Map Reduce Application(Join)
We are going to explain how join works in MR , we will focus on reduce side join and map side join.
Reduce Side Join
Assuming we have 2 datasets , one is user information(id, name...) , the other is comments made by users(user id, content, date...). We want to join the 2 datasets to select the username and comment they posted. So, this is a typical join example. You can implement all types of join including innter join/outer join/full outer join... As the name indicates, the join is done in reducer.
- We use 2/n mappers for each dataset(table in RDBMS). So, we set this with code below.
MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job,filePath,TextInputFormat.class,UserMapper.class)
MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job,filePath,TextInputFormat.class,CommentsMapper.class)
3 ....
4 MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job,filePath,TextInputFormat.class,OtherMapper.class)
.... - In each mapper, we just need to output the key/value pairs as the job is most done in reducer. In reduce function, when it iterators the values for a given key, reduce function needs to know the value is from which dataset to perform the join. Reducer itself may not be able to distinguish which value is from which mapper(UserMapper or CommentsMapper) for a given key. So, in the map function, we have a chance to mark the value like prefix the value with the mapper name something like that.
outkey.set(userId);
//mark this value so reduce function knows
outvalue.set("UserMapper"+value.toString);
context.write(outkey,outvalue) - In reducer, we get the join type from configuration, perform the join. there can be multiple reducers and with multiple threads.
public void setup(Context context){
joinType = context.getConfiguration().get("joinType");
}
public void reduce(Text text, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws Exception {
listUser.clear();
listComments.clear();
for (Text t: values){
if(isFromUserMapper(t)){
listUser.add(realContent(t));
}else if (isFromCommentsMapper(t)){
listUser.add(realContent(t));
}
}
doJoin(context);
}
private void doJoin(Context context) throws Exception{
if (joinType.equals("inner")){
if(both are not empty){
for (Text user:listUser){
for (Text comm: listComments){
context.write(user,comm);
}
}
}
}else if (){
}.....
}
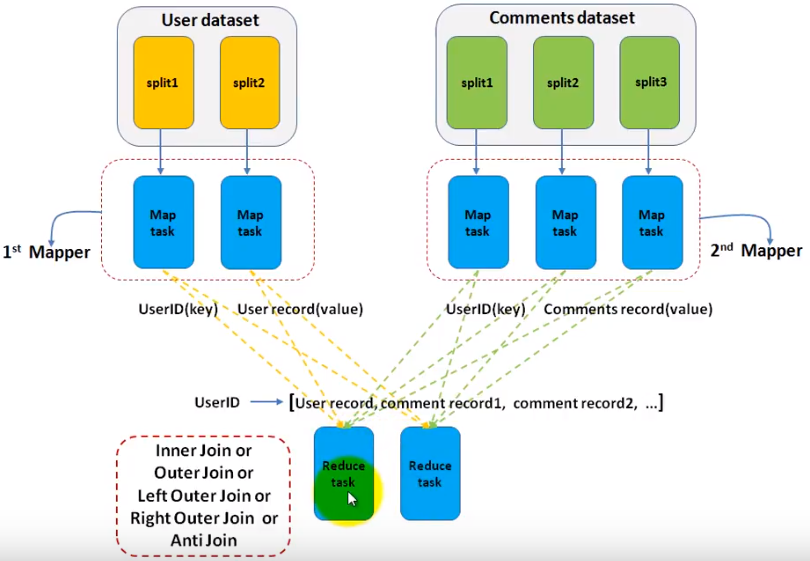
In reducer side join, all data will be sent to reducer side, so, the overall network bandwith is required.
Map Side Join/Replicated Join
As the name indicates , the join operation is done in map side . So, there is no reducer. It is very suitable for join datasets which has only 1 large dataset and others are small dataset and can be read into small memory in a single machine. It is faster than reduce side join (as no reduce phase, no intermediate output, no network transfer)
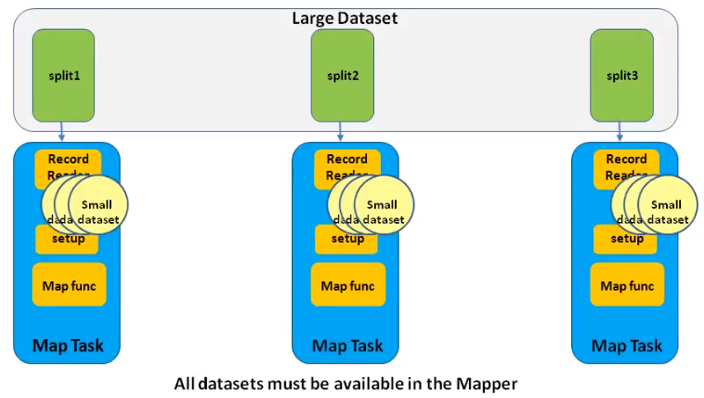
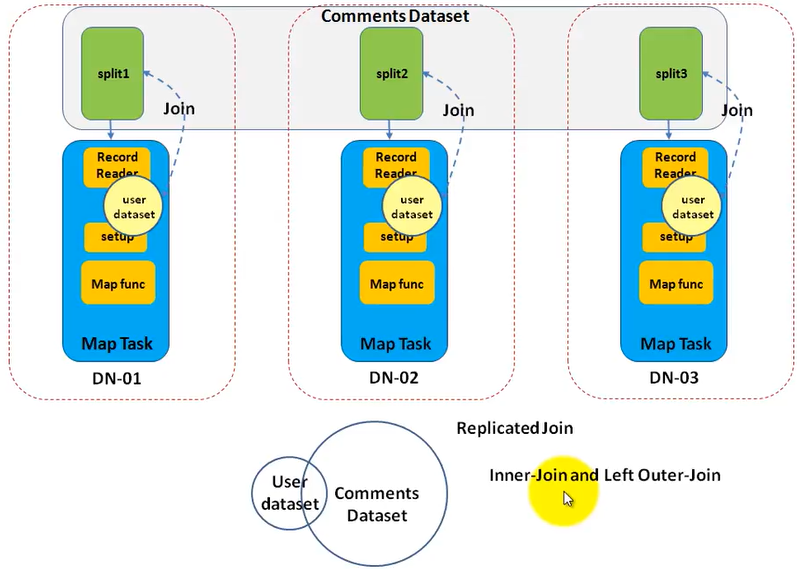
We still use the sample example that is to join user(small) and comments(large) datasets. How to implement it?
- Set the number of reduce to 0.
job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
- Add the small datasets to hadoop distribute cache.The first one is deprecated.
DistributedCache.addCacheFile(new Path(args[]).toUri(),job.getConfiguration)
job.addCacheFile(new Path(filename).toUri());
- In mapper setup function, get the cache by code below. The first one is deprecated. Read the file and put the the key / value in an instance variable like HashMap. This is single thread, so it is safe.
Path[] localPaths = context.getLocalCacheFiles();
URI[] uris = context.getCacheFiles()
- In the mapper function, since, you have the entire user data set in the HashMap, you can try to get the key(comes from the split of comment dataset) from the HashMap. If it exists, you get a match. Because only one split of comments dataset goes into each mapper task, you can only perform an inner join or a left outer join.
What is Hadoop Distributed Cache?
"DistributedCache is a facility provided by the Map-Reduce framework to cache files needed by applications. Once you cache a file for your job, hadoop framework will make it available on(or broadcast to) each and every data nodes (in file system, not in memory) where you map/reduce tasks are running. Then you can access the cache file as local file in your Mapper Or Reducer job. Now you can easily read the cache file and populate some collection (e.g Array, Hashmap etc.) in your code" The cache will be removed once the job is done as they are temporary files.
The size of the cache can be configured in mapred-site.xml.
How to use Distributed Cache(the API has changed)?
- Add cache in driver.
Note the # sign in the URI. Before it, you specify the absolute data path in HDFS. After it, you set a name(symlink) to specify the local file path in your mapper/reducer.
job.addCacheFile(new URI("/user/ricky/user.txt#user"));
job.addCacheFile(new URI("/user/ricky/org.txt#org"));
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
- Read cache in your task(mapper/reduce), probably in setup function.
@Override
protected void setup(
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (context.getCacheFiles() != null
&& context.getCacheFiles().length > 0) { File some_file = new File("user");
File other_file = new File("org");
}
super.setup(context);
}
Reference:
https://www.youtube.com/user/pramodnarayana/videos
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/19678412/number-of-mappers-and-reducers-what-it-means
Map Reduce Application(Join)的更多相关文章
- Map Reduce Application(Partitioninig/Binning)
Map Reduce Application(Partitioninig/Group data by a defined key) Assuming we want to group data by ...
- Map Reduce Application(Top 10 IDs base on their value)
Top 10 IDs base on their value First , we need to set the reduce to 1. For each map task, it is not ...
- Map/Reduce中Join查询实现
张表,分别较data.txt和info.txt,字段之间以/t划分. data.txt内容如下: 201001 1003 abc 201002 1005 def 201003 ...
- hadoop 多表join:Map side join及Reduce side join范例
最近在准备抽取数据的工作.有一个id集合200多M,要从另一个500GB的数据集合中抽取出所有id集合中包含的数据集.id数据集合中每一个行就是一个id的字符串(Reduce side join要在每 ...
- hadoop的压缩解压缩,reduce端join,map端join
hadoop的压缩解压缩 hadoop对于常见的几种压缩算法对于我们的mapreduce都是内置支持,不需要我们关心.经过map之后,数据会产生输出经过shuffle,这个时候的shuffle过程特别 ...
- HIVE 的MAP/REDUCE
对于 JOIN 操作: Map: 以 JOIN ON 条件中的列作为 Key,如果有多个列,则 Key 是这些列的组合 以 JOIN 之后所关心的列作为 Value,当有多个列时,Value 是这些列 ...
- mapreduce: 揭秘InputFormat--掌控Map Reduce任务执行的利器
随着越来越多的公司采用Hadoop,它所处理的问题类型也变得愈发多元化.随着Hadoop适用场景数量的不断膨胀,控制好怎样执行以及何处执行map任务显得至关重要.实现这种控制的方法之一就是自定义Inp ...
- 基于python的《Hadoop权威指南》一书中气象数据下载和map reduce化数据处理及其可视化
文档内容: 1:下载<hadoop权威指南>中的气象数据 2:对下载的气象数据归档整理并读取数据 3:对气象数据进行map reduce进行处理 关键词:<Hadoop权威指南> ...
- Reduce Side Join实现
关于reduce边join,其最重要的是使用MultipleInputs.addInputPath这个api对不同的表使用不同的Map,然后在每个Map里做一下该表的标识,最后到了Reduce端再根据 ...
随机推荐
- oracle之DQL
一.单表查询 语法:select * from table where 条件 group by 分组 having 过滤分组 order by 排序 --查询平均工资低于2000的部门的最大工资和平均 ...
- 浅析OC语言
学习一门开发语言,首先要掌握的它的基本语法,这可能几天就能学会,但如果要融会贯通,就得去学习这门语言的框架和一些库,再结合一些项目的应用,这可能需要花几年的时间. OC是C语言的一个超集,是一门面向对 ...
- 国产Linux下开发正式开工(deepin)
配置开发环境 1.一般工具 在深度商店安装QQ,微信,安装一般软件WPS,Navicat数据库工具,文本编辑notepadqq. 影视娱乐爱奇艺,优酷,酷狗. 2.安装主要的开发环境 (1)c# 深度 ...
- stack permutation
#include <iostream> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; bool ch ...
- POJ 2208--Pyramids(欧拉四面体体积计算)
Pyramids Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 3451 Accepted: 1123 Specia ...
- 奇(qi)谋(ji)巧(yin)计(qiao)
一.打表法 0.http://oeis.org/ 1.差分序列:https://blog.csdn.net/wu_tongtong/article/details/79115921 对于一个多项式产生 ...
- springboot-redis缓存
Redis缓存使用 1. 引入依赖(可能已经引入了):spring-boot-starter-cache 2. 在application.yml配置文件中配置spring:redis:host/p ...
- 转型大数据之学前准备,掌握linux(一)
导语:为什么要学习linux?学到什么程度? 大数据技术是运行在集群,且是linux操作系统这样的集群当中的,所以学习大数据之前,你得先掌握了linux的简单操作,没错,我们不是专门的做linux工作 ...
- MySQL必知必会 读书笔记三:检索数据和数据排序
检索数据 SELECT语句 它的用途是从一个或多个表中检索信息. 为了使用SELECT检索表数据,必须至少给出两条信息--想选择什 么,以及从什么地方选择. 检索单个列 SELECT col_1 FR ...
- 慎使用sql的enum字段类型
在sql的优化中,会有同学提到一点:使用enum字段类型,代替其他tinyint等类型.以前这也是不少人喜欢优化的,但是现在细想,是非常不合理的. 优点: 1.可以设置区间范围,比如设置性别:1男2女 ...
