ethereum/EIPs-100 挖矿难度计算
https://github.com/ethereum/EIPs/blob/master/EIPS/eip-100.md
创世纪区块的难度是131,072,有一个特殊的公式用来计算之后的每个块的难度。如果某个区块比前一个区块验证的更快,以太坊协议就会增加区块的难度。
区块的难度影响nonce,它是在挖矿时必须要使用proof-of-work算法来计算的一个hash值。
区块难度和nonce之间的关系用数学形式表达就是:
Hd代表的是难度。
找到符合难度阈值的nonce唯一方法就是使用proof-of-work算法来列举所有的可能性。找到解决方案预期时间与难度成正比—难度越高,找到nonce就越困难,因此验证一个区块也就越难,这又相应地增加了验证新块所需的时间。所以,通过调整区块难度,协议可以调整验证区块所需的时间。(挖矿的过程就是要找出正确的nonce值)
另一方面,如果验证时间变的越来越慢,协议就会降低难度。这样的话,验证时间自我调节以保持恒定的速率—平均每15s一个块。
这就是以太坊的出块时间能够保持15秒的原因,因为当验证时间变长,就会降低难度;验证时间变短,则会加强难度,那么难度是怎么计算的呢?
| eip | title | author | type | category | status | created |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
100
|
Change difficulty adjustment to target mean block time including uncles
|
Vitalik Buterin
|
Standards Track
|
Core
|
Final
|
2016-04-28
|
就是告诉了当前区块的难度是怎么计算的:
adj_factor = max( - ((timestamp - parent.timestamp) // 10), -99)
child_diff = int(max(parent.difficulty + (parent.difficulty // BLOCK_DIFF_FACTOR) * adj_factor, min(parent.difficulty, MIN_DIFF)))
然后如果block.number >= BYZANTIUM_FORK_BLKNUM(拜占庭硬分叉),则难度的计算的第一个公式变为:
adj_factor = max(( if len(parent.uncles) else ) - ((timestamp - parent.timestamp) // 9), -99)
即Byzantium版本
diff = (parent_diff +(parent_diff / * max(( if len(parent.uncles) else ) - ((timestamp - parent.timestamp) // 9), -99))) + 2^(periodCount - 2)
有关上面的拜占庭版本的详细介绍看:https://blog.csdn.net/t46414704152abc/article/details/81538361
以太坊挖矿过程:
这个地方没有太懂为什么,之后再多多查查资料
这里主要是看:
以太坊挖矿难度调整
以太坊中的区块的难度调整公式如下图所示。
参数说明
区块链难度调整中,创始块的难度被设置为D0=131072 ,此后每个区块的难度都与其父区块的难度相关。D(H)是本区块的难度,由P(H)Hd+x×ζ2和难度炸弹ϵ构成。
P(H)Hd为父区块的难度,每个区块的难度都是在父区块难度的基础上进行调整。
x×ζ2用于自适应调节出块难度,维持稳定的出块速度(15秒)。
- ϵ表示难度炸弹。
- 难度有最低下限,即不能低于D0=131072
根据EIP-100给出的式子,可以得出:
P(H)Hd = parent_diff
x = parent_diff /
ζ2 = max((2 if len(parent.uncles) else 1) - ((timestamp - parent.timestamp) // 9), -99)
ϵ = 2^(periodCount - 2)
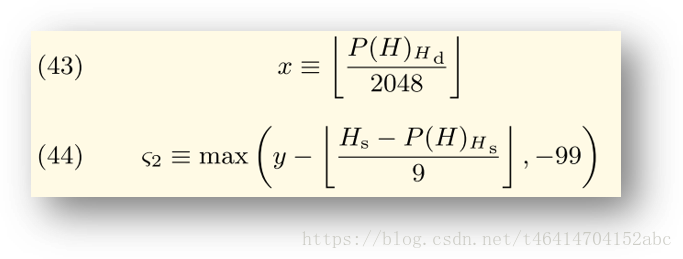
其中x和ζ2的计算方式如下图所示。
- x 是父区块难度的2048的取整,是调整的单位。
- ζ2是调整系数,其最小只能是-99。
- y的取值依赖于父区块是否包含叔父区块,如果包含,则y=2,否则y=1。y = (2 if len(parent.uncles) else 1)
- HS是本区块的时间戳,P(H)Hs是父区块的时间戳,单位为秒,并且HS>P(H)Hs。
- 难度降低的上界设置为−99 ,主要是应对被黑客攻击或其他目前想不到的黑天鹅事件。
假设当父区块不带叔父区块的时候(y=1),出块时间 = (timestamp - parent.timestamp),调整过程如下:
- 出块时间在[1,8]之间,出块时间过短,难度调大一个单位。
- 出块时间在[9,17]之间,出块时间可以接受,难度保持不变。
- 出块时间在[18,26]之间,出块时间过长,难度调小一个单位。
- …
这里发现,出块时间变长,区块的整体难度就会调小,假若有的矿工,故意将区块的时间戳改的比较晚(矿工是可以更改时间戳的),那么是不是就可以抢先发布区块呢?比如说将时间戳延迟写15秒,会怎么样呢?这样就会导致该矿工计算出来的难度比别的矿工计算的难度低,其他矿工15秒发布一个区块,而该矿工可以在10秒内发布区块,可以拿到区块奖励。但是问题在于假如刚好也有别的区块在10秒内发布了区块,此时根据POW的规则,另外一个矿工发布的区块难度更大,因此其他矿工会以最大工作量标准,选择15秒内挖出的区块所在的链作为主链,而该矿工发布的区块便成了叔父区块。
难度炸弹计算公式如下图所示。
ϵ是2的指数函数,每十万个块扩大一倍,后期增长非常快,这就是难度“炸弹”的由来。
H′i称为fake block number,由真正的block number Hi减少三百万得到。之所以减少三百万,是因为目前proof of stake的工作量证明方式还存在一些问题,pos协议涉及不够完善,但是难度炸弹已经导致挖矿时间变成了30秒左右,为了减小难度,就会减去三百万。
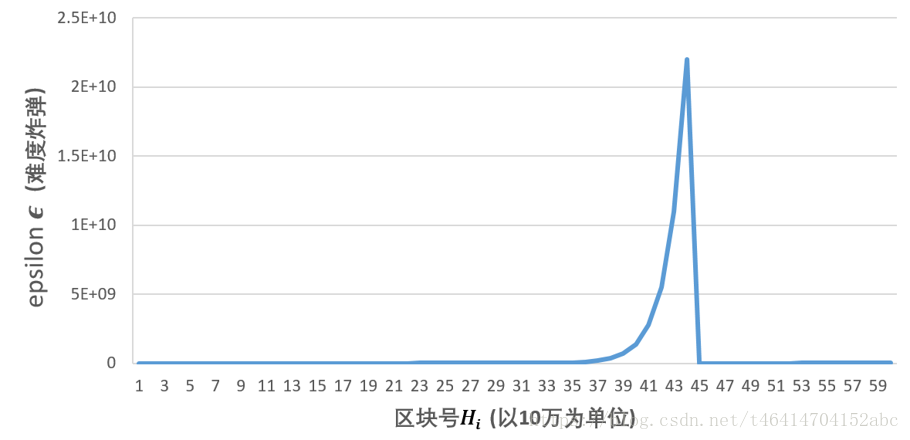
设置难度炸弹的原因是要降低迁移到PoS协议时发生fork的风险,假若矿工联合起来抵制POS的工作量证明模式,那就会导致以太坊产生硬分叉;有了难度炸弹,挖矿难度越来越大,矿工就有意愿迁移到PoS协议上了。难度炸弹的威力,可以通过下图看出。
区块数量到370万之后,挖矿难度突然递增,到430万时,难度已经非常之大了,这时候挖矿时间已经变为为30秒,但是POS协议还没有完善,于是以太坊将挖矿难度公式进行调整,使得每次计算时,当前区块号减去三百万,这样就降低了挖矿难度,并且在这个时期,对以太坊出块奖励进行了调整,从原来的5个ETH变为3个ETH。
// CalcDifficulty is the difficulty adjustment algorithm. It returns
// the difficulty that a new block should have when created at time
// given the parent block's time and difficulty.
func (ethash *Ethash) CalcDifficulty(chain consensus.ChainReader, time uint64, parent *types.Header) *big.Int {
return CalcDifficulty(chain.Config(), time, parent)
} // CalcDifficulty is the difficulty adjustment algorithm. It returns
// the difficulty that a new block should have when created at time
// given the parent block's time and difficulty.
func CalcDifficulty(config *params.ChainConfig, time uint64, parent *types.Header) *big.Int {
next := new(big.Int).Add(parent.Number, big1)
switch {
case config.IsByzantium(next):
return calcDifficultyByzantium(time, parent)
case config.IsHomestead(next):
return calcDifficultyHomestead(time, parent)
default:
return calcDifficultyFrontier(time, parent)
}
} // Some weird constants to avoid constant memory allocs for them.
var (
expDiffPeriod = big.NewInt()
big1 = big.NewInt()
big2 = big.NewInt()
big9 = big.NewInt()
big10 = big.NewInt()
bigMinus99 = big.NewInt(-)
big2999999 = big.NewInt()
)
以太坊中难度计算公式如下图所示,由于目前处于以太坊发展的Metropolis中的Byzantium阶段,所以难度计算公式的函数名称为calcDifficultyByzantium
// calcDifficultyByzantium is the difficulty adjustment algorithm. It returns
// the difficulty that a new block should have when created at time given the
// parent block's time and difficulty. The calculation uses the Byzantium rules.
func calcDifficultyByzantium(time uint64, parent *types.Header) *big.Int {
// https://github.com/ethereum/EIPs/issues/100.
// algorithm:
// diff = (parent_diff +
// (parent_diff / 2048 * max((2 if len(parent.uncles) else 1) - ((timestamp - parent.timestamp) // 9), -99))
// ) + 2^(periodCount - 2) bigTime := new(big.Int).SetUint64(time)
bigParentTime := new(big.Int).Set(parent.Time) // holds intermediate values to make the algo easier to read & audit
x := new(big.Int)
y := new(big.Int) // (2 if len(parent_uncles) else 1) - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) //
x.Sub(bigTime, bigParentTime) // x = block_timestamp - parent_timestamp
x.Div(x, big9) // x = (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) //9,整除9
if parent.UncleHash == types.EmptyUncleHash {//判断有无叔父区块
x.Sub(big1, x) //无为1, x = 1 - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) //9
} else {
x.Sub(big2, x)//有为2 , x = 2 - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) //9
}
// max((2 if len(parent_uncles) else 1) - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) // 9, -99)
if x.Cmp(bigMinus99) < { x与-99比,看谁大,小于0则说明-99大
x.Set(bigMinus99) //x的值设为-99,此时x = ζ2
}
// parent_diff + (parent_diff / 2048 * max((2 if len(parent.uncles) else 1) - ((timestamp - parent.timestamp) // 9), -99))
y.Div(parent.Difficulty, params.DifficultyBoundDivisor) //y = parent_diff / 2048
x.Mul(y, x) // x = y * ζ2
x.Add(parent.Difficulty, x) // x = parent_diff + y * ζ2 // minimum difficulty can ever be (before exponential factor)
if x.Cmp(params.MinimumDifficulty) < { //与创世区块的难度比较,创世区块的难度是难度的最低值,如果算出来的难度低于它,那就设置为创世区块的难度
x.Set(params.MinimumDifficulty)
}
// calculate a fake block number for the ice-age delay:
// https://github.com/ethereum/EIPs/pull/669
// fake_block_number = max(0, block.number - 3_000_000)
fakeBlockNumber := new(big.Int)
if parent.Number.Cmp(big2999999) >= { //当父区块号 >= 2999999,说明本区块 >= 3000000,所以要减去3百万,以此来降低难度,所以用父区块数 - 2999999即可
fakeBlockNumber = fakeBlockNumber.Sub(parent.Number, big2999999) // Note, parent is 1 less than the actual block number
}
// for the exponential factor
periodCount := fakeBlockNumber
periodCount.Div(periodCount, expDiffPeriod) //periodCount = periodCount / 100000 // the exponential factor, commonly referred to as "the bomb"
// diff = diff + 2^(periodCount - 2)
if periodCount.Cmp(big1) > {
y.Sub(periodCount, big2) //
y.Exp(big2, y, nil)
x.Add(x, y)
}
return x
}
frontier版本已经不使用了,它存在的问题是没有考虑到到13秒的距离。出块1秒和12秒有同样的难度计算值
然后还找到了另一个很好地解释了难度的帖子,但是它讲的是Homestead的版本:
以太坊(Ethereum ETH)是如何计算难度的
https://blog.csdn.net/Metal1/article/details/80151535
这个是Homestead版本的计算方法,与Byzantium版本的不同之处就在于adj_factor = max(1 - ((timestamp - parent.timestamp) // 10), -99)
block_diff = parent_diff + 难度调整 + 难度炸弹
难度调整 = parent_diff // 2048 * MAX(1 - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) // 10, -99)
即难度调整 = parent_diff // 2048 * adj_factor (BLOCK_DIFF_FACTOR在这里设置为2048)
难度炸弹 = INT(2**((block_number // 100000) - 2)) (向下取整)
该版本是在区块数还没有到达三百万时候的版本,想在超过三百万后,为了降低难度,减少出块的时间,都用上面的Byzantium版本了
https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/master/consensus/ethash/consensus.go
// calcDifficultyHomestead is the difficulty adjustment algorithm. It returns
// the difficulty that a new block should have when created at time given the
// parent block's time and difficulty. The calculation uses the Homestead rules.
func calcDifficultyHomestead(time uint64, parent *types.Header) *big.Int {
// https://github.com/ethereum/EIPs/blob/master/EIPS/eip-2.md
// algorithm:
// diff = (parent_diff +
// (parent_diff / 2048 * max(1 - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) // 10, -99))
// ) + 2^(periodCount - 2) bigTime := new(big.Int).SetUint64(time)
bigParentTime := new(big.Int).Set(parent.Time) // holds intermediate values to make the algo easier to read & audit
x := new(big.Int)
y := new(big.Int) // 1 - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) //
x.Sub(bigTime, bigParentTime)
x.Div(x, big10)
x.Sub(big1, x) // max(1 - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) // 10, -99)
if x.Cmp(bigMinus99) < {
x.Set(bigMinus99)
}
// (parent_diff + parent_diff // 2048 * max(1 - (block_timestamp - parent_timestamp) // 10, -99))
y.Div(parent.Difficulty, params.DifficultyBoundDivisor)
x.Mul(y, x)
x.Add(parent.Difficulty, x) // minimum difficulty can ever be (before exponential factor)
if x.Cmp(params.MinimumDifficulty) < {
x.Set(params.MinimumDifficulty)
}
// for the exponential factor
periodCount := new(big.Int).Add(parent.Number, big1) //这里与Byzantium版本不同处是不减三百万,直接父区块数加1得如今的区块数即可
periodCount.Div(periodCount, expDiffPeriod) // the exponential factor, commonly referred to as "the bomb"
// diff = diff + 2^(periodCount - 2)
if periodCount.Cmp(big1) > {
y.Sub(periodCount, big2)
y.Exp(big2, y, nil)
x.Add(x, y)
}
return x
}
ethereum/EIPs-100 挖矿难度计算的更多相关文章
- [ethereum源码分析](3) ethereum初始化指令
前言 在上一章介绍了关于区块链的一些基础知识,这一章会分析指令 geth --datadir dev/data/02 init private-geth/genesis.json 的源码,若你的eth ...
- (转)以太坊(Ethereum)全零地址(0x000000...)揭秘
最近,一位小伙伴向我咨询问题,说他发现了一个诡异的现象.以太坊的区块链中居然有全是0的地址:0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 这究竟是怎么回事儿呢? ...
- 使用Geth 构建以太坊区块链并模拟挖矿过程
使用Geth 构建以太坊区块链并模拟挖矿过程 Go-ethereum 是以太坊官方的一个Golang 实现,我们可以使用Geth 工具来创建创世区块并启动区块链,使用Clef 实现以太坊钱包的功能,以 ...
- 【转】干货 | 【虚拟货币钱包】从 BIP32、BIP39、BIP44 到 Ethereum HD Wallet
虚拟货币钱包 钱包顾名思义是存放$$$.但在虚拟货币世界有点不一样,我的帐户资讯(像是我有多少钱)是储存在区块链上,实际存在钱包中的是我的帐户对应的 key.有了这把 key 我就可以在虚拟货币世界证 ...
- Bitcoin挖矿
目录 为什么要挖矿? 比特币挖矿 为什么要挖矿? 增加恶意行为的成本 增加记账权力,获取相应的奖励 比特币挖矿 每开采210000个区块,挖矿奖励减半 2009年1月-2012年11月,奖励50BTC ...
- 【Ethereum】以太坊ERC20 Token标准完整说明
什么是ERC20 token 市面上出现了大量的用ETH做的代币,他们都遵守REC20协议,那么我们需要知道什么是REC20协议. 概述 token代表数字资产,具有价值,但是并不是都符合特定的规范. ...
- 比特币 难度值(difficulty)
难度(Difficulty) 难度是对挖矿困难程度的度量,即指:计算符合给定目标的一个HASH值的困难程度.比特币网络有一个全局的区块难度,有效的区域必须有一个HASH值,该HASH值必须小于给定的目 ...
- js中进行金额计算parseFloat
在js中进行以元为单位进行金额计算时 使用parseFloat会产生精度问题var price = 10.99;var quantity = 7;var needPay = parseFloat(pr ...
- CSS网页布局错位:CSS宽度计算
为什么计算宽度计算网页像素宽度是为了CSS网页布局整齐与兼容.常见的我们布局左右结构网页或使用padding.margin布局的时候将计算整页宽度,如果不计算无论是宽度过大过小就会出现错位问题. 怎么 ...
随机推荐
- vue.js 使用时间组件 日期少一天的问题
<el-form :inline="true" class="demo-form-inline padding-top-20"> <el-fo ...
- ArrayList和LinkedList的区别以及优缺点
作用 ArrayList和LinkedList都是实现了List接口的容器类,用于存储一系列的对象引用.他们都可以对元素的增删改查进行操作. 对于ArrayList,它在集合的末尾删除或添加元素所用的 ...
- java——线程
线程与进程 1.线程:程序中单独顺序的控制流 线程本身是通过程序进行运行 线程是程序中的顺序控制流,只能使用分配给程序的资源与环境 2.进程:执行中的程序 一个进程可以包含一个或多个线程 一个进程至少 ...
- canvas-tangram.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- pygame编组(精灵组)Group中的常用方法介绍
说明: 1.以下所用的Group均为Group类的对象实例 2.Group类是对AbstractGroup类的继承 sprite.py文档中描述如下: class Group(AbstractGrou ...
- c++中的this指针和c#中的this引用
先总结一下: 在c++中this为指针,使用"->"操作符来获取当前实例中的成员 在c#中this为引用,使用"."操作符来获取当前实例中的成员 下面内容 ...
- sql server:alter database name
--step 1 : 修改数据库名称 USE master GO ALTER DATABASE GeovinDuCms SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE ...
- 【读书笔记】iOS-storyBoard-为一个按钮添加一个点击事件
按照故事板的用语,应用中的一个界面屏幕被称作一个”场景(Scene)",以后添加额外的场景时,停靠区中将有另一个部分. 一,新建立一个工程,如图所示. 二,选中Main.storyboard ...
- git将本地项目推送到远程仓库
一.三个基本配置: Git全局设置 git config --global user.name "账户名称" git config --global user.email &quo ...
- python第二十三天-----作业中
#!usr/bin/env python #-*-coding:utf-8-*- # Author calmyan import os ,sys,time from core import trans ...