[Algorithms] Topological Sort
Topological sort is an important application of DFS in directed acyclic graphs (DAG). For each edge (u, v) from node u to node v in the graph, u must appear before v in the topological sort.
Topological sort has many interesting applications. One of them is job scheduling, in which you are assigned many jobs, each of the job has some prerequisite jobs, that means some jobs must be finished before you can move on to a particular job. If we express this dependency using a DAG (each job is represented as a node; if job u must be finished before job v, there is a directed edge from node u to node v), the topological sort of the graph will be a feasible schedule for the jobs.
The implementation of topogical sort is based on the previous graph representation and the DFS algorithms in this passage. I also implement a function read_digraph to input a directed graph manually. It is basically the same to the function read_graph in the above link. You may refer to it for the formatting style of the graph and more information.
The following graph is used to test the code.
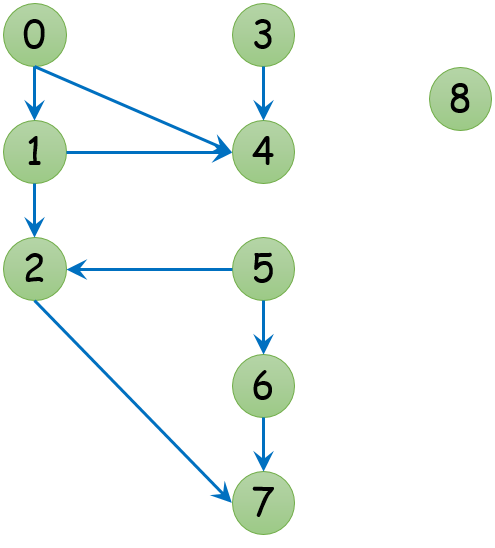
The code is as follows.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set> using namespace std; struct GraphNode {
int label;
vector<GraphNode*> neighbors;
GraphNode(int _label) : label(_label) {}
}; vector<GraphNode*> read_digraph(void) {
int num_nodes, num_edges;
scanf("%d %d", &num_nodes, &num_edges);
vector<GraphNode*> graph(num_nodes);
for (int i = ; i < num_nodes; i++)
graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
int node, neigh;
for (int i = ; i < num_edges; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &node, &neigh);
graph[node] -> neighbors.push_back(graph[neigh]);
}
return graph;
} void topological(vector<GraphNode*>& graph, GraphNode* node, \
unordered_set<GraphNode*>& visited, vector<GraphNode*>& nodes) {
visited.insert(node);
for (GraphNode* neigh : node -> neighbors)
if (visited.find(neigh) == visited.end())
topological(graph, neigh, visited, nodes);
nodes.push_back(node);
} vector<GraphNode*> topological_sort(vector<GraphNode*>& graph) {
vector<GraphNode*> nodes;
unordered_set<GraphNode*> visited;
for (GraphNode* node : graph)
if (visited.find(node) == visited.end())
topological(graph, node, visited, nodes);
reverse(nodes.begin(), nodes.end());
return nodes;
} void graph_test(void) {
vector<GraphNode*> graph = read_digraph();
// Topological Sort
printf("Topological Sort:\n");
vector<GraphNode*> topo_sort = topological_sort(graph);
for (GraphNode* node : topo_sort)
printf("%d ", node -> label);
printf("\n");
} int main(void) {
graph_test();
system("pause");
return ;
}
The above graph is input as as follows:
The output is as follows:
Topological Sort:
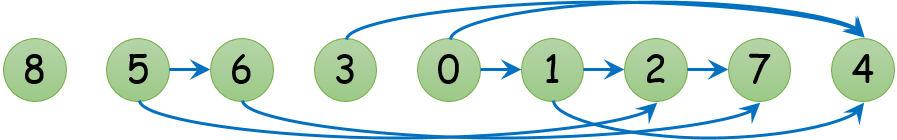
Now if you reorder the nodes of the graph in the order of the topological sort, all the edges will be pointing from left to right, as shown in the graph below.
[Algorithms] Topological Sort的更多相关文章
- 【拓扑排序】【线段树】Gym - 101102K - Topological Sort
Consider a directed graph G of N nodes and all edges (u→v) such that u < v. It is clear that this ...
- topological sort~~~~初学
今天讲了topological sort 问题: 判环:记录入队的点数,若<n则有环,可证: 算法:o(n):queue or stack,而不是o(n^2)枚举 #. 关系运算图(vijos ...
- topological sort
A topological sortof a dag G is a linear ordering of all its vertices such that if G contains anedg ...
- 拓扑排序(Topological Sort)
Graph 拓扑排序(Topological Sort) 假设一个应用场景:你用 C 编写了一个爬虫工具,其中有很多自定义的库:queue.c.queue.h.stack.c.stack.h.heap ...
- Some facts about topological sort
Definition: a topological sort of a DAG G is a sort such that for all edge (i,j) in G, i precedes j. ...
- 6-16 Topological Sort(25 分)
Write a program to find the topological order in a digraph. Format of functions: bool TopSort( LGrap ...
- [MIT6.006] 14. Depth-First Search (DFS), Topological Sort 深度优先搜索,拓扑排序
一.深度优先搜索 它的定义是:递归探索图,必要时要回溯,同时避免重复. 关于深度优先搜索的伪代码如下: 左边DFS-Visit(V, Adj.s)是只实现visit所有连接某个特定点(例如s)的其他点 ...
- Leetcode: Alien Dictionary && Summary: Topological Sort
There is a new alien language which uses the latin alphabet. However, the order among letters are un ...
- [Algorithms] Radix Sort
Radix sort is another linear time sorting algorithm. It sorts (using another sorting subroutine) the ...
随机推荐
- 【HTML+CSS】(2)CSS Sprite雪碧图
1. 雪碧图的使用场景 (1). 静态图片.不随用户信息的变化而变化 (2). 小图片.图片容量比較小 (3). 载入量比較大 一些大图不建议拼成雪碧图,比如淘宝站点的导航图片都是使用的雪碧图. 2. ...
- 总结文件操作函数(一)-C语言
在进程一開始执行,就自己主动打开了三个相应设备的文件.它们是标准输入.输出.错误流.分别用全局文件指针stdin.stdout.stderr表示,相应的文件描写叙述符为0.1.2:stdin具有可读属 ...
- 定时检测Memcached进程是否存在,若不存在自动启动它
由于一台WEB服务器的Memcached死掉而导致在访问网站的某些页面时候打不开.下面脚本会自动检测Memcached的进程,如果挂掉则自动重启Memcached服务. vim memcached_c ...
- android 建数据库 SQLite 存储sd 卡或者内存
android 创建数据库调用SQLiteOpenHelper,一般不直接操作SQLiteDatabase . 是通过SQLiteOpenHelper来获取 public class DBOpenHe ...
- HDU 4969 Just a Joke(积分)
HDU 4969 Just a Joke pid=4969" target="_blank" style="">题目链接 推公式,r′=dr/d ...
- poj 3617 Best Cow Line (字符串反转贪心算法)
Best Cow Line Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 9284 Accepted: 2826 Des ...
- iOS图片上传及压缩
提到从摄像头/相册获取图片是面向终端用户的,由用户去浏览并选择图片为程序使用.在这里,我们需要过UIImagePickerController类来和用户交互. 使用UIImagePickerContr ...
- hdu1025 最大上升字串
Constructing Roads In JGShining's Kingdom Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65 ...
- sublimtext3 自定义编译环境
sublime text是一个非常神奇到编辑器,对于我这种小白来说,感觉比vim好用,但是如果用sublime自带到编译环境到话,是没法向程序汇总输入数据的,所以要自己新建编译命令 { "c ...
- C1编译器的实现
总览 词法.语法分析 分析方案 词法 语法 符号表 类型系统 AST 语义检查 EIR代码生成器 MIPS代码生成器 寄存器分配 体系结构相关特性优化 使用说明 编译 运行 总览 C1语言编译器及流程 ...
