Spring 使用介绍(十二)—— Spring Task
一、概述
1、jdk的线程池和任务调用器分别由ExecutorService、ScheduledExecutorService定义,继承关系如下:

ThreadPoolExecutor:ExecutorService的实现类,其构造函数提供了灵活的参数配置,可构造多种类型的线程池,详细可参考JAVA进阶----ThreadPoolExecutor机制
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor:ScheduledExecutorService的实现类,用于任务调度
2、spring task对定时任务的两个抽象:
- TaskExecutor:与jdk中Executor相同,引入的目的是为定时任务的执行提供线程池的支持
- TaskScheduler:对定时任务的抽象
继承关系如下:
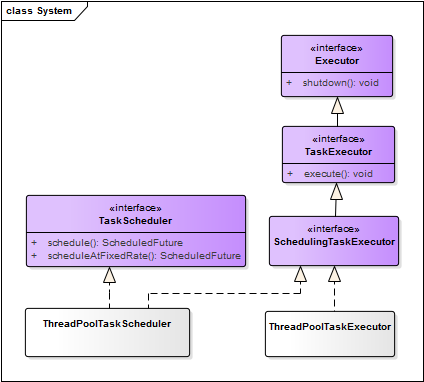
任务执行器与调度器的实现类分别为ThreadPoolTaskExecutor、ThreadPoolTaskScheduler
TaskScheduler需要传入一个Runnable的任务做为参数,并指定需要周期执行的时间或者触发器(Trigger)。
spring定义了Trigger接口的实现类CronTrigger,支持使用cron表达式指定定时策略,使用如下:
scheduler.schedule(task, new CronTrigger("30 * * * * ?"));
二、定时任务
spring定时任务的使用和配置非常简单,支持xml配置和注解两个方式
1、XML配置方式
任务类
@Component
public class TestTask {
public void job() {
System.out.println("hello matt!");
}
}
配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/task
http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-4.1.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.matt.schedule"/> <!-- 任务调度器-->
<task:scheduler id="myScheduler" pool-size="10"/> <!-- 任务配置-->
<task:scheduled-tasks scheduler="myScheduler">
<task:scheduled ref="testTask" method="job" cron="0/2 * * * * ?"/>
</task:scheduled-tasks>
</beans>
测试
public class TaskTest {
@Test
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-context.xml");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
}
}
2、注解方式
任务类
@Component
public class TestTask {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/2 * * * * ?")
public void job() {
System.out.println("hello matt!");
}
}
配置
<!-- 任务调度器-->
<task:scheduler id="myScheduler" pool-size="10"/> <!-- 开启任务注解-->
<task:annotation-driven scheduler="myScheduler"/>
测试代码与xml配置方式相同
补充说明:
- 使用<task:executor>配置任务执行器,即实例化ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
- 使用<task:scheduler>配置任务调度器,即实例化ThreadPoolTaskScheduler
- 两种方式的任务调度器不指定时,默认会使用只有一个线程的调用器,关于配置的详细介绍和默认参数,可参考xsd文档 http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-4.1.xsd
疑问:
有些项目同时指定任务执行器和调度器,如下:
<!-- 启用注解驱动的定时任务 -->
<task:annotation-driven scheduler="myScheduler" executor="myExecutor"/>
<!-- 配置定时任务的线程池 -->
<task:scheduler id="myScheduler" pool-size="10"/>
<task:executor id="myExecutor" pool-size="10" />
存在两个线程池,两者的关系是怎样的?执行器用的是哪个线程池?
经验证,定时任务执行时,使用的是任务调度器的线程池,任务执行器的设置对定时任务的执行没有影响,测试代码如下:
任务类
@Component
public class TestTask {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?")
public void job1() {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(String.format("%s*******%s", sdf.format(new Date()), "job1"));
} @Scheduled(cron = "0/10 * * * * ?")
public void job2() {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(String.format("%s*******%s", sdf.format(new Date()), "job2")); try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
}
配置与疑问中相同
测试(测试时,通过改变线程池的大小进行验证)
public class TaskTest {
@Test
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-context.xml");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1000);
}
}
3、cron表达式
spring支持6个参数的cron表达式,格式如下:
{秒} {分} {时} {日期} {月} {星期}
- 秒:必填项,允许的值范围是0-59,支持的特殊符号包括'-*/,',','表示特定的某一秒才会触发任务,'-'表示一段时间内会触发任务,'*'表示每一秒都会触发,'/'表示从哪一个时刻开始,每隔多长时间触发一次任务。
- 分:必填项,允许的值范围是0-59,支持的特殊符号和秒一样,含义类推
- 时:必填项,允许的值范围是0-23,支持的特殊符号和秒一样,含义类推
- 日期:必填项,允许的值范围是1-31,支持的特殊符号相比秒多了
?,表示与{星期}互斥,即意味着若明确指定{星期}触发,则表示{日期}无意义,以免引起冲突和混乱 - 月:必填项,允许的值范围是1-12(JAN-DEC),支持的特殊符号与秒一样,含义类推
- 星期:必填项,允许值范围是1~7 (SUN-SAT),1代表星期天(一星期的第一天),以此类推,7代表星期六,支持的符号相比秒多了
?,表达的含义是与{日期}互斥,即意味着若明确指定{日期}触发,则表示{星期}无意义。
示例:
0 0 12 * * ? 每天中午12点触发
0 * 14 * * ? 每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发
0 0/5 14 * * ? 每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发
0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发
关于cron表达式的详细介绍可参考spring定时任务详解
三、异步调用
spring提供@Async注解,可很方便的实现异步调用,简单示例如下:
接口及实现类
public interface Hello {
void doSomething1();
void doSomething2();
}
@Component
public class HelloImpl implements Hello {
@Async
@Override
public void doSomething1() {
System.out.println(String.format("thread:%d **** doSomething1", Thread.currentThread().getId())); } @Async("myExecutor2")
@Override
public void doSomething2() {
System.out.println(String.format("thread:%d **** doSomething2", Thread.currentThread().getId()));
}
}
配置
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.matt.schedule"/>
<!-- 开启@Async注解支持 -->
<task:annotation-driven executor="myExecutor1"/>
<!-- 定义执行器 -->
<task:executor id="myExecutor1" pool-size="10" />
<task:executor id="myExecutor2" pool-size="10" />
测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:spring-context.xml")
public class SpringTestBase {}
public class AsyncTest extends SpringTestBase {
@Autowired
private Hello hello;
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println(String.format("main thread:%d **** doSomething1", Thread.currentThread().getId()));
hello.doSomething1();
hello.doSomething2();
}
}
// 输出:
// main thread:1 **** doSomething1
// thread:20 **** doSomething2
// thread:19 **** doSomething1
说明:@Async默认使用<task:annotation-driven/>指定的执行器,当存在多个执行器时,可通过@Async的value属性单独指定
参考:
Spring 使用介绍(十二)—— Spring Task的更多相关文章
- spring boot / cloud (十二) 异常统一处理进阶
spring boot / cloud (十二) 异常统一处理进阶 前言 在spring boot / cloud (二) 规范响应格式以及统一异常处理这篇博客中已经提到了使用@ExceptionHa ...
- Spring Cloud(十二):分布式链路跟踪 Sleuth 与 Zipkin【Finchley 版】
Spring Cloud(十二):分布式链路跟踪 Sleuth 与 Zipkin[Finchley 版] 发表于 2018-04-24 | 随着业务发展,系统拆分导致系统调用链路愈发复杂一个前端请 ...
- thinkPHP 模板中的语法知识 详细介绍(十二)
原文:thinkPHP 模板中的语法知识 详细介绍(十二) 本章节:介绍模板中的语法,详细的语法介绍 一.导入CSS和JS文件 ==>记住常量的是大写 1.css link .js sc ...
- Spring Cloud第十二篇 | 消息总线Bus
本文是Spring Cloud专栏的第十二篇文章,了解前十一篇文章内容有助于更好的理解本文: Spring Cloud第一篇 | Spring Cloud前言及其常用组件介绍概览 Spring ...
- Spring Boot2 系列教程(三十二)Spring Boot 整合 Shiro
在 Spring Boot 中做权限管理,一般来说,主流的方案是 Spring Security ,但是,仅仅从技术角度来说,也可以使用 Shiro. 今天松哥就来和大家聊聊 Spring Boot ...
- Spring Security(十二):5. Java Configuration
General support for Java Configuration was added to Spring Framework in Spring 3.1. Since Spring Sec ...
- (转)Spring Boot 2 (十):Spring Boot 中的响应式编程和 WebFlux 入门
http://www.ityouknow.com/springboot/2019/02/12/spring-boot-webflux.html Spring 5.0 中发布了重量级组件 Webflux ...
- Spring Boot 2 (十):Spring Boot 中的响应式编程和 WebFlux 入门
Spring 5.0 中发布了重量级组件 Webflux,拉起了响应式编程的规模使用序幕. WebFlux 使用的场景是异步非阻塞的,使用 Webflux 作为系统解决方案,在大多数场景下可以提高系统 ...
- Spring学习(十)Spring知识点汇总
一.基础概念 Q:Spring是什么? 定义:Spring是一个轻量级的IoC(控制反转)和AOP容器框架. 目的:用于简化企业应用程序的开发,使得开发者只需要关心业务需求. 常见的配置方式: 基于X ...
- Spring实战(十)Spring AOP应用——为方法引入新功能、为对象引入新方法
切面最基本的元素是通知和切点,切点用于准确定位应该在什么地方应用切面的通知. 1.Spring借助AspectJ的切点表达式语言来定义Spring切面 在Spring中,要使用AspectJ的切点表达 ...
随机推荐
- 【原创】分布式之redis的三大衍生数据结构
引言 说起redis的数据结构,大家可能对五大基础数据类型比较熟悉:String,Hash,List,Set,Sorted Set.那么除此之外,还有三大衍生数据结构,大家平时是很少接触的,即:bit ...
- ASP.NET MVC5+EF6+EasyUI 后台管理系统(90)-EF 扩展操作
上一篇讲了EF直接执行SQL与存储过程的用 法 这次我们来看 EntityFramework-Plus(免费开源) 库的用法相比其他扩展库,这个更加新并且用法更加简单 这是一个对Entity Fram ...
- WCF系列教程之WCF服务配置工具
本文参考自http://www.cnblogs.com/wangweimutou/p/4367905.html Visual studio 针对服务配置提供了一个可视化的配置界面(Microsoft ...
- SNMP 获取交换机端口相关信息
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ysdaniel/article/details/37927541 我们想用snmpwalk查看网络设备的端口,MIB库中相关定义的信息如下: [ ...
- H5 id选择器和class选择器
11-id选择器和class选择器 第一段文字 第二段文字 第三段文字 --> 第一段文字 第二段文字 第三段文字 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=&qu ...
- 最值反演 min-max容斥
说实话这些博客早晚都要整理后上m***999. 最值反演是针对一个集合中最大/最小值的反演. \[ \max\{S\}=\sum_{T\subset S}(-1)^{|T|+1}\min\{T\} \ ...
- POJ - 3264 线段树模板题 询问区间最大最小值
这是线段树的一个模板题,给出一串数字,然后询问区间的最大最小值. 这个其实很好办,只需把线段树的节点给出两个权值,一个是区间的最小值,一个是区间的最大值,初始化为负无穷和正无穷,然后通过不断地输入节点 ...
- ElasticSearch 入门
http://www.oschina.net/translate/elasticsearch-getting-started?cmp ElasticSearch 简单入门 返回原文英文原文:Getti ...
- 软工网络15团队作业7——Alpha冲刺之事后诸葛亮
Deadline: 2018-5-16 22:00PM,以博客提交至班级博客时间为准 事后诸葛亮分析 Alpha冲刺,很多同学经历了"Learning by doing"的学一门新 ...
- 前端开发之jQuery库
使用jquery开发的时候,如果我们不想使用自己的jquery文件,那么可以引用现成的地址.方便日常开发使用 jquery-2.0以上版本 (注!不再支持IE 6/7/8) jquery-2.0.0百 ...
