动态规划-Stock Problem
2018-04-19 19:28:21
股票问题是leetcode里一条非常经典的题目,因为其具有一定的现实意义,所以还是在数学建模方面还是有很多用武之地的。这里会对stock的给出一个比较通用的解法,然后会针对各个细分问题用通解去解决,主要采用的算法是动态规划算法。
问题描述:Given an array representing the price of stock on each day, what determines the maximum profit we can obtain?
问题求解:首先很容易想到的是最大收入和具体结算时间以及这些天里的最多交易笔数有关,因此我们可以定义一个数组T[i][k],表示在第i天结束时,最多经过k笔交易所产生的最大收入。很显然的,我们可以得到一个初始条件T[-1][k] = T[i][0] = 0,也就是说在第-1天,无论经过多少笔交易都没有收益,在第i天,如果最多为0次交易,那么也将不会产生收益。根据动态规划的一般思路,我们现在需要做的就是建立T[i][k]和T[i-1][k], T[i][k-1], T[i-1][k-1], ...之间的关系下面将介绍如何建立这种关系。
对于第i天的交易,我们可以采取的策略有sell,buy,rest。我们当然在最初的时候并不知道哪个选择是最优的,所以我们需要去判断一下哪个选择对于我们来说能得到一个好的结果。由于有每次只能手持一股的限制,所以我们无法在已经买过股票的情况下再购买股票,同时也无法在已经卖空股票的情况下再继续卖股票,因此,我们需要一个变量来揭示第i天结束时,手里剩余的股票数量。
因此T[i][k]的定义需要被拆分成两个:T[i][k][0] and T[i][k][1]。并且我们还可以得到如下的初始条件和递推关系:
Base cases:
T[-1][k][0] = 0, T[-1][k][1] = -InfinityT[i][0][0] = 0, T[i][0][1] = -InfinityRecurrence relations:
T[i][k][0] = max(T[i-1][k][0], T[i-1][k][1] + prices[i])T[i][k][1] = max(T[i-1][k][1], T[i-1][k-1][0] - prices[i])
注意:定义一次交易为买入的时候就算作一笔交易,不可等到卖出才算作交易。
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
问题描述:
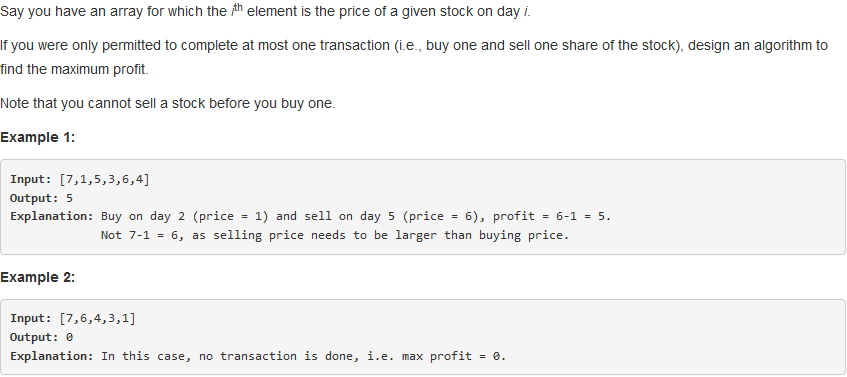
问题求解:
k = 1,则递推式变为:
T[i][1][0] = max(T[i - 1][1][0],T[i - 1][1][1] + prices[i])
T[i][1][1] = max(T[i - 1][1][1],0 - prices[i])
对空间复杂度进行优化,可以在<O(n),O(1)>完成求解。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int Ti10 = 0;
int Ti11 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int price : prices) {
Ti10 = Math.max(Ti10, Ti11 + price);
Ti11 = Math.max(Ti11, -price);
}
return Math.max(Ti10, Ti11);
}
122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
问题描述:
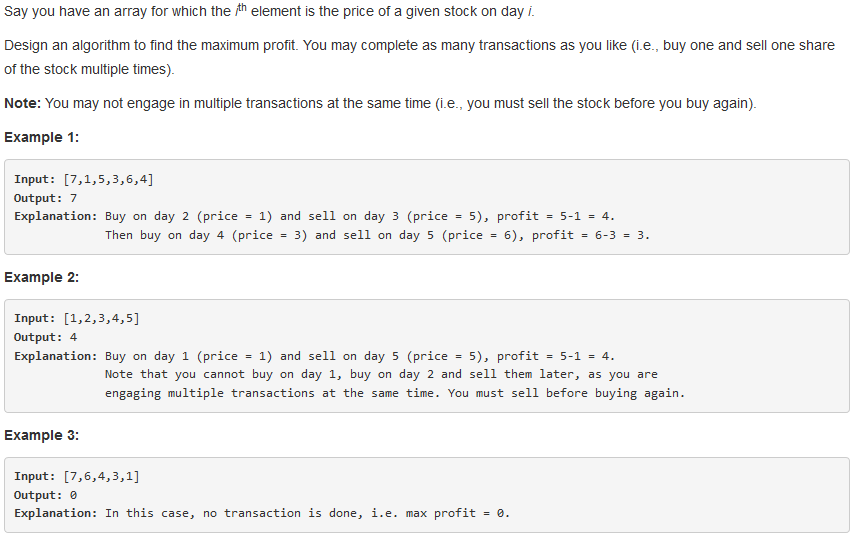
问题求解:
k = INF,则递推式变为:
T[i][k][0] = max(T[i - 1][k][0],T[i - 1][k][1] + prices[i])
T[i][k][1] = max(T[i - 1][k][1],T[i - 1][k][0] - prices[i])
对空间复杂度进行优化,可以在<O(n),O(1)>完成求解。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int Tik0 = 0;
int Tik1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int price : prices) {
int tmp = Tik0;
Tik0 = Math.max(Tik0, Tik1 + price);
Tik1 = Math.max(Tik1, tmp - price);
}
return Math.max(Tik0, Tik1);
}
714. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Transaction Fee
问题描述:
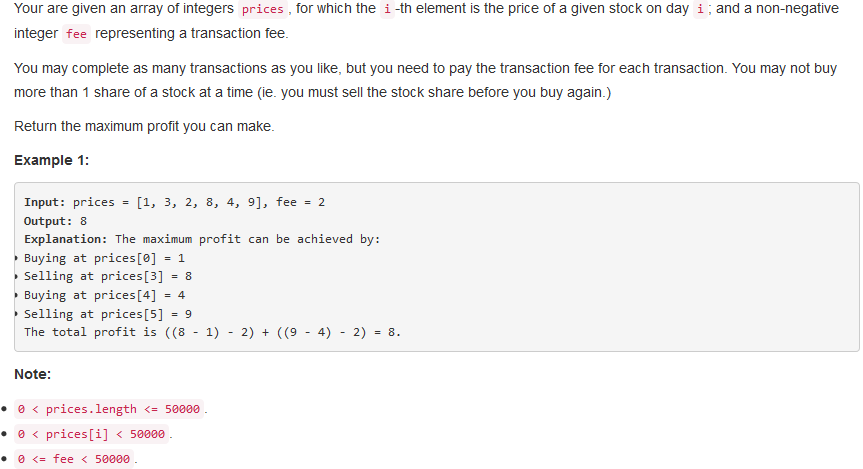
问题求解:
k = INF with fee,则递推式变为:
T[i][k][0] = max(T[i - 1][k][0],T[i - 1][k][1] + prices[i])
T[i][k][1] = max(T[i - 1][k][1],T[i - 1][k][0] - prices[i] - fee)
对空间复杂度进行优化,可以在<O(n),O(1)>完成求解。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
int Tik0 = 0;
int Tik1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
int tmp = Tik0;
Tik0 = Math.max(Tik0, Tik1 + prices[i]);
Tik1 = Math.max(Tik1, tmp - prices[i] - fee);
}
return Tik0;
}
309. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
问题描述:
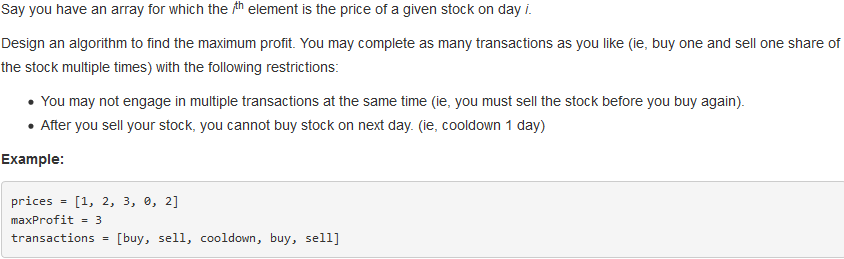
问题求解:
k = INF with cooldown,则递推式变为:
T[i][k][0] = max(T[i - 1][k][0],T[i - 1][k][1] + prices[i])
T[i][k][1] = max(T[i - 1][k][1],T[i - 2][k][0] - prices[i] )
对空间复杂度进行优化,可以在<O(n),O(1)>完成求解。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int Tik0 = 0;
int Tik1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int prev = 0;
for (int price : prices) {
int tmp = Tik0;
Tik0 = Math.max(Tik0, Tik1 + price);
Tik1 = Math.max(Tik1, prev - price); // T[i - 1][k][0] 若是 rest,则T[i - 1][k][0] = T[i - 2][k][0],若卖出,则对于第 i 天 buy 只能选择T[i - 2][k][0]
prev = tmp;
}
return Math.max(Tik0, Tik1);
}
123. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
问题描述:
问题求解:
k = 2,则递推式变为:
T[i][2][0] = max(T[i - 1][2][0],T[i - 1][2][1] + prices[i])
T[i][2][1] = max(T[i - 1][2][1],T[i - 1][1][0] - prices[i])
T[i][1][0] = max(T[i - 1][1][0],T[i - 1][1][1] + prices[i])
T[i][1][1] = max(T[i - 1][1][1],0 - prices[i])
对空间复杂度进行优化,可以在<O(n),O(1)>完成求解。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int Ti20 = 0;
int Ti21 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int Ti10 = 0;
int Ti11 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int price : prices) {
Ti20 = Math.max(Ti20, Ti21 + price);
Ti21 = Math.max(Ti21, Ti10 - price);
Ti10 = Math.max(Ti10, Ti11 + price);
Ti11 = Math.max(Ti11, -price);
}
return Math.max(Ti20, Ti21);
}
188. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
问题描述:
问题求解:
回到最初讨论的问题,k是一个有限常数,则递推式为:
T[i][k][0] = max(T[i - 1][k][0],T[i - 1][k][1] + prices[i])
T[i][k][1] = max(T[i - 1][k][1],T[i - 1][k - 1][0] - prices[i])
需要注意到,当k > n / 2的时候,k就可以看作是INF,因为同一天卖出买入等效于这一天没有操作,所以最多的k次有效交易为n / 2,超过了这个数就有废操作了。
另外,此时每一天有k个状态,所以可以用两个k + 1大小的数组来保存状态量,最终在<O(kn),O(k)>完成求解。
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
if (k > prices.length >>> 1) {
int Tik0 = 0;
int Tik1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int price : prices) {
int tmp = Tik0;
Tik0 = Math.max(Tik0, Tik1 + price);
Tik1 = Math.max(Tik1, tmp - price);
}
return Math.max(Tik0, Tik1);
}
int[] Tik0 = new int[k + 1];
int[] Tik1 = new int[k + 1];
Arrays.fill(Tik1, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
for (int price : prices) {
for (int i = k; i > 0; i--) {
Tik0[i] = Math.max(Tik0[i], Tik1[i] + price);
Tik1[i] = Math.max(Tik1[i], Tik0[i - 1] - price);
}
}
return Math.max(Tik0[k], Tik1[k]);
}
本题如果使用原始的递推式来解的话可以这么修改,因为-1在数组中是没有办法进行初始化的,于是我们可以这样定义递推公式:
dp[i][k][0] : 经过了i天并使用了k次交易后剩余0股的最大利润;
dp[i][k][1] : 经过了i天并使用了k次交易后剩余1股的最大利润;
于是dp[0][k][0] = 0;dp[0][k][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE,这样就可以避免上述的问题。
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if (k >= n / 2) return helper(prices);
int[][][] dp = new int[k + 1][n + 1][2];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
dp[0][i][0] = 0;
dp[0][i][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
dp[i][0][0] = 0;
dp[i][0][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[i][j][0] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1][0], dp[i][j - 1][1] + prices[j - 1]);
dp[i][j][1] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1][1], dp[i - 1][j - 1][0] - prices[j - 1]);
}
}
return dp[k][n][0];
}
private int helper(int[] prices) {
int tik0 = 0;
int tik1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int price : prices) {
int tmp = tik0;
tik0 = Math.max(tik0, tik1 + price);
tik1 = Math.max(tik1, tmp - price);
}
return tik0;
}
【注意】
这次在解决这个问题的时候出现了MLE的情况,原本以为是三维的数组超了内存,但是实际是没有对k的大小进行判断。
所以这里对k的大小进行提前判断是必要的,如果不判断,直接使用dp那么就会MLE。
这里还有一个问题需要考虑,就是一般来说,我们会将问题规约到可以解决的更小的问题上,而且一般是对k进行外层遍历。
换言之,就是和问题给的方式相同,我们先算k次交易各个天数的最大结果,之后下一轮计算k + 1次的,这里没有这么计算的原因很简单,就是在递推式中第i天的交易总额和第i - 1天的k + 1次交易也有关联,也就是在子问题中k的规模并没有更小,所以必须针对每一天算出所有的k后在计算下一天。
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int days = prices.length;
if (k >= days / 2) return helper(prices);
int[][] dp = new int[k + 1][2];
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 0;
dp[i][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
for (int price : prices) {
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i][0], dp[i][1] + price);
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i][1], dp[i - 1][0] - price);
}
}
return Math.max(dp[k][0], dp[k][1]);
}
private int helper(int[] prices) {
int Tik0 = 0;
int Tik1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int price : prices) {
Tik0 = Math.max(Tik0, Tik1 + price);
Tik1 = Math.max(Tik1, Tik0 - price);
}
return Math.max(Tik0, Tik1);
}
动态规划-Stock Problem的更多相关文章
- 二维剪板机下料问题(2-D Guillotine Cutting Stock Problem) 的混合整数规划精确求解——数学规划的计算智能特征
二维剪板机下料问题(2-D Guillotine Cutting Stock Problem) 的混合整数规划精确求解——数学规划的计算智能特征 二维剪板机下料(2D-GCSP) 的混合整数规划是最优 ...
- LeetCode 309. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown (stock problem)
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i. Design an al ...
- LeetCode 188. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV (stock problem)
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i. Design an al ...
- LeetCode 123. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III (stock problem)
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i. Design an al ...
- 精帖转载(关于stock problem)
Note: this is a repost(重新投寄) of my original post here with updated solutions(解决方案) for this problem ...
- LeetCode 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II (stock problem)
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i. Design an al ...
- LeetCode 121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock (stock problem)
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i. If you were ...
- Codeforces Round #598 (Div. 3)- E. Yet Another Division Into Teams - 动态规划
Codeforces Round #598 (Div. 3)- E. Yet Another Division Into Teams - 动态规划 [Problem Description] 给你\( ...
- 2019-ACM-ICPC-南京区网络赛-D. Robots-DAG图上概率动态规划
2019-ACM-ICPC-南京区网络赛-D. Robots-DAG图上概率动态规划 [Problem Description] 有向无环图中,有个机器人从\(1\)号节点出发,每天等概率的走到下 ...
随机推荐
- OneThink后台模型怎么玩?
OneThink 后台模型有个模型类型: 模型下——>设计——>表单显示分组(怎么玩?) 这个将会显示在:内——>发布文章内容的时候: 单选按钮: 内容模块显示: 枚举类型可以这样玩 ...
- 【NotePad++】使用指南
身为一名程序员,这绝对是很常用的工具,但是你真的用了他的全部功能么? 教程参考: [crifan 推荐]轻量级文本编辑器,Notepad 最佳替代品:Notepad++ 注:一个很详细的教程,虽然老, ...
- 8.ajax查询数据
<!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <m ...
- 深究AngularJS——自定义服务详解(factory、service、provider)
前言 3种创建自定义服务的方式. Factory Service Provider 大家应该知道,AngularJS是后台人员在工作之余发明的,他主要应用了后台早就存在的分层思想.所以我们得了解下分 ...
- I/O排查命令
I/O可以说是问题大户,线上的问题经常都是它引起的,很多人却不知道怎么定位这种问题.今天简单介绍一下,在此抛砖引玉. 此类问题我们一般分三步定位:按系统级I/O.进程级I/O.业务级I/O定位即可,一 ...
- Python爬虫基础(一)urllib2库的基本使用
爬虫也就是所谓的网络数据采集,是一种通过多种手段收集网络数据的方式,不光是通过与 API 交互(或者直接与浏览器交互)的方式.最常用的方法是写一个自动化程序向网络服务器请求数据(通常是用 HTML 表 ...
- RabbitMQ(转)
add by zhj: 如果用Python,那可以用celery,它是一个分布式任务队列,它的broker可以选择Rabbitmq/Redis/Mongodb等, celery通过Kombu这个lib ...
- (2.13)Mysql之SQL基础——触发器
(2.13)Mysql之SQL基础——触发器 关键词:Mysql触发器 1.一般形式 -- 0.查看触发器[1]SHOW TRIGGERS;[2]SELECT * FROM `information_ ...
- mysql 约束条件 primary key 主键
primary key字段的值不为空且唯一 约束:not null unique 存储引擎:innodb 对于innodb来说,一张表内必须有一个主键 单列做主键多列做主键(复合主键) 通常都是id字 ...
- 103-advanced-上下文
上下文提供了一种通过组件树传递数据的方法,无需在每个级别手动传递道具. 在典型的React应用程序中,数据通过prop自上而下(父到子)传递,但对于应用程序中许多组件所需的某些类型的道具(例如场所偏好 ...
