最简 Spring AOP 源码分析!

前言
最近在研究 Spring 源码,Spring 最核心的功能就是 IOC 容器和 AOP。本文定位是以最简的方式,分析 Spring AOP 源码。
基本概念
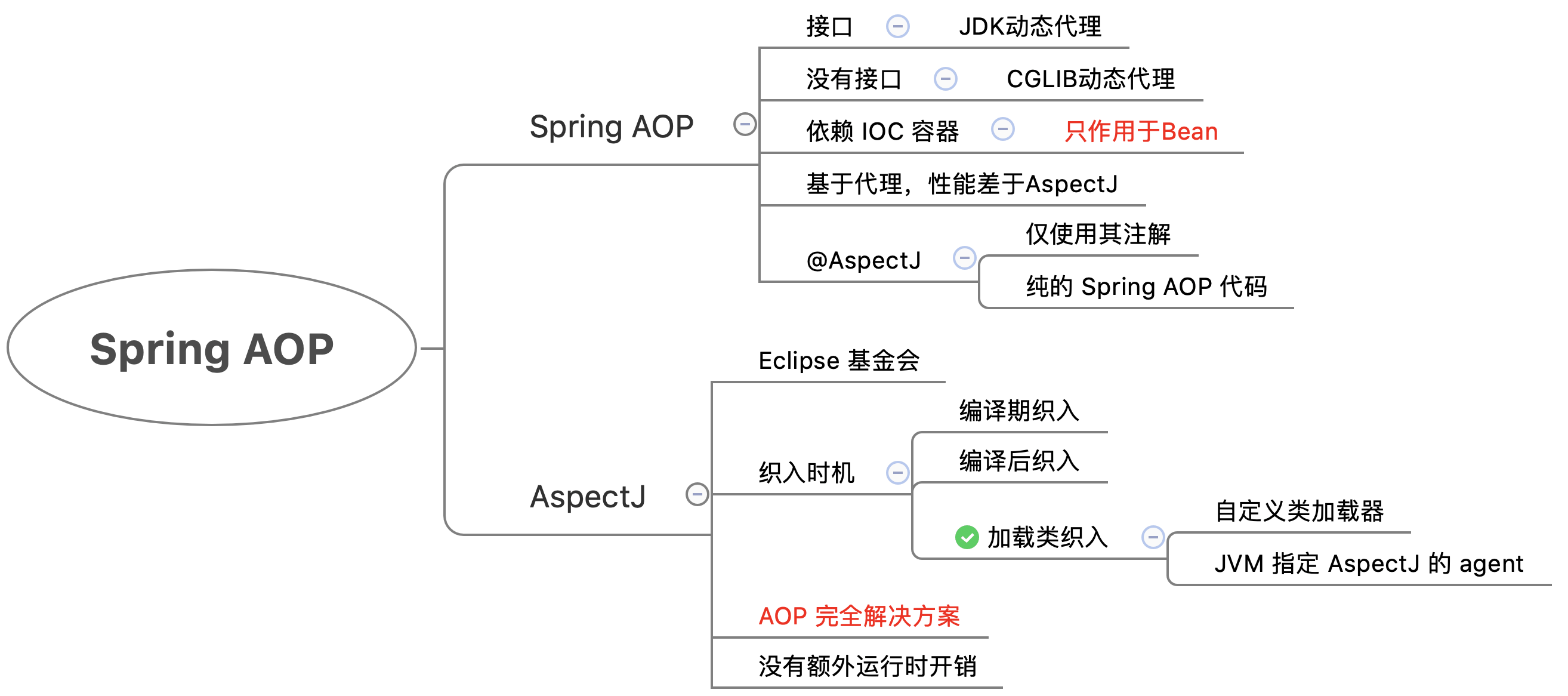
上面的思维导图能够概括了 Spring AOP,其最重要的是 Spring AOP 只能作用于 Bean,而 AspectJ 能够在编译期、类加载期对字节码进行更改。
猜测实现原理
Spring AOP 的实现原理是动态代理,但是具体又是怎么实现的呢?
在 Spring 容器中,我们使用的每个 bean 都是 BeanDefinition 的实例,容器会在合适的时机根据 BeanDefinition 的基本信息实例化 bean 对象。
所以比较简单的做法是,Spring 会自动生成代理对象的代理类。我们在获取 bean 时,Spring 容器返回代理类对象,而不是实际的 bean。
调试代码
本文使用的代码,安装了 lombok,并基于 Spring Boot,是一个完全基于注解的最简调试代码。
注解配置类 AopConfig:
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class AopConfig {
@Pointcut("within(com.life.demo..*)")
public void pointCut() {
}
@Before("com.life.demo.AopConfig.pointCut()")
public void log() {
log.info("this is point cut...");
}
}
Spring 启动类 AppApplication:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AppApplication.class, args);
}
}
Controller HelloWorldController:
package com.life.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class HelloWorldController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String greeting() {
return "hello!";
}
}
运行 Web 应用,在浏览器输入网址 http://localhost:11111/hello,会看到 log:
INFO 96257 --- [io-11111-exec-1] com.life.demo.AopConfig : this is point cut...
验证出成功配置了代理。
使用说明
- @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 开启 AOP。
- 使用 @Aspect 注解的 bean 都会被 Spring 当做用来实现 AOP 的配置类。
- 配置 Advice,不做详细介绍,具体参考 Spring AOP 官方文档。
- @Pointcut,用来匹配 Spring 容器中的所有 bean 的方法的。
@Pointcut("execution(* transfer(..))")// the pointcut expression
private void anyOldTransfer() {}// the pointcut signature
@Pointcut 中使用了 execution 来正则匹配方法签名,这也是最常用的,除了 execution,我们再看看其他的几个比较常用的匹配方式:
within:指定所在类或所在包下面的方法(Spring AOP 独有)
如 @Pointcut("within(com.javadoop.springaoplearning.service..*)")@annotation:方法上具有特定的注解,如 @Subscribe 用于订阅特定的事件。
如 @Pointcut("execution(* .(..)) && @annotation(com.javadoop.annotation.Subscribe)")bean(idOrNameOfBean):匹配 bean 的名字(Spring AOP 独有)
如 @Pointcut("bean(*Service)")
Tips:上面匹配中,通常 "." 代表一个包名,".." 代表包及其子包,方法参数任意匹配使用两个点 ".."。
源码深入分析
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 开启 AOP
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解定义:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
boolean exposeProxy() default false;
}
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy != null) {
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}
}
在 AppApplication 启动类上要加入 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解开启 AOP,查看该注解源码,其 proxyTargetClass() 是在 AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar 类中调用,而 AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar 是一个 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar。再往上追根溯源,可以看到是在接口 ConfigurableApplicationContext 中 void refresh() 调用。
IOC 容器管理 AOP 实例
在创建 bean 时,会调用 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean(...)。
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// 初始化 bean
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 1. 创建实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
...
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 2. 装载属性
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
// 3. 初始化
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
...
}
着重看第3步 initializeBean(...) 方法:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 执行每个 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法!
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
Spring IOC 容器创建 bean 实例时,最后都会对 bean 进行处理,来实现增强。对于 Spring AOP 来说,就是创建代理类。
上面代码中函数 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(...) 最终调用了 AbstractAutoProxyCreator 实现的 postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法。
/**
* Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is
* identified as one to proxy by the subclass.
* @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
wrapIfNecessary(...)方法在需要时返回了代理类。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 1. Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 2. 核心!重点!重要!
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
上述代码第 1 步 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(...) 方法是返回某个 beanName 下的 Advice 和 Advisor,如果返回结果不为空的话,才会创建代理。其核心方法就是 createProxy(...)。
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// 1. 获取合适的 ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 2. 创建并返回合适的 AOP 对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
ProxyFactory
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
查看代码最终发现是在 DefaultAopProxyFactory#createAopProxy(...) 方法中实现。
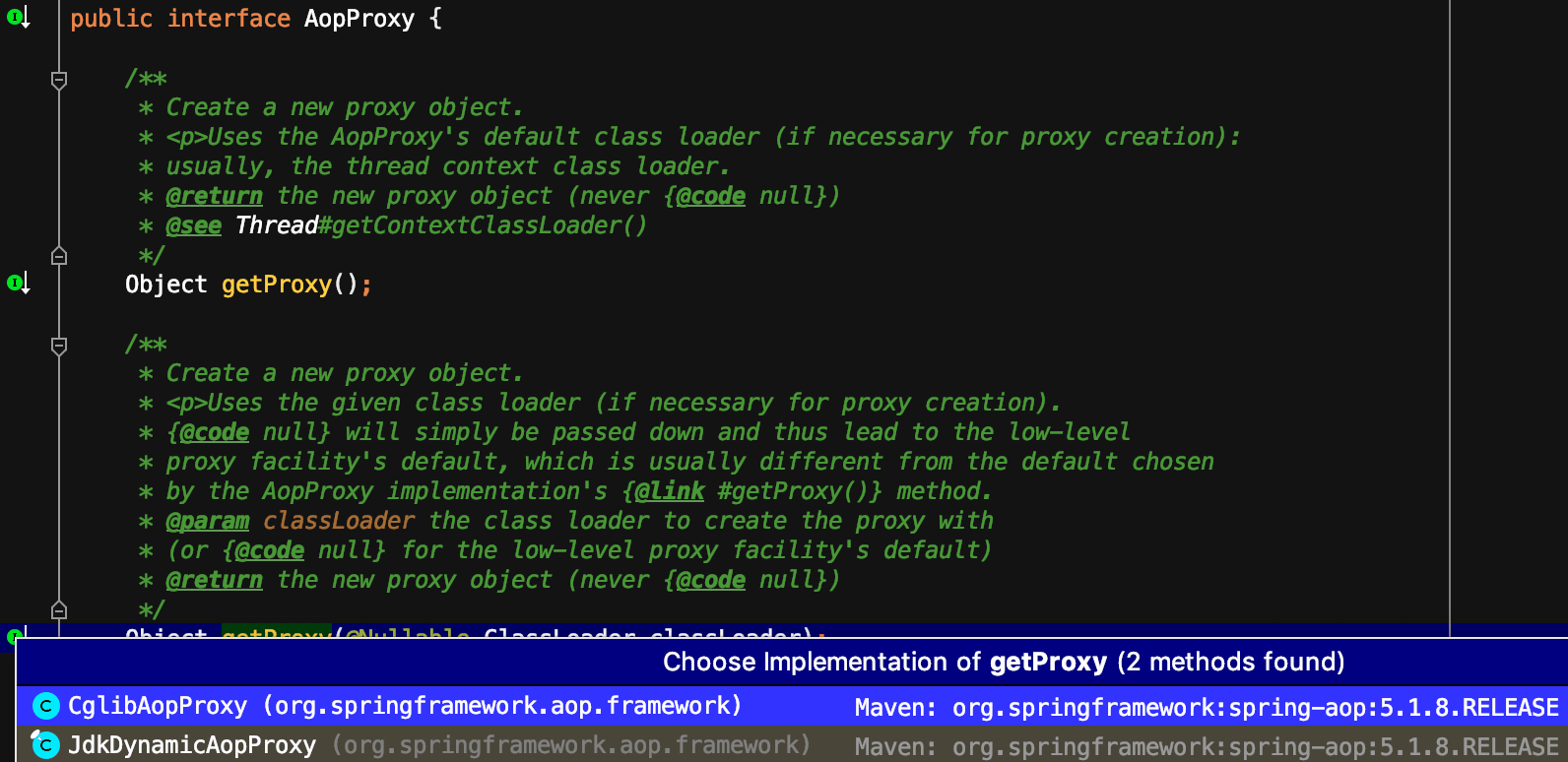
AopProxy 接口的 2 个实现类:CglibAopProxy 和 JdkDynamicAopProxy。这里就不分析 JdkDynamicAopProxy 类,仅分析 CglibAopProxy 类。CglibAopProxy 类实现的 getProxy(...) 方法如下:
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
CGLIB 生成代理的核心是 Enhancer,详情见Enhancer API 文档、cglib 官网。
总结
Spring AOP 使用了动态代理,作用于 IOC 容器管理的 bean。在获取 bean 时会根据需要创建代理类,并返回代理类。在 Spring Boot 中使用 Spring AOP 时应该先用 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解开启代理,定义代理类和代理规则,不需要 XML 或其他配置。
Spring 的源码太庞杂,调用链太深,在研究源码的时候应该明确目标,掌握核心原理。就像学汉语字典,并不需要掌握其中的每一个汉字(况且 Spring 源码更新频率很快)。
公众号
coding 笔记、点滴记录,以后的文章也会同步到公众号(Coding Insight)中,希望大家关注_
代码和思维导图在 GitHub 项目中,欢迎大家 star!

最简 Spring AOP 源码分析!的更多相关文章
- spring AOP源码分析(三)
在上一篇文章 spring AOP源码分析(二)中,我们已经知道如何生成一个代理对象了,那么当代理对象调用代理方法时,增强行为也就是拦截器是如何发挥作用的呢?接下来我们将介绍JDK动态代理和cglib ...
- Spring AOP 源码分析 - 拦截器链的执行过程
1.简介 本篇文章是 AOP 源码分析系列文章的最后一篇文章,在前面的两篇文章中,我分别介绍了 Spring AOP 是如何为目标 bean 筛选合适的通知器,以及如何创建代理对象的过程.现在我们的得 ...
- Spring AOP 源码分析 - 创建代理对象
1.简介 在上一篇文章中,我分析了 Spring 是如何为目标 bean 筛选合适的通知器的.现在通知器选好了,接下来就要通过代理的方式将通知器(Advisor)所持有的通知(Advice)织入到 b ...
- Spring AOP 源码分析 - 筛选合适的通知器
1.简介 从本篇文章开始,我将会对 Spring AOP 部分的源码进行分析.本文是 Spring AOP 源码分析系列文章的第二篇,本文主要分析 Spring AOP 是如何为目标 bean 筛选出 ...
- Spring AOP 源码分析系列文章导读
1. 简介 前一段时间,我学习了 Spring IOC 容器方面的源码,并写了数篇文章对此进行讲解.在写完 Spring IOC 容器源码分析系列文章中的最后一篇后,没敢懈怠,趁热打铁,花了3天时间阅 ...
- Spring AOP源码分析(三):基于JDK动态代理和CGLIB创建代理对象的实现原理
AOP代理对象的创建 AOP相关的代理对象的创建主要在applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation方法实现: protected Object applyBea ...
- 5.2 Spring5源码--Spring AOP源码分析二
目标: 1. 什么是AOP, 什么是AspectJ 2. 什么是Spring AOP 3. Spring AOP注解版实现原理 4. Spring AOP切面原理解析 一. 认识AOP及其使用 详见博 ...
- 5.2 spring5源码--spring AOP源码分析二--切面的配置方式
目标: 1. 什么是AOP, 什么是AspectJ 2. 什么是Spring AOP 3. Spring AOP注解版实现原理 4. Spring AOP切面原理解析 一. 认识AOP及其使用 详见博 ...
- spring aop 源码分析(三) @Scope注解创建代理对象
一.源码环境的搭建: @Component @Scope(scopeName = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON,proxyMode = ScopedP ...
随机推荐
- Mybatis执行SQL的流程
前篇:Mybatis初始化过程 SqlSession : SqlSession是一个接口,它有两个实现类:DefaultSqlSession (默认)和 SqlSessionManager (弃用,不 ...
- 329. Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix(核心在于缓存遍历过程中的中间结果)
Given an integer matrix, find the length of the longest increasing path. From each cell, you can eit ...
- 查找数组中第k大的数
问题: 查找出一给定数组中第k大的数.例如[3,2,7,1,8,9,6,5,4],第1大的数是9,第2大的数是8-- 思考:1. 直接从大到小排序,排好序后,第k大的数就是arr[k-1]. 2. ...
- fcntl函数用法——操纵文件描述符状态
fcntl函数:操纵文件描述符,改变已经打开的文件的属性int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... //arg );cmd选项:一.复制文件描述符:F_DUPFD二.更改设置文件描 ...
- binary hacks读数笔记(nm命令)
nm命令(names):输出包含三个部分:1 符号值.默认显示十六进制,也可以指定: 2 符号类型.小写表示是本地符号,大写表示全局符号(external); 3 符号名称. 例如:nm Simple ...
- Python面试题_初级版
1.如何在一个函数内部修改全局变量 a=5 def fn(): a=4 fn() print(a) # 5 #在一个函数内部修改全局变量 a=5 def fn(): global a a=4 fn() ...
- 基于udp的scoket通信
1.udp例子1 udpserver.py # udp的server,不需要进行监听也不需要建立连接 # 在启动服务之后只能被动的等待客户端发送消息过来 # 客户端发送消息的同时还会自带地址信息 # ...
- centos 6 系统下同步本地时间
1.date显示系统时间 [root@oldboy ~]# dateTue Mar 31 22:45:55 CST 2020 #CST是指是指某中标准时间 非东八区时间 更改时间的三种方法 1.c ...
- phpstudy搭建网站只能访问首页,其他路由访问404
今天博主遇到了一个很奇葩的问题,电脑下载了一个phpstudy搭建网站,框架用的是tp,但是除了输入域名能访问,其他页面都访问不了 经过博主的疯狂问大佬,以及百度,终于解决了这个问题 这次出现问题的原 ...
- 使用Camtasia制作蒙面唱将揭面视频
要说之前的<蒙面唱将猜猜猜>还是属于比较火的歌唱综艺节目了.这档歌唱类型的综艺节目的精彩点不在于歌唱的水平,而在于猜想的环节.演唱时,嘉宾们都会蒙上面具,直到被评委猜中时才会揭开面具. 我 ...
