谣言检测()《Data Fusion Oriented Graph Convolution Network Model for Rumor Detection》
论文信息
论文标题:Data Fusion Oriented Graph Convolution Network Model for Rumor Detection
论文作者:Erxue Min, Yu Rong, Yatao Bian, Tingyang Xu, Peilin Zhao, Junzhou Huang,Sophia Ananiadou
论文来源:2020,IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
1 Introduction
本文不仅考虑了用户的基本信息和文本内容等静态特征,还考虑了谣言传播关系等动态特征。我们还对特征融合模块和池化模块进行了优化,使模型具有更好的性能。
本文贡献:
- Considering the real dataset from social media, we extract static features such as users’ basic information and text contents, as well as dynamic features such as rumor propagation relations, and propose the data fusion method.
- GCN is introduced into the rumor detection task, which represents the rumor propagation mode. And we propose to select the suitable graph convolution operator to update the node vectors, and improve the feature fusion and pooling module.
- Experiments based on Sina Weibo dataset validate the performance of the propsed GCN-based model for rumor detection.
2 Main
整体框架如下:
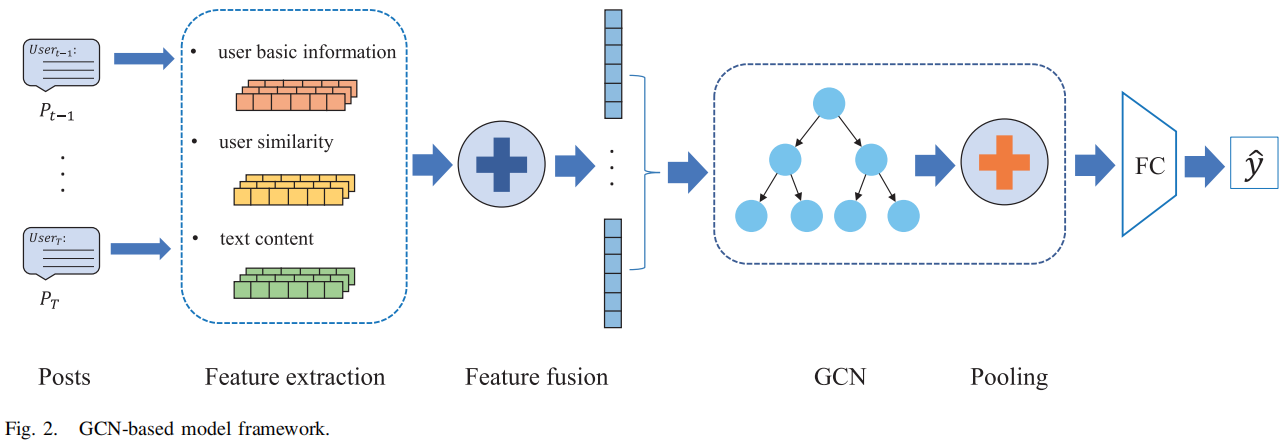
主要包括如下四个模块:
- the feature extraction module
- the feature fusion module
- the graph convolution module
- the pooling module
2.1.1 Features of User Basic Information
常见的 User basic information:
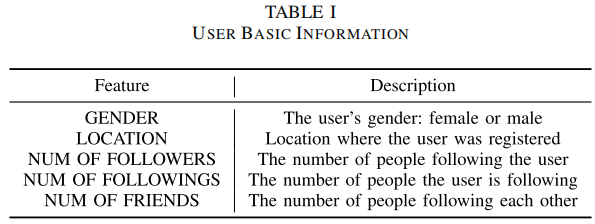
加入这些特征的原因:如 gender 为 女的情况下,是谣言的概率更高。
特征预处理:
对于 gender 采用 One-hot 向量;
对于追随者特征,采用的是 Min-Max normalization ,但是这对于普通用户(如拥有 follower 小的用户)用以造成大部分的数值为 $0$,所以本文采用 $\text{log}$ 处理,如下:
$x^{*}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}\frac{\log x-\log x_{\min }}{\log x_{\max }-\log x_{\min }} & x>0 \\0 & x=0\end{array}\right\} \quad\quad\quad(2)$
其中,$x$ 代表归一化前的追随者数量,$x^{*} $ 表示标准化值,$x_{\min }$ 和 $x_{\max }$ 表示中的最小和最大追随者数量。
2.1.2 User Similarity Feature
考虑用户相似性,首先构造一个 user-event matrix $M$,其中 User 有 $N_{1}$ 个,event 有 $N_{2}$ 个,所以 $M \in N_{1} \times N_{2}$ 。可以预见的是 $M$ 是一个稀疏矩阵,所以本文采用 SVD 分解:
$A=U \Sigma V^{T}\quad\quad\quad(3)$
其中 $A$ 为需要分解的矩阵,$U$ 为左奇异值矩阵,$\Sigma$ 为对角矩阵,对角元素为奇异值,$V$ 为右奇异值矩阵。根据奇异值分解在推荐系统中的应用思想,我们可以取前 $N$ 个奇异值,计算 $\Sigma$ 与 $U$ 之间的点积,得到用户的向量表示,从而实现降维的目的。最后,每个用户都将有一个 $N$ 维的向量表示。两个用户向量之间的距离越近,它们共同参与的事件的数量就越多。基于同样的思想,还可以构建 users-users 之间的矩阵,矩阵元素表示两个用户都参与的事件的数量。然后使用相同的方法为用户生成另一组向量特征,并将基于用户-事件矩阵分解为用户相似性特征的向量相结合。
2.1.3 Representation of Text Content
使用 $BERT_{base}$ Chinese model 提取文本表示。
2.1.4 Feature Fusion Module
$\begin{array}{l}\mu \leftarrow \frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i=0}^{m} h_{i} \\\sigma^{2} \leftarrow \frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i=0}^{m}\left(h_{i}-\mu\right)^{2} \\\hat{h}_{l} \leftarrow \frac{h_{i}-\mu}{\sqrt{\sigma^{2}+\varepsilon}} \\w_{i} \leftarrow \gamma \hat{h}_{i}+\beta\end{array}$
其中,$\gamma$ 和 $\beta$ 是可学习参数。
最后再执行 concat 。
2.1.5 Graph Convolution Module
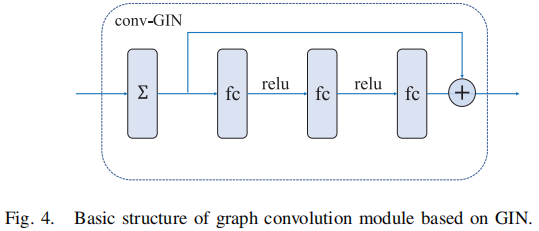
GCN 可以编码局部图的结构和节点特征。其正向传播公式如下:
$H^{(l+1)}=\sigma\left(\tilde{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} \tilde{A} \tilde{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} H^{(l)} W^{(l)}\right) \quad\quad\quad(8)$
$w_{v}^{k}=N N^{k}\left(\left(1+\varepsilon^{k}\right) \cdot w_{v}^{k-1}+\sum\limits _{u \in N(v)} w_{u}^{k-1}\right)$
2.1.6 Pooling Module
常见的池化操作包括 average pooling 和 maximum pooling,分别如 $\text{Eq.11}$ $\text{Eq.12}$ 所示:
$\begin{array}{l}h_{G}=\frac{1}{m} \sum\limits _{i=0}^{m} \widetilde{w_{i}} \\h_{G}=\max \left(\widetilde{w_{0}}, \widetilde{w_{1}}, \ldots, \widetilde{w_{m}}\right)\end{array}$
平均池化是为了获得图中所有节点的平均向量作为图向量,最大池化是选择此维度中所有节点的最大值作为每个维度的输出。
Note:一种新的池化方案,先将节点的表示向量按值降序排列后,选择顶部的 $k$ 个节点,拼接 $k$ 节点向量后,采用一维卷积法进行特征压缩,压缩后的向量为最终的图表示。
本文采取的池化过程:将GIN 每层的输入进行concat ,然后使用 Note 中的池化策略。
$h_{G}=\operatorname{Pooling}\left(\text { Concat }\left(\left\{\widetilde{w_{v}^{k}} \mid k=0,1, \ldots, K\right\}\right) \mid v \in V\right)$
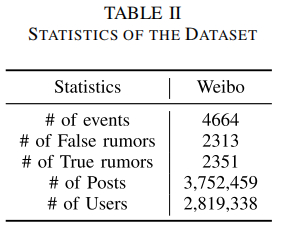
3 Experiment
Dataset
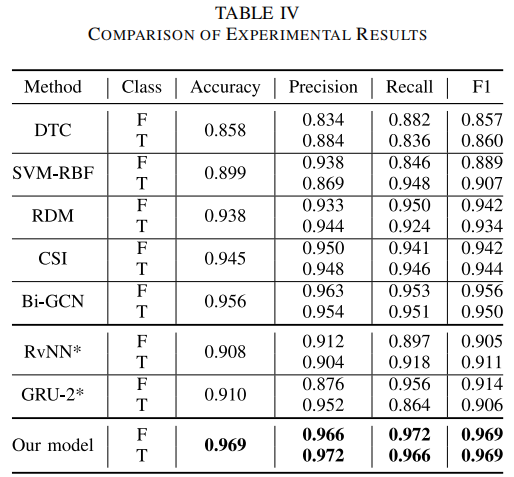
Results
谣言检测()《Data Fusion Oriented Graph Convolution Network Model for Rumor Detection》的更多相关文章
- 谣言检测——《MFAN: Multi-modal Feature-enhanced Attention Networks for Rumor Detection》
论文信息 论文标题:MFAN: Multi-modal Feature-enhanced Attention Networks for Rumor Detection论文作者:Jiaqi Zheng, ...
- 论文解读(FedGAT)《Federated Graph Attention Network for Rumor Detection》
论文信息 论文标题:Federated Graph Attention Network for Rumor Detection论文作者:Huidong Wang, Chuanzheng Bai, Ji ...
- 谣言检测(ClaHi-GAT)《Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks论文作者:Erx ...
- 谣言检测(PSIN)——《Divide-and-Conquer: Post-User Interaction Network for Fake News Detection on Social Media》
论文信息 论文标题:Divide-and-Conquer: Post-User Interaction Network for Fake News Detection on Social Media论 ...
- 谣言检测()——《Debunking Rumors on Twitter with Tree Transformer》
论文信息 论文标题:Debunking Rumors on Twitter with Tree Transformer论文作者:Jing Ma.Wei Gao论文来源:2020,COLING论文地址: ...
- 谣言检测(PLAN)——《Interpretable Rumor Detection in Microblogs by Attending to User Interactions》
论文信息 论文标题:Interpretable Rumor Detection in Microblogs by Attending to User Interactions论文作者:Ling Min ...
- 谣言检测(RDEA)《Rumor Detection on Social Media with Event Augmentations》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Social Media with Event Augmentations论文作者:Zhenyu He, Ce Li, Fan Zhou, Y ...
- 谣言检测()《Rumor Detection with Self-supervised Learning on Texts and Social Graph》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection with Self-supervised Learning on Texts and Social Graph论文作者:Yuan Gao, Xian ...
- 目标检测系列 --- RCNN: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation Tech report
目标检测系列 --- RCNN: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation Te ...
- 谣言检测——(PSA)《Probing Spurious Correlations in Popular Event-Based Rumor Detection Benchmarks》
论文信息 论文标题:Probing Spurious Correlations in Popular Event-Based Rumor Detection Benchmarks论文作者:Jiayin ...
随机推荐
- flush方法和close方法的区别和字符输出流写数据的其他方法和字符输出流的续写和换行
flush方法和close方法的区别 flush:刷新缓冲区,流对象可以继续使用 close:先刷新缓冲区,然后通知系统释放资源.刘对象不可以再被使用了. public class demo02 { ...
- YII自定义小部件
案例如下 common/widgets/TopMenu.php(地址可以自定义位置,命名空间一定要对应) <?php /** * Created by PhpStorm. * Date: 201 ...
- 后端统一处理返回前端日期LocalDateTime格式化去T,Long返回前端损失精度问题
一.前言 我们在实际开发中肯定会遇到后端的时间传到前端是这个样子的:2022-08-02T15:43:50 这个时候前后端就开始踢皮球了,!! 后端说:前端来做就可! 前端说:后端来做就可! 作为一名 ...
- java-循环的应用环境以及数组的创建
1.三种循环结构的更佳适用情况: 1)while:"当..."循环 2)do...while:"直到..."循环 要素1与要素3相同时首选do...while ...
- java学习第一天.day06
方法 方法的优点 1. 使程序变得更简短而清晰. 2. 有利于程序维护. 3. 可以提高程序开发的效率. 4. 提高了代码的重用性. static的作用 static在方法中如果没有添加就只能用对象调 ...
- Magicodes.Pay已支持Volo Abp
Magicodes.Pay已支持Volo Abp 简介 Magicodes.Pay希望打造一个统一支付库,相关库均使用.NET标准库编写,支持.NET Framework以及.NET Core.目前已 ...
- spring使用junit单元测试
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test& ...
- 面向对象06---static关键字
public class Preson { { System.out.println("匿名代码块");// 2 } static { System.out.println(&qu ...
- KingbaseES V8R6 vacuum index_cleanup 选项
描述: 由于索引页的复用不像HEAP TABLE的PAGE复用机制那么简单只要有空闲空间就可以插入.索引页的空闲空间被复用,必须是PAGE的边界内的值才允许插入. 因此索引一旦膨胀,很难收缩,常用的方 ...
- git 根据历史 commitID 拉分支
1. git log -g 查看已commit的信息 2. 根据commit信息找到对应的commitID 3. 执行一下命令来创建新的分支 ### 1. 方法一:创建一个基于commitId的分支, ...
