ConcurrentLinkedQueue (一)
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
主要讲一下在JDK8中,ConcurrentLikedQueue是如何入队,出队的。
首先我们要明白,ConcurrentLikedQueue是一种安全的没有边界的基于链表的队列,有头节点head,尾结点tail。
类似于 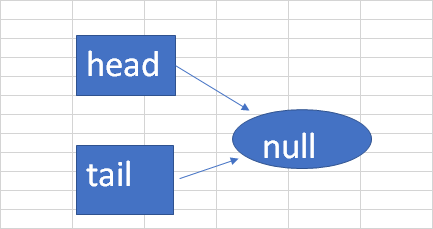 ,上图是创建一个空的队列,只有head和tail节点,以下为源码:
,上图是创建一个空的队列,只有head和tail节点,以下为源码:
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() {
head = tail = new Node<E>(null);
}
对于入队来说,我们要了解的是tail节点不一定是最后一个节点,这是非常重要的。一般来说,当tail节点的next不为空时,在队尾加入新节点,更新tail指向尾节点;当tail的next节点为空时,在队尾加入新节点,不更新tail的位置。
源码中有一个注释:Both head and tail are permitted to lag. In fact, failing to update them every time one could is a significant optimization (fewer CASes). As with LinkedTransferQueue (see the internal documentation for that class), we use a slack threshold of two; that is, we update head/tail when the current pointer appears to be two or more steps away from the first/last node.
大概的意思是说不用每次都更新头尾节点,这是一个非常重要的优化。 使用的松弛阈值为2; 也就是说,当当前指针距离第一个/最后一个节点有两个或更多节点的距离时,我们更新head/tail。
在入队的时候,我们就能够很容易的看到上述所描述tail的特点。
入队:
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue.
* As the queue is unbounded, this method will never return {@code false}.
* 将指定的元素插入到此队列的末尾。因为队列是无界的,所以这个方法永远不会返回{@code false}。 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e); //入队前构建节点 //从尾结点开始入队
for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {
Node<E> q = p.next;
if (q == null) { //tail是尾结点
// p is last node
//如果p是尾结点,设置p节点的next为newNode
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) { //如果新节点添加入尾节点后面
// Successful CAS is the linearization point
// for e to become an element of this queue,
// and for newNode to become "live".
//成功的CAS是使e成为这个队列的一个元素,使newNode成为“活的”的线性化点。
if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a time一次跳转两个节点
casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.
return true;
}
// Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next
//丢失的CAS争用到另一个线程;重读next
}
else if (p == q)
// We have fallen off list. If tail is unchanged, it
// will also be off-list, in which case we need to
// jump to head, from which all live nodes are always
// reachable. Else the new tail is a better bet. p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else
// Check for tail updates after two hops.
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
上述的offer(E e)方法,即是向队列尾部添加元素。
首先,入队前构建结点newNode,接下来无限for循环,保证入队成功,所以该方法返回总是true。

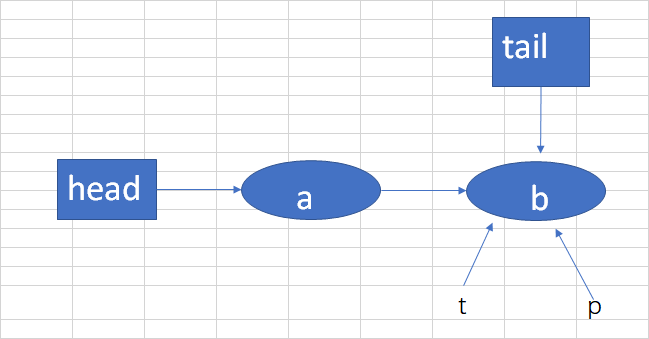
假设现在队列中有两个结点a,b,tail指向b。t->tail,p->t,如下图:
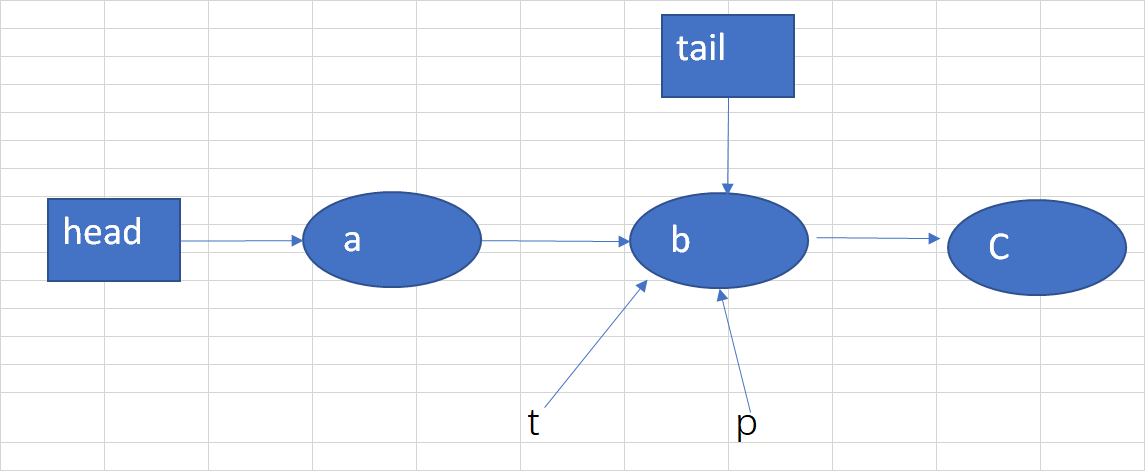
假设现在要添加一个c结点,那么会出现下图情况:
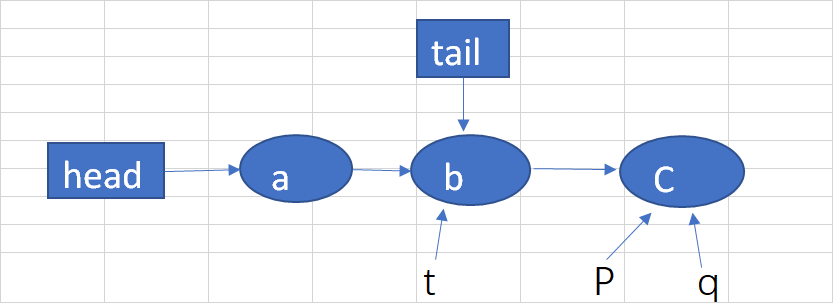
如果再添加一个D结点,
(1)因为p结点的后继结点q不为null,并且q也不等于p,所以经过判断后,p指向q,tail不变。如下图:
(2)q继续指向p的next结点,因为q为null,所以把d结点设置为p结点的next结点,因为p不指向t,所以把t指向为尾结点。如下图:
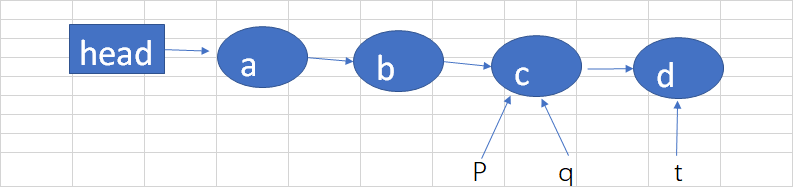
总结下来,我们发现,首先总会获取到尾结点,然后用CAS算法进行结点入队。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue (一)的更多相关文章
- 队列送券的实际应用--ConcurrentLinkedQueue并发队列
1.TicketQueue.java--队列封装类,负责如下职责:a.把活动登记对象放入队列中b.从队列中获取活动登记对象,并派券 package com.datong.pear.ticket; im ...
- 【JUC】JDK1.8源码分析之ConcurrentLinkedQueue(五)
一.前言 接着前面的分析,接下来分析ConcurrentLinkedQueue,ConcurerntLinkedQueue一个基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列.此队列按照 FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素 ...
- Java 线程 — ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 在考虑并发的时候可以先考虑单线程的情况,然后再将并发的情况考虑进来. 比如ConcurrentLinkedQueue: 先考虑单线的offer 再考虑多线程 ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC集合”10之 ConcurrentLinkedQueue
概要 本章对Java.util.concurrent包中的ConcurrentHashMap类进行详细的介绍.内容包括:ConcurrentLinkedQueue介绍ConcurrentLinkedQ ...
- [Java 基础] 并发队列ConcurrentLinkedQueue和阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue用法
reference : http://www.cnblogs.com/linjiqin/archive/2013/05/30/3108188.html 在Java多线程应用中,队列的使用率很高,多数生 ...
- 并发队列ConcurrentLinkedQueue和阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue用法
在Java多线程应用中,队列的使用率很高,多数生产消费模型的首选数据结构就是队列(先进先出).Java提供的线程安全的Queue可以分为阻塞队列和非阻塞队列,其中阻塞队列的典型例子是BlockingQ ...
- 阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue和并发队列ConcurrentLinkedQueue
LinkedBlockingQueue: public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implem ...
- CAS无锁算法与ConcurrentLinkedQueue
CAS:Compare and Swap 比较并交换 java.util.concurrent包完全建立在CAS之上的,没有CAS就没有并发包.并发包借助了CAS无锁算法实现了区别于synchroni ...
- java线程控制、状态同步、volatile、Thread.interupt以及ConcurrentLinkedQueue
在有些严格的系统中,我们需要做到干净的停止线程并清理相关状态.涉及到这个主题会带出很多的相关点,简单的总结如下: 我们知道,在java中,有一个volatile关键字,其官方说明(https://do ...
- java LinkedBlockingQueue和ConcurrentLinkedQueue的区别
实现上看,两者都继承于AbstractQueue,但是ConcurrentLinkedQueue实现了Queue,而LinkedBlockingQueue实现了BlockingQueue,Blocki ...
随机推荐
- Ingress-nginx 部署使用
Ingress-nginx 部署使用 一.Ingress 简介 在Kubernetes中,服务和Pod的IP地址仅可以在集群网络内部使用,对于集群外的应用是不可见的.为了使外部的应用能够访问集群内 ...
- SD-WAN基础---SD-WAN简单了解
一:推文(摘录.转载自) 关于SD-WAN,你不得不了解的10个常识 那些让人怦然心动的SD-WAN功能(上) 那些让人怦然心动的SD-WAN功能(中) 二:SD-WAN是什么 SD-WAN,即软件定 ...
- Python 初级 6 循环 (三)
一.复习 1 计算循环(for循环) for looper in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]: print("hello") 1) looper的值从第0个数1开始 2) 对应 ...
- CentOS离线状态下安装Python3.7.0
1.下载python安装包以及依赖的包 python安装包:Python-3.7.0 下载地址:www.python.org/ftp/python/3.7.0/Python-3.7.0.tar.xz ...
- server2008r2 安装CentOS
一:安装CentOS 二:配置虚拟网络: 三:设置创建的虚拟机使用刚才创建的网卡: 四:运行CentOs,输入用户:root 密码:root,登录后输入: dhclient 自动获取IP ip ...
- FormsAuthentication使用指南,实现登录
一般情况下,在我们做访问权限管理的时候,会把用户的正确登录后的基本信息保存在Session中,以后用户每次请求页面或接口数据的时候,拿到Session中存储的用户基本信息,查看比较他有没有登录和能否访 ...
- 【linux基础err】bash: cannot create temp file for here-document: No space left on device
博主的device还有剩余空间也出现了这个问题,不知是什么原因,不过删除一些无用的内容,或者将某些有用的内容移动到其他硬盘,之后就可以正常使用了. 参考: 1. cannot create temp ...
- [LeetCode] 727. Minimum Window Subsequence 最小窗口子序列
Given strings S and T, find the minimum (contiguous) substring W of S, so that T is a subsequenceof ...
- 面试之哈希表leetcode
1 案例1 leetcode-----242 给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词. 示例 1: 输入: s = "anagram", t ...
- jenkins自动打tag
思路: 1.手动输入需要tag的版本号,如“build001”,填写svn有权限的密码(账号默认值),填写打tag的说明 2.脚本根据tag的版本号,自动创建目录(版本号为目录名称) 3.将需要打ta ...
