required.
*/
@Override
public Object getTarget() throws BeansException {
++this.invocationCount;
Object target = this.targetInThread.get();
if (target == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No target for prototype '" + getTargetBeanName() + "' bound to thread: " +
"creating one and binding it to thread '" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "'");
}
// Associate target with ThreadLocal.
target = newPrototypeInstance();
this.targetInThread.set(target);
synchronized (this.targetSet) {
this.targetSet.add(target);
}
}
else {
++this.hitCount;
}
return target;
}
/**
* Dispose of targets if necessary; clear ThreadLocal.
* @see #destroyPrototypeInstance
*/
@Override
public void destroy() {
logger.debug("Destroying ThreadLocalTargetSource bindings");
synchronized (this.targetSet) {
for (Object target : this.targetSet) {
destroyPrototypeInstance(target);
}
this.targetSet.clear();
}
// Clear ThreadLocal, just in case.
this.targetInThread.remove();
}
//省略无关代码......
}
ThreadLocalTargetSource也就是和线程绑定的TargetSource,可以理解,其底层实现必然使用的是ThreadLocal。既然使用了ThreadLocal,也就是说我们需要注意两个问题:
- 目标对象必须声明为prototype类型,因为每个线程都会持有一个不一样的对象;
- 目标对象必须是无状态的,因为目标对象是和当前线程绑定的,而Spring是使用的线程池处理的请求,因而每个线程可能处理不同的请求,因而为了避免造成问题,目标对象必须是无状态的。
实现自定义的TargetSource
package com.github.dqqzj.springboot.target;
import org.springframework.aop.TargetSource;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @author qinzhongjian
* @date created in 2019-08-25 12:43
* @description: TODO
* @since JDK 1.8.0_212-b10z
*/
public class DqqzjTargetSource implements TargetSource {
private final AtomicInteger idx = new AtomicInteger();
private final Object[] target;;
public DqqzjTargetSource(Object[] target) {
Assert.notNull(target, "Target object must not be null");
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getTargetClass() {
return target.getClass();
}
@Override
public boolean isStatic() {
return false;
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() throws Exception {
return this.target[this.idx.getAndIncrement() & this.target.length - 1];
}
@Override
public void releaseTarget(Object target) throws Exception {
}
}
实现自定义TargetSource主要有两个点要注意,一个是getTarget()方法,该方法中需要实现获取目标对象的逻辑,另一个是isStatic()方法,这个方法告知Spring是否需要缓存目标对象,在非单例的情况下一般是返回false。
小结
本文主要首先讲解了Spring是如果在源码层面支持TargetSource的,然后讲解了TargetSource的使用原理,接着对Spring提供的常见`TargetSource`进行了讲解,最后使用一个自定义的TargetSource讲解了其使用方式。Springboot源码分析之TargetSource的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot源码分析之SpringBoot的启动过程
SpringBoot源码分析之SpringBoot的启动过程 发表于 2017-04-30 | 分类于 springboot | 0 Comments | 阅读次数 SpringB ...
- Springboot源码分析之项目结构
Springboot源码分析之项目结构 摘要: 无论是从IDEA还是其他的SDS开发工具亦或是https://start.spring.io/ 进行解压,我们都会得到同样的一个pom.xml文件 4. ...
- 从SpringBoot源码分析 配置文件的加载原理和优先级
本文从SpringBoot源码分析 配置文件的加载原理和配置文件的优先级 跟入源码之前,先提一个问题: SpringBoot 既可以加载指定目录下的配置文件获取配置项,也可以通过启动参数( ...
- Springboot源码分析之代理三板斧
摘要: 在Spring的版本变迁过程中,注解发生了很多的变化,然而代理的设计也发生了微妙的变化,从Spring1.x的ProxyFactoryBean的硬编码岛Spring2.x的Aspectj注解, ...
- springboot源码分析-SpringApplication
SpringApplication SpringApplication类提供了一种方便的方法来引导从main()方法启动的Spring应用程序 SpringBoot 包扫描注解源码分析 @Spring ...
- Springboot源码分析之jar探秘
摘要: 利用IDEA等工具打包会出现springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar,springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.original,前面说过它们之间的关系了, ...
- Springboot源码分析之事务拦截和管理
摘要: 在springboot的自动装配事务里面,InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator ,TransactionInterceptor,PlatformTrans ...
- Springboot源码分析之Spring循环依赖揭秘
摘要: 若你是一个有经验的程序员,那你在开发中必然碰到过这种现象:事务不生效.或许刚说到这,有的小伙伴就会大惊失色了.Spring不是解决了循环依赖问题吗,它是怎么又会发生循环依赖的呢?,接下来就让我 ...
- SpringBoot源码分析(二)启动原理
Springboot的jar启动方式,是通过IOC容器启动 带动了Web容器的启动 而Springboot的war启动方式,是通过Web容器(如Tomcat)的启动 带动了IOC容器相关的启动 一.不 ...
随机推荐
- jsp定义全局变量:读取properties文件
<%java.util.Properties prop = new java.util.Properties();java.io.InputStream in;in = getClass().g ...
- 0728 history
-- :: cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ -- :: wget http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/rpm/rhel/virtualbox. ...
- Centos7配置BIND开机自启动
Centos7上面已经把/etc/init.d/服务的启动方式更改为systemctl启动. 当然编译安装仍然可以/etc/init.d/手动启动但是chkconfig –add named就用不了. ...
- jango简介
Django简介 Django框架简介 MVC框架和MTV框架 MVC,全名是Model View Controller,是软件工程中的一种软件架构模式,把软件系统分为三个基本部分:模型(Mode ...
- 去掉matlab图像显示刻度
图像显示后面加 set( gca, 'XTick', [], 'YTick', [] );
- 通过自制yum源离线安装ansible
系统环境 --CentOS release 7 python版本--Python 3.5.4 背景:在企业环境中,安装ansible的服务器往往不能访问互联网,简单的下载ansible源码安装,会 ...
- 【原创】NES第一波:如何用通用型6502宏汇编器,制用NES/FC游戏。
在163的博客关了呀.在这边重新开张了. 以后若网友有什么要长篇解答的问题,也在这儿作答. 作为第一波原创文章,我打算做一次小白示范.那就是一步一步的展示某个汇编编译器的用法. 一.科普 很多人认为程 ...
- oracle 正确删除归档日志,并清除 V$ARCHIVED_LOG 数据
1. 连接 RMAN 管理 rman target / 2. 查看归档日志列表 RMAN> crosscheck archivelog all; 3. 删除所有归档日志 RMAN> DEL ...
- 高性能MySQL之基础架构
一.背景 为什么我们需要先学习MYSQL的基础架构先呢? 原因很简单,当我们需要了解一件事物的时候,我们只有站在宏观的层面,才能层层剥丝抽茧的去理解问题.举个例子,我们要看一个框架的源码,一开始就想进 ...
- 深扒JVM,对它进行“开膛破肚”式解析!
1. 打怪升级,你绕不开JVM JVM,对Java程序员进阶而言,是一个绝对绕不开,也不能绕开的话题. 在你打怪升级.进阶蜕变的路上,势必会遇到项目上线中各种OOM.GC等问题,此时JVM的功底就至关 ...
