《Using Python to Access Web Data》Week4 Programs that Surf the Web 课堂笔记
Coursera课程《Using Python to Access Web Data》 密歇根大学
Week4 Programs that Surf the Web
12.3 Unicode Characters and Strings
Representing Simple Strings
使用ASCII码,每个字符都被一个0到256的数字表示来存在8bits的内存里。
使用ord()函数可以查询,指定字符所对应的ASCII码。
>>> print(ord('H'))
72
>>> print(ord('e'))
101
>>> print(ord('\n'))
10
Multi-Byte Characters
unicode是为了解决之前编码只考虑英文字符的问题而出现的,因为以前的ASCII码只使用一个字节来表示字符,所以它最多也只能表示256个字符, 如果只使用英文是够用的,但是事实是世界要发展,所以出现各种字符,那么它就不够用了。于是就出现了许多的编码方式,例如中国就出了GBK编码。 但是这是不适于国家与国家之间的交流的,于是ISO就指定了unicode这个编码标准。
unicode现在通常是使用两个字节来表示一个字符,但是其实它可以被看成一个字符集,它将所有字符都定义了一个唯一的ID,这样网络就能有一个统一的字符表,不再出现之前的需要相互转化的问题。
那么新的问题就是直接使用unicode来表示字符时,它有时候会浪费空间,在编码表中靠前的字符,例如英文字符,它前一字节就是0000,后一字节才是它真正的序号。 于是,在网络传输中,由于网络带宽并没有这么的理想,大家肯定就会嫌弃unicode编码浪费带宽,所以,于1992年创建,由Ken Thompson创建了UTF传输标准,它的全名是Unicode Transformation Format,这个全名就能明白了UTF的意思。
UTF是针对unicode的一种网络传输标准,按照我们通信的人来说,它就是一种针对unicode的编码方式。 它现在有UTF-7、UTF-7.5、UTF-8、UTF-16、UTF-32几种格式,当然现在最为流行的就是其中的UTF-8。 它是一种变长的编码方式,这样就能减少网络传输中的数据量,所以在网络传输中,大家都用它。
Two Kinds of Strings in Python
# python 2.7.10
>>> x = '我爱你'
>>> type(x)
<type 'str'>
>>> x = u'我爱你'
>>> type(x)
<type 'unicode'>
# python 3.5.1
>>> x = '我爱你'
>>> type(x)
<class 'str'>
>>> x = u'我爱你'
>>> type(x)
<class 'str'>
Python2 Versus Python3
# Python 2.7.10
>>> x = b'abc'
>>> type(x)
<type 'str'>
>>> x = '我爱你'
>>> type(x)
<type 'str'>
>>> x = u'我爱你'
>>> type(x)
<type 'unicode'>
# Python 3.5.1
>>> x = b'abc'
>>> type(x)
<class 'bytes'>
>>> x = '我爱你'
>>> type(x)
<class 'str'>
>>> x = u'我爱你'
>>> type(x)
<class 'str'>
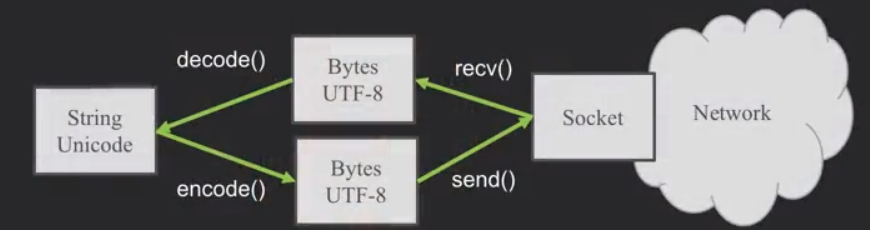
在python3内部,所有的字符都是unicode编码,unicode与UTF-8并不能直接通用,所有在字符出入的时候就要加上encode()与decode()。
Python Strings to Bytes
当我们与外部资源通信时,比如说一个网络socket,我们就要发送bytes。所以我们要把Python3的strings来encode。
当我们读取外部资源发来的数据时,我们就要把它decode变成strings。
while True:
data = mysock.recv(512)
if (len(data) < 1):
break
mystring = data.decode()
print(mystring)
也就是说,在网络上大家用bytes(它包含UTF-8等)交流,而在自己的程序里使用unicode。
12.4 Retrieving Web Pages
Using urllib in Python
由于HTTP现在太普遍了,所以我们有一个库可以做所有的socket工作,以及让网页看起来像文件一样。
import urllib.request, urllib.parse, urllib.error
fhand = urllib.request.urlopen('http://data.pr4e.org/romeo.txt')
for line in fhand:
print(line.decode().strip())
这个urllib.request.urlopen()函数看起来就跟打开文件一样。
Reading Web Pages
import urllib.request,urllib.parse,urllib.error
fhand = urllib.request.urlopen('http://www.dr-chuck.com/page1.htm')
for line in fhand:
print(line.decode().strip())
输出结果
<h1>The First Page</h1>
<p>If you like, you can switch to the <ahref="http://www.dr-chuck.com/page2.htm">Second Page</a>
</p>
其实读取html文件是一样的。
12.5 Parsing Web Pages
What is Web Scraping?
网络数据采集。使用搜索引擎来采集网页数据,我们叫"spidering the web"或者"web crawling"。
The Easy Way - Beautiful Soup
BeautifulSoup是一个额外的模块,可以使用pip来安装。
pip install bs4
具体的用处,官方解释如下
Beautiful Soup提供一些简单的、python式的函数用来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。它是一个工具箱,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据,因为简单,所以不需要多少代码就可以写出一个完整的应用程序。
Beautiful Soup自动将输入文档转换为Unicode编码,输出文档转换为utf-8编码。你不需要考虑编码方式,除非文档没有指定一个编码方式,这时,Beautiful Soup就不能自动识别编码方式了。然后,你仅仅需要说明一下原始编码方式就可以了。
Beautiful Soup已成为和lxml、html6lib一样出色的python解释器,为用户灵活地提供不同的解析策略或强劲的速度。
import urllib.request,urllib.parse,urllib.error
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = input('Enter -')
html = urllib.request.urlopen(url).read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
# Retrieve all of the anchor tags
tags = soup('a')
for tag in tags:
print(tag.get('href',None))
其中第6行的soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')代码,就是把我们的html文件处理成了一个soup对象.
第9行的tags = soup('a')是把html文件中的anchor tag读成了一个anchor tag的list。
而第11行的tag对象相当于一个字典,可以获取'href'或None的值。
再复杂的学习可以参看三夜灯的blog文章(文后参考2)
Worked Example: BeautifulSoup
# To run this, you can install BeautifulSoup
# https://pypi.python.org/pypi/beautifulsoup4
# Or download the file
# http://www.py4e.com/code3/bs4.zip
# and unzip it in the same directory as this file
import urllib.request, urllib.parse, urllib.error
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import ssl
# Ignore SSL certificate errors
ctx = ssl.create_default_context()
ctx.check_hostname = False
ctx.verify_mode = ssl.CERT_NONE
url = input('Enter - ')
html = urllib.request.urlopen(url, context=ctx).read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
# Retrieve all of the anchor tags
tags = soup('a')
for tag in tags:
print(tag.get('href', None))
作业:Scraping HTML Data with BeautifulSoup
# To run this, you can install BeautifulSoup
# https://pypi.python.org/pypi/beautifulsoup4
# Or download the file
# http://www.py4e.com/code3/bs4.zip
# and unzip it in the same directory as this file
from urllib.request import urlopen
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import ssl
# Ignore SSL certificate errors
ctx = ssl.create_default_context()
ctx.check_hostname = False
ctx.verify_mode = ssl.CERT_NONE
url = input('Enter - ')
html = urlopen(url, context=ctx).read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
# Retrieve all of the anchor tags
tags = soup('span')
count = 0
sum = 0
for tag in tags:
# Look at the parts of a tag
sum = sum + int(tag.contents[0])
count += 1
print ('Count ',count)
print('Sum ', sum)
使用的是python3与bs4。
作业:Following Links in HTML Using BeautifulSoup
# To run this, you can install BeautifulSoup
# https://pypi.python.org/pypi/beautifulsoup4
# Or download the file
# http://www.py4e.com/code3/bs4.zip
# and unzip it in the same directory as this file
import urllib.request, urllib.parse, urllib.error
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import ssl
import re
# Ignore SSL certificate errors
ctx = ssl.create_default_context()
ctx.check_hostname = False
ctx.verify_mode = ssl.CERT_NONE
count = int(input("Enter count:"))
position = int(input("Enter position:"))
first_name = input("Start with:")
def retrievinghtml(name):
url = "http://py4e-data.dr-chuck.net/known_by_%s.html"%(name)
html = urllib.request.urlopen(url, context=ctx).read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
# Retrieve all of the anchor tags
tags = soup('a')
temp_tag = tags[position-1]
temp_site = temp_tag.get('href', None)
temp_name = (re.findall('known_by_(\S+).html',temp_site))[0]
print("Retrieving: "+"http://py4e-data.dr-chuck.net/known_by_%s.html"%(temp_name))
return temp_name
name = []
name.append(first_name)
print("Retrieving: "+"http://py4e-data.dr-chuck.net/known_by_%s.html"%(first_name))
for i in range(count):
temp_name = retrievinghtml(name[i])
name.append(temp_name)
print(name)
使用的仍然是python3与bs4。
【参考】
[1]龙的博客
《Using Python to Access Web Data》Week4 Programs that Surf the Web 课堂笔记的更多相关文章
- Python Web-第四周-Programs that Surf the Web(Using Python to Access Web Data)
1.Understanding HTML 1.最简单的爬虫 import urllib fhand=urllib.urlopen('http://www.dr-chuck.com/page1.htm' ...
- Python Web-第二周-正则表达式(Using Python to Access Web Data)
0.课程地址与说明 1.课程地址:https://www.coursera.org/learn/python-network-data/home/welcome 2.课程全名:Using Python ...
- 【Python学习笔记】Coursera课程《Using Python to Access Web Data》 密歇根大学 Charles Severance——Week6 JSON and the REST Architecture课堂笔记
Coursera课程<Using Python to Access Web Data> 密歇根大学 Week6 JSON and the REST Architecture 13.5 Ja ...
- 【Python学习笔记】Coursera课程《Using Python to Access Web Data 》 密歇根大学 Charles Severance——Week2 Regular Expressions课堂笔记
Coursera课程<Using Python to Access Web Data > 密歇根大学 Charles Severance Week2 Regular Expressions ...
- 《Using Python to Access Web Data》 Week5 Web Services and XML 课堂笔记
Coursera课程<Using Python to Access Web Data> 密歇根大学 Week5 Web Services and XML 13.1 Data on the ...
- 《Using Python to Access Web Data》 Week3 Networks and Sockets 课堂笔记
Coursera课程<Using Python to Access Web Data> 密歇根大学 Week3 Networks and Sockets 12.1 Networked Te ...
- paip. 解决php 以及 python 连接access无效的参数量。参数不足,期待是 1”的错误
paip. 解决php 以及 python 连接access无效的参数量.参数不足,期待是 1"的错误 作者Attilax 艾龙, EMAIL:1466519819@qq.com 来源 ...
- Python之路【第十八篇】:Web框架们
Python之路[第十八篇]:Web框架们 Python的WEB框架 Bottle Bottle是一个快速.简洁.轻量级的基于WSIG的微型Web框架,此框架只由一个 .py 文件,除了Pytho ...
- Python之路【第十五篇】:Web框架
Python之路[第十五篇]:Web框架 Web框架本质 众所周知,对于所有的Web应用,本质上其实就是一个socket服务端,用户的浏览器其实就是一个socket客户端. 1 2 3 4 5 6 ...
随机推荐
- PAT Basic 1071 小赌怡情 (15 分)
常言道“小赌怡情”.这是一个很简单的小游戏:首先由计算机给出第一个整数:然后玩家下注赌第二个整数将会比第一个数大还是小:玩家下注 t 个筹码后,计算机给出第二个数.若玩家猜对了,则系统奖励玩家 t 个 ...
- openCV for python的使用
一.openCV简介 OpenCV是一个开源的跨平台计算机视觉库.它轻量级而且高效——由一系列 C 函数和少量C++类构成,同时提供了Python.Ruby.MATLAB等语言的接口,实现了图像处理和 ...
- PCRE does not support \L, \l, \N{name}, \U, or \u...
PCRE does not support \L, \l, \N{name}, \U, or \u... 参考文章:YCSUNNYLIFE 的 <php 正则匹配中文> 一.报错情景: 使 ...
- SugarCRM开发入门
SugarCRM官网下载地址:https://sourceforge.net/projects/sugarcrm/ 概述 Sugar最初是基于LAMP(Linux.Apache.MySQL和PHP)运 ...
- 2018 ACM-ICPC 区域赛(青岛站)题解整理
题目链接 C - Flippy Sequence(组合数学+分类讨论) 两区间异或一下,分段考虑,如果全为0则任选两相同区间,答案为$C_{n+1}^{2}=\frac{n(n+1)}{2}$,只有一 ...
- div中的图片跑出来
一:div中的图片跑出来 <style> /* 图片在一行 */ #div1 li{ float: left; list-style: none; } </style> < ...
- 初识Python,利用turtle画图
目录 我的第三篇博客 一.初识Python 1.变量 2.注释 3.turtle库 我的第三篇博客 一.初识Python 1.变量 变量就是可变的的量,用来描述某个事物的属性.本质作用就是描述和接收变 ...
- 误删除mysql的root账号
误删除mysql的root账号 mysql 测试通过 # mysql 误删除root最高权限用户 操作步骤: .停止mysql服务 (如果你删除了root用户,但没有退出操作对话框,恭喜节省了些麻烦, ...
- JUnit——单元测试步骤
步骤: 1. New Package(一般命名为*.Test,测试类与开发类放在不同的包中)2. New JUnit Text Case(一般命名为*Test)3. 选择需要测试的方法 4. 可以下载 ...
- eclipse中使用maven搭建多模块项目
暂时参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u012343297/article/details/79883870
