spring bean 加载过程(spring)
以classpathXmlApplication为例
入口方法包含3个部分,
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
1.继承父类,没什么东西
2.设置配置文件
3.执行refresh方法(关键)。下面我们就这两个方法看看内部实现
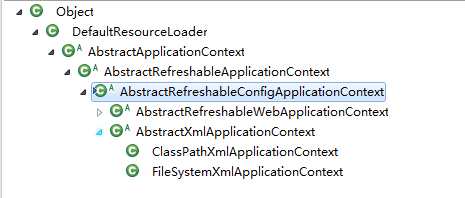
设置配置文件,这块其实没什么东西,就是给context对象设置一个configLocations的数组,我们看一下context类的继承关系
下面看重点的refresh方法
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {//锁住一个对象,防止多线程同时执行初始化的操作
// Prepare this context for refreshing.准备上下文,这里设置一下开始实现,准备propery等
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
这个代码有点长,我们把每个方法干什么先研究一下,在深入看每个方法怎么实现的。
从7行开始看,这个方法是为了一个refreshBeanFactory。返回的类是ConfigurableListableBeanFactory,而这个factory是一个接口,我们待会看看这个接口有哪些实现,先看看这个方法内部实现
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
我们看到最后return的beanFactory就是ConfigurableListableBeanFactory。而这个接口只有一个default实现类DefaultListableBeanFactory。我们看看这个类主要有哪些成员变量
private boolean allowEagerClassLoading = true;
/** Optional OrderComparator for dependency Lists and arrays */
private Comparator<Object> dependencyComparator;
/** Resolver to use for checking if a bean definition is an autowire candidate */
private AutowireCandidateResolver autowireCandidateResolver = new SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver();
/** Map from dependency type to corresponding autowired value */
private final Map<Class<?>, Object> resolvableDependencies = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, Object>(16);
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>(256);
/** Map of singleton and non-singleton bean names, keyed by dependency type */
private final Map<Class<?>, String[]> allBeanNamesByType = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, String[]>(64);
/** Map of singleton-only bean names, keyed by dependency type */
private final Map<Class<?>, String[]> singletonBeanNamesByType = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, String[]>(64);
/** List of bean definition names, in registration order */
private volatile List<String> beanDefinitionNames = new ArrayList<String>(256);
/** List of names of manually registered singletons, in registration order */
private volatile Set<String> manualSingletonNames = new LinkedHashSet<String>(16);
/** Cached array of bean definition names in case of frozen configuration */
private volatile String[] frozenBeanDefinitionNames;
/** Whether bean definition metadata may be cached for all beans */
private volatile boolean configurationFrozen = false;
这些成员变量有机会我们一个个分析下,我们知道每个bean 有一个beanDefinition对象来定义。在13行,我们看到有一个BeanDefinition的Map,我们随便调试一下,看看这个里面存了什么东西。
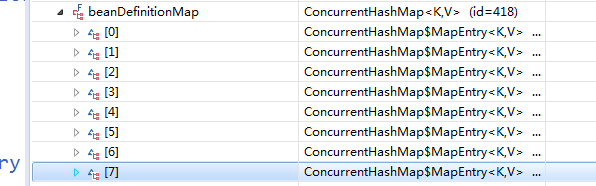
这里面竟然只有7个对象,分别是:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor、DefaultEventListenerFactory、MessageResolver、EventListenerMethodProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、PropertiesFactoryBean、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。这七个对象怎么来的呢,举个例子来看ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,这个类说明是,当配置文件中
Registered by default when using {@code <context:annotation-config/>} or
* {@code <context:component-scan/>}有这两个配置的时候,便会注入这么个类。好吧,那我们看看在哪里register的。我们猜测是在
refreshBeanFactory();这个方法里面。那看看这个方法
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
我们看到第7行,创建了一个DefaultListableBeanFactory ,第10行有loadBeanDefinition。应该是在这里处理的。我们还是先调试下看看。执行7行代码,这个时候beanDefinitionMap是空的。执行完10行代码,我们的beanDefinitionMap有值了。这里面为了加深理解,我们在我们的spring-config.xml文件中加一个bean看看会怎么样。原来的spring-config.xml文件如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.1.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <context:component-scan base-package="com.newbie.common"></context:component-scan> <util:properties id="systemProperties" location="classpath:conf/user.properties" /> </beans>
我们随便加一个bean,如下图所示,有多个一个beanDefinition。所以这个地就是定义所以beanDefinition的入口,而我们从autowire的bean是由相关processor处理的,这个今后如果有时间的话,我们在分析。我们继续往下看

我们回到原来的refresh方法里面。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
我们现在知道第7行返回的这个ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 有我们所有的beanDefintion。这个方法是给ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 设置了若干预设变量,现在我们也不清楚这个变量是干嘛的,我们先跳过这个方法,等回头再分析他。
第14行postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory )。我们看看这个代码是做什么事情,我们有一个关注点,我们@autowired的bean是怎么被处理的。这个代码,会根据不同context子类加入不同Processors,这个我们也暂时不分析他,等回头再看
第17行invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory )。这个方法应该就是能看到bean是如何创建的。这个代码比较长,我们先把调用关系简单画出来
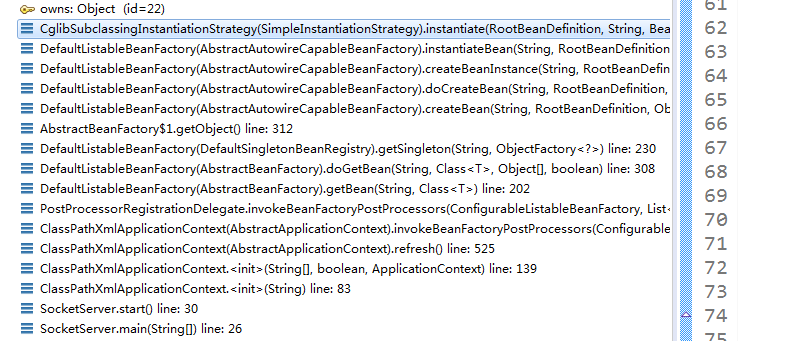
执行invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors之后,这里主要是讲各个processors类注册进去,这里需要获得具体的bean了,根据beanName和BeanDefinition。如何获得bean,通过DefaultListableBeanFactory的getBean方法,这里判断bean是单利还是原型的,进入不同的getBean的逻辑,之后调用的AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的createBean方法,之后通过反射来获得对应的bean。注意看一下doCreateBean方法里面的populateBean()方法,这里能够完成对属性的注入。
上面这个方法,我们调用的时候发现就注册了一个ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,也不知道干嘛的。后来通过搜索了解到这个方法主要是用于处理spring的后置处理器的相关内容,参考https://www.cnblogs.com/sishang/p/6588542.html和https://www.cnblogs.com/sishang/p/6576665.html。
spring bean 加载过程(spring)的更多相关文章
- Spring bean加载2--FactoryBean情况处理
Spring bean加载2--FactoryBean情况处理 在Spring bean加载过程中,每次bean实例在返回前都会调用getObjectForBeanInstance来处理Factory ...
- 工厂模式模拟Spring的bean加载过程
一.前言 在日常的开发过程,经常使用或碰到的设计模式有代理.工厂.单例.反射模式等等.下面就对工厂模式模拟spring的bean加载过程进行解析,如果对工厂模式不熟悉的,具体可以先去学习一下工厂 ...
- Spring IOC bean加载过程
首先我们不要在学习Spring的开始产生畏难情绪.Spring没有臆想的那么高深,相反,它帮我们再项目开发中制定项目框架,简化项目开发.它的主要功能是将项目开发中繁琐的过程流程化,模式化,使用户仅在固 ...
- 07.Spring Bean 加载 - BeanDefinitionReader
基本概念 BeanDefinitionReader ,该接口的作用就是加载 Bean. 在 Spring 中,Bean 一般来说都在配置文件中定义.而在配置的路径由在 web.xml 中定义.所以加载 ...
- SSH 之 Spring的源码(一)——Bean加载过程
看看Spring的源码,看看巨人的底层实现,拓展思路,为了更好的理解原理,看看源码,深入浅出吧.本文基于Spring 4.0.8版本. 首先Web项目使用Spring是通过在web.xml里面配置 o ...
- 看看Spring的源码(一)——Bean加载过程
首先Web项目使用Spring是通过在web.xml里面配置org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener初始化IOC容器的. <li ...
- spring bean加载顺序指定方式之一
在某些情况下,我们在容器启动的时候做一些事情,举个例子,加载缓存等.. 此时我们会希望某个bean先被加载并执行其中的afterpropertiesset方法. 因为spring默认是通过contex ...
- Spring bean加载之1:BeanFactory和FactoryBean
BeanFactory BeanFactory:以Factory结尾,表示它是一个工厂类(接口),用于管理Bean的一个工厂.在Spring中,BeanFactory是IOC容器的核心接口,它的职责包 ...
- Spring bean加载多个配置文件
除了写很简单的加载一个xml,加载多个的情况一直没用到,在公司里也不会由自己处理这个问题,现在需要用到了,就研究验证一下. 使用的案例还是上面的例子. 只有,将原来的beans.xml分成两个部分. ...
随机推荐
- 利用marquee对html页面文本滚动
<marquee direction="up" style="width:200px;height:80px; " scrolldelay="3 ...
- QT5.5.1 为Qtcreator 编译的程序添加管理员权限
QT版本:5.5.1 QT Creator QT Creator 编译出来的程默认是不带管理员权限的.有时是需要管理员权限. 第一步: 创建文件 uac.manifest 添加如下代码 <?xm ...
- Android官方教程翻译(4)——启动另一个Activity
Starting Another Activity 启动另一个Activity PREVIOUSNEXT THIS LESSON TEACHES YOU TO 这节课教你 1. Respond t ...
- vs2008 命令窗口 命令窗口 和 反汇编窗口的使用
visual studio 的功能相当强大,用了一年多,也只是了解了皮毛.今天学习了一下VS2008 的 即时窗口 命令窗口 和 反汇编窗口的使用.之所以会想到要使用即时窗口是因为最近开发遇到了一个问 ...
- Cannot refer to a non-final variable inside an inner class defined in a different method
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1299837/cannot-refer-to-a-non-final-variable-inside-an-inner-clas ...
- Python小技巧1
原文: http://blog.csdn.net/jclass/article/details/6144647 一. 打印并输出到文件 >>> print("aa" ...
- WPF 图形绘制 及各种线帽、箭头的实现
原文:WPF 图形绘制 及各种线帽.箭头的实现 /// <summary> /// 矩形类 /// </summary> public sealed ...
- 关闭Mac OS 的Rootless
今天在使用mac的时候,需要删除 /usr/bin/下的 自带的php文件.然后提示Operation not permitted 使用sudo 依然不可以,通过google 得到解决方案. 需要关闭 ...
- glibc头文件和宏定义
头文件没啥好说的,无非就是" "和< >的区别,这估计只要是学过C/C++的人都明白.现在的编译器对头文件的包含顺序没有要求,但老的C实现则不一样.当然,我们现在无需关 ...
- Bootstrap路径导航
@{ Layout = null;}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <meta name="viewport&q ...
