采用C++实现哈夫曼树的创建并输出哈夫曼编码
一、问题源自一道信息论的作业题:

二、完整代码如下 1 #include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
Node *parent, *lchild, *rchild;
pair<float, string> value;
};
class Tree{
public:
int max;
deque<pair<float, string>> leafs; //存放所有叶子
Node *root;
void hfTree(); //将所有叶子组合成哈夫曼树
Tree(deque<pair<float, string>>); //构造函数
bool findLeaf(const pair<float, string> &); //查找叶子
bool deleteLeaf(const pair<float, string> &); //删除叶子
void sortLeafs();
};
//重载pair的加法运算
pair<float, string> operator+(pair<float, string> pr1, pair<float, string> pr2){
return pair<float, string>(pr1.first + pr2.first, pr1.second + pr2.second);
}
//Tree的构造函数
Tree::Tree(deque<pair<float, string>> lf){
int count = ;
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it = lf.begin(); it != lf.end(); it++){
this->leafs.push_front(*it);
count++;
}
this->max = count;
this->root = NULL;
} //根据键值对判断是否存在该叶子
bool Tree::findLeaf(const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it = this->leafs.begin(); it != this->leafs.end(); it++){
if ((*it) == pr){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//根据键值对删除一个叶子
bool Tree::deleteLeaf(const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it = this->leafs.begin(); it != this->leafs.end(); it++){
if ((*it) == pr){
pair<float, string> temp = this->leafs.back();
while (temp != (*it)){
this->leafs.pop_back();
this->leafs.push_front(temp);
temp = this->leafs.back();
}
this->leafs.pop_back();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//删除deque<Node*>中的一个元素
void deleteNode(deque<Node *> &temp, const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<Node *>::iterator it = temp.begin(); it != temp.end(); it++){
if ((*it)->value == pr){
Node *nd = temp.back();
while (nd->value != pr){
temp.pop_back();
temp.push_front(nd);
nd = temp.back();
}
temp.pop_back();
return;
}
}
}
//根据键值对找到节点并返回其地址
Node *findNode(deque<Node *> &temp, const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<Node *>::iterator it = temp.begin(); it != temp.end(); it++){
if ((*it)->value == pr){
return *it;
}
}
return NULL;
}
bool isIn(deque<Node *> &temp, const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<Node *>::iterator it = temp.begin(); it != temp.end(); it++){
if ((*it)->value == pr){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//根据所存的叶子节点构造哈夫曼树
void Tree::hfTree(){
deque<Node *> temp;
temp.push_front(NULL);
while (this->leafs.begin() != this->leafs.end()){
//对所有叶子排序并取出概率最小的两个叶子节点
this->sortLeafs();
pair<float, string> pr1;
pair<float, string> pr2;
if (this->leafs.back() == this->leafs.front()){//只剩一个叶子了
pr1 = pr2 = this->leafs.front();
this->leafs.pop_front();
}else{
pr1 = this->leafs.front();
this->leafs.pop_front();
pr2 = this->leafs.front();
this->leafs.pop_front();
}
//首次合并,特殊处理
if (temp.front() == NULL){
temp.pop_front();
Node *node = new Node;
if (pr1 == pr2){
node->lchild = node->parent = node->rchild = NULL, node->value = pr1;
}else{
Node *node1 = new Node;
Node *node2 = new Node;
node1->value = pr1, node2->value = pr2, node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node1->lchild = node1->rchild = node2->rchild = node2->lchild = node->parent = NULL;
node1->parent = node2->parent = node, node->lchild = node1, node->rchild = node2;
}
this->leafs.push_front(node->value);
temp.push_front(node);
}else{
Node *node = new Node;
if (pr1 == pr2){//只剩一个节点了而且是被处理过的,表明所有节点处理完毕,直接退出
break;
}else{//新选出的两个节点都是已经处理后得到的根节点
if (isIn(temp, pr1) && isIn(temp, pr2)){
Node *node1 = findNode(temp, pr1);
Node *node2 = findNode(temp, pr2);
node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node->parent = NULL;
node1->parent = node2->parent = node, node->lchild = node1, node->rchild = node2;
this->deleteLeaf(pr1), this->deleteLeaf(pr2), deleteNode(temp, pr1), deleteNode(temp, pr2); //删除选出来的两个节点
this->leafs.push_front(node->value);
}else if (isIn(temp, pr1)){
Node *tp = findNode(temp, pr1);
Node *node2 = new Node;
node2->value = pr2, node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node2->rchild = node2->lchild = node->parent = NULL;
node2->parent = tp->parent = node, node->rchild = node2, node->lchild = tp;
this->deleteLeaf(pr1), this->deleteLeaf(pr2); //删除选出来的节点
this->leafs.push_front(node->value), deleteNode(temp, pr1); //将合并的节点放到生成树和原始集合中
}else if (isIn(temp, pr2)){
Node *tp = findNode(temp, pr2);
Node *node1 = new Node;
node1->value = pr1, node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node1->rchild = node1->lchild = node->parent = NULL;
node1->parent = tp->parent = node, node->lchild = node1, node->rchild = tp;
this->deleteLeaf(pr1), this->deleteLeaf(pr2); //删除选出来的节点
this->leafs.push_front(node->value), deleteNode(temp, pr2); //将合并的节点放到生成树和原始集合中
}else{
Node *node1 = new Node;
Node *node2 = new Node;
node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node->parent = NULL;
node1->value = pr1, node2->value = pr2;
node1->parent = node2->parent = node, node->lchild = node1, node->rchild = node2;
node1->lchild = node2->lchild = node1->rchild = node2->rchild = node->parent = NULL;
this->deleteLeaf(pr1), this->deleteLeaf(pr2); //删除选出来的两个节点
this->leafs.push_front(node->value);
}
}
temp.push_front(node);
}
}
this->root = temp.front();
} //前序遍历一棵树
void prelook(Node *root,string str){
if (root != NULL){
if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL){
cout << "weight:\t" << root->value.first << "\tcontent:\t" << root->value.second << "\tcode:\t"<<str<<endl;
}
if (root->lchild != NULL){
str+="";
prelook(root->lchild,str);
str.pop_back();
}
if (root->rchild != NULL){
str+="";
prelook(root->rchild,str);
str.pop_back();
}
}
}
//重载操作符,实现两个集合的笛卡儿积
Tree operator+(Tree tr1, Tree tr2){
deque<pair<float, string>> temp;
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it1 = tr1.leafs.begin(); it1 != tr1.leafs.end(); it1++){
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it2 = tr2.leafs.begin(); it2 != tr2.leafs.end(); it2++){
temp.push_back(pair<float, string>((*it1).first * (*it2).first, (*it1).second + (*it2).second));
}
}
return Tree(temp);
}
//对一棵树的叶子节点进行排序
void Tree::sortLeafs(){
sort(this->leafs.begin(), this->leafs.end());
}
int main(){
deque<pair<float, string>> temp;
temp.push_front(pair<float, string>(0.5, "a1"));
temp.push_front(pair<float, string>(0.3, "a2"));
temp.push_front(pair<float, string>(0.2, "a3"));
Tree tr = Tree(temp)+Tree(temp)+Tree(temp);
tr.hfTree();
prelook(tr.root,"");
system("pause");
return ;
}
三、修改源代码第276行可以实现对任意次方笛卡尔积结果的编码,第三问输出结果如下:
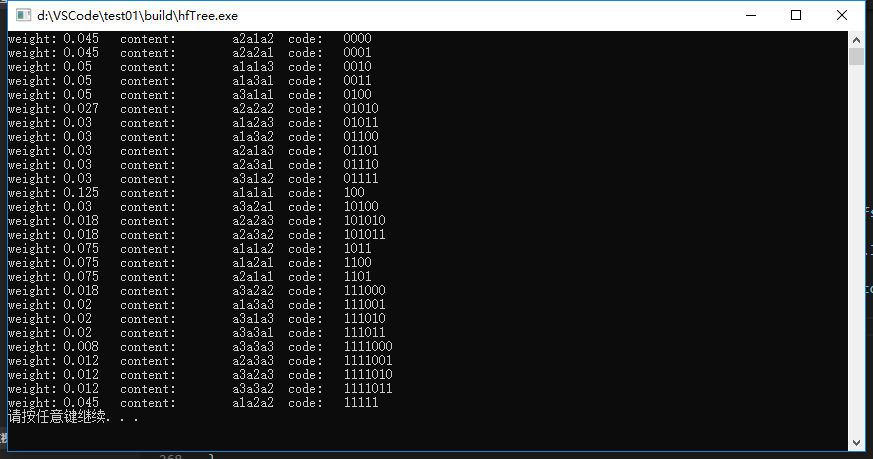
//表明只剩一个叶子了
采用C++实现哈夫曼树的创建并输出哈夫曼编码的更多相关文章
- [C++]哈夫曼树(最优满二叉树) / 哈夫曼编码(贪心算法)
一 哈夫曼树 1.1 基本概念 算法思想 贪心算法(以局部最优,谋求全局最优) 适用范围 1 [(约束)可行]:它必须满足问题的约束 2 [局部最优]它是当前步骤中所有可行选择中最佳的局部选择 3 [ ...
- 数据结构之C语言实现哈夫曼树
1.基本概念 a.路径和路径长度 若在一棵树中存在着一个结点序列 k1,k2,……,kj, 使得 ki是ki+1 的双亲(1<=i<j),则称此结点序列是从 k1 到 kj 的路径. 从 ...
- 【算法】赫夫曼树(Huffman)的构建和应用(编码、译码)
参考资料 <算法(java)> — — Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne <数据结构> ...
- 20172332 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》Java哈夫曼编码实验--哈夫曼树的建立,编码与解码
20172332 2017-2018-2 <程序设计与数据结构>Java哈夫曼编码实验--哈夫曼树的建立,编码与解码 哈夫曼树 1.路径和路径长度 在一棵树中,从一个结点往下可以达到的孩子 ...
- java实现哈弗曼树和哈夫曼树压缩
本篇博文将介绍什么是哈夫曼树,并且如何在java语言中构建一棵哈夫曼树,怎么利用哈夫曼树实现对文件的压缩和解压.首先,先来了解下什么哈夫曼树. 一.哈夫曼树 哈夫曼树属于二叉树,即树的结点最多拥有2个 ...
- C++哈夫曼树编码和译码的实现
一.背景介绍: 给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree).哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的 ...
- 哈夫曼树(三)之 Java详解
前面分别通过C和C++实现了哈夫曼树,本章给出哈夫曼树的java版本. 目录 1. 哈夫曼树的介绍 2. 哈夫曼树的图文解析 3. 哈夫曼树的基本操作 4. 哈夫曼树的完整源码 转载请注明出处:htt ...
- 哈夫曼树(二)之 C++详解
上一章介绍了哈夫曼树的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了哈夫曼树.本章是哈夫曼树的C++实现. 目录 1. 哈夫曼树的介绍 2. 哈夫曼树的图文解析 3. 哈夫曼树的基本操作 4. 哈夫曼树的完整源码 转载 ...
- 哈夫曼树(一)之 C语言详解
本章介绍哈夫曼树.和以往一样,本文会先对哈夫曼树的理论知识进行简单介绍,然后给出C语言的实现.后续再分别给出C++和Java版本的实现:实现的语言虽不同,但是原理如出一辙,选择其中之一进行了解即可.若 ...
随机推荐
- 维生素D补充过多会中毒
虽然我们的物质生活越来越丰富,各种食材几乎一年四季都能够吃到,然而却越来越多的人选择进行补充各种维生素,但是你知道吗?维生素不是我们想象中多吃无害的,补充过多也会要人命,特别是最近非常流行补充的一种维 ...
- 使用 Hexo 在 GitHub 上建立博客 · Utopia's Daily Note
使用 Hexo 在 GitHub 上建立博客 # 写在前面 其实我在一月份的就开始写了三篇博客文章,你没有看错,只是写了三篇,然后,就没有然后了.我还在其中一篇文章中写着,不知道自己能够坚持多久.事实 ...
- javascript中this的四种用法
javascript中this的四种用法 投稿:hebedich 字体:[增加 减小] 类型:转载 时间:2015-05-11我要评论 在javascript当中每一个function都是一个对象,所 ...
- Linux 下的/usr/bin /usr/sbin /usr/local/bin /usr/local/sbin区别
一./usr/sbin与/usr/bin区别: 1./usr/sbin:root权限下的命令属于基本的系统命令,如shutdown,reboot,用于启动系统,修复系统: 2./usr/bin普通用户 ...
- HTTP Continuation or non-HTTP traffic
发现一个 HTTP Continuation or non-HTTP traffic的数据包,之前没有碰到过.不懂其意义,一看长度,显示1460,与TCP segment of a reas ...
- 一个很实用的css技巧简析
我是小雨小雨,专注于更新有趣.实用内容的小伙,如果内容对大家有一点帮助,那么就请动动手指,给个关注.点赞支持一下吧. ^ - ^ 序言 前两天接到一个需求,其中包括一个有序的列表,我们今天就来看看这个 ...
- C++扬帆远航——1
问题及代码: /* * Copyright (c) 2016,烟台大学计算机与控制工程学院 * All rights reserved. * 文件名:test.cpp * 作者:常轩 * 完成日期:2 ...
- 2、【Spark】Spark环境搭建(集群方式)
Spark集群方式搭建结构如图所示,按照主从方式.
- 没有图片的freemarker下载,备份
没有图片的freemarker下载,备份 //以下代码也可以使用/* public String exportApproveCase(@PathVariable("proId") ...
- Web网页布局的主要方式
一.静态布局(static layout) 即传统Web设计,网页上的所有元素的尺寸一律使用px作为单位. 1.布局特点 不管浏览器尺寸具体是多少,网页布局始终按照最初写代码时的布局来显示.常规的pc ...
