【Flink】Flink 底层RPC框架分析
1. 前言
对于Flink中各个组件(JobMaster、TaskManager、Dispatcher等),其底层RPC框架基于Akka实现,本文着重分析Flink中的Rpc框架实现机制及梳理其通信流程。
2. Akka介绍
由于Flink底层Rpc是基于Akka实现,我们先了解下Akka的基本使用。
Akka是一个开发并发、容错和可伸缩应用的框架。它是Actor Model的一个实现,和Erlang的并发模型很像。在Actor模型中,所有的实体被认为是独立的actors。actors和其他actors通过发送异步消息通信。Actor模型的强大来自于异步。它也可以显式等待响应,这使得可以执行同步操作。但是,强烈不建议同步消息,因为它们限制了系统的伸缩性。每个actor有一个邮箱(mailbox),它收到的消息存储在里面。另外,每一个actor维护自身单独的状态。一个Actors网络如下所示:
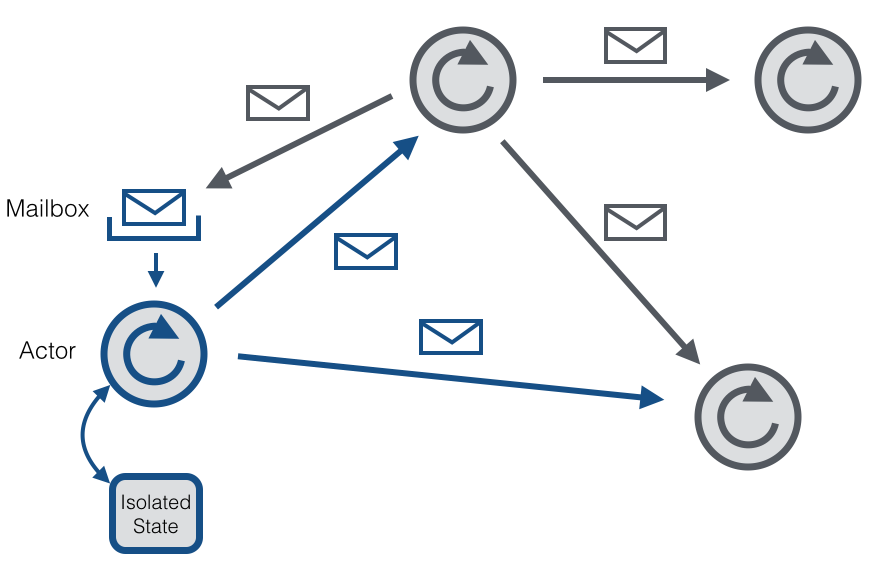
每个actor是一个单一的线程,它不断地从其邮箱中poll(拉取)消息,并且连续不断地处理。对于已经处理过的消息的结果,actor可以改变它自身的内部状态或者发送一个新消息或者孵化一个新的actor。尽管单个的actor是自然有序的,但一个包含若干个actor的系统却是高度并发的并且极具扩展性的。因为那些处理线程是所有actor之间共享的。这也是我们为什么不该在actor线程里调用可能导致阻塞的“调用”。因为这样的调用可能会阻塞该线程使得他们无法替其他actor处理消息。
2.1. 创建Akka系统
Akka系统的核心ActorSystem和Actor,若需构建一个Akka系统,首先需要创建ActorSystem,创建完ActorSystem后,可通过其创建Actor(注意:Akka不允许直接new一个Actor,只能通过 Akka 提供的某些 API 才能创建或查找 Actor,一般会通过 ActorSystem#actorOf和ActorContext#actorOf来创建 Actor),另外,我们只能通过ActorRef(Actor的引用, 其对原生的 Actor 实例做了良好的封装,外界不能随意修改其内部状态)来与Actor进行通信。如下代码展示了如何配置一个Akka系统。
// 1. 构建ActorSystem
// 使用缺省配置
ActorSystem system = ActorSystem.create("sys");
// 也可显示指定appsys配置
// ActorSystem system1 = ActorSystem.create("helloakka", ConfigFactory.load("appsys"));
// 2. 构建Actor,获取该Actor的引用,即ActorRef
ActorRef helloActor = system.actorOf(Props.create(HelloActor.class), "helloActor");
// 3. 给helloActor发送消息
helloActor.tell("hello helloActor", ActorRef.noSender());
// 4. 关闭ActorSystem
system.terminate();
在Akka中,创建的每个Actor都有自己的路径,该路径遵循 ActorSystem 的层级结构,大致如下:
本地:akka://sys/user/helloActor
远程:akka.tcp://sys@l27.0.0.1:2020/user/remoteActor
其中本地路径含义如下:
- sys,创建的ActorSystem的名字;
- user,通过ActorSystem#actorOf和ActorContext#actorOf 方法创建的 Actor 都属于/user下,与/user对应的是/system, 其是系统层面创建的,与系统整体行为有关,在开发阶段并不需要对其过多关注;
- helloActor,我们创建的HelloActor。
其中远程部分路径含义如下:
- akka.tcp,远程通信方式为tcp;
- sys@127.0.0.1:2020,ActorSystem名字及远程主机ip和端口号。
2.2. 根据path获取Actor
若提供了Actor的路径,可以通过路径获取到ActorRef,然后与之通信,代码如下所示:
ActorSystem system = ActorSystem.create("sys");
ActorSelection as = system.actorSelection("/path/to/actor");
Timeout timeout = new Timeout(Duration.create(2, "seconds"));
Future<ActorRef> fu = as.resolveOne(timeout);
fu.onSuccess(new OnSuccess<ActorRef>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(ActorRef actor) {
System.out.println("actor:" + actor);
actor.tell("hello actor", ActorRef.noSender());
}
}, system.dispatcher());
fu.onFailure(new OnFailure() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable failure) {
System.out.println("failure:" + failure);
}
}, system.dispatcher());
由上面可知,若需要与远端Actor通信,路径中必须提供ip:port。
2.3. 与Actor通信
2.3.1. tell方式
当使用tell方式时,表示仅仅使用异步方式给某个Actor发送消息,无需等待Actor的响应结果,并且也不会阻塞后续代码的运行,如:
helloActor.tell("hello helloActor", ActorRef.noSender());
其中:第一个参数为消息,它可以是任何可序列化的数据或对象,第二个参数表示发送者,通常来讲是另外一个 Actor 的引用, ActorRef.noSender()表示无发送者((实际上是一个 叫做deadLetters的Actor)。
2.3.2. ask方式
当我们需要从Actor获取响应结果时,可使用ask方法,ask方法会将返回结果包装在scala.concurrent.Future中,然后通过异步回调获取返回结果。 如调用方:
// 异步发送消息给Actor,并获取响应结果
Future<Object> fu = Patterns.ask(printerActor, "hello helloActor", timeout);
fu.onComplete(new OnComplete<Object>() {
@Override
public void onComplete(Throwable failure, String success) throws Throwable {
if (failure != null) {
System.out.println("failure is " + failure);
} else {
System.out.println("success is " + success);
}
}
}, system.dispatcher());
HelloActor处理消息方法的代码大致如下:
private void handleMessage(Object object) {
if (object instanceof String) {
String str = (String) object;
log.info("[HelloActor] message is {}, sender is {}", str, getSender().path().toString());
// 给发送者发送消息
getSender().tell(str, getSelf());
}
}
上面主要介绍了Akka中的ActorSystem、Actor,及与Actor的通信;Flink借此构建了其底层通信系统。
3. RPC类图结构
下图展示了Flink中RPC框架中涉及的主要类。
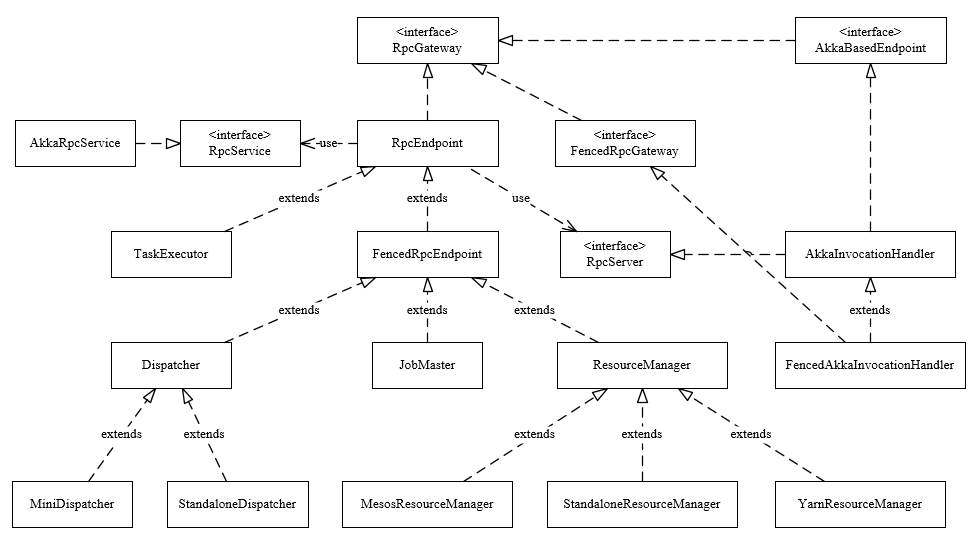
3.1. RpcGateway
Flink的RPC协议通过RpcGateway来定义;由前面可知,若想与远端Actor通信,则必须提供地址(ip和port),如在Flink-on-Yarn模式下,JobMaster会先启动ActorSystem,此时TaskExecutor的Container还未分配,后面与TaskExecutor通信时,必须让其提供对应地址,从类继承图可以看到基本上所有组件都实现了RpcGateway接口,其代码如下:
public interface RpcGateway {
/**
* Returns the fully qualified address under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable.
*
* @return Fully qualified (RPC) address under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable
*/
String getAddress();
/**
* Returns the fully qualified hostname under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable.
*
* @return Fully qualified hostname under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable
*/
String getHostname();
}
3.2. RpcEndpoint
每个RpcEndpoint对应了一个路径(endpointId和actorSystem共同确定),每个路径对应一个Actor,其实现了RpcGateway接口,其构造函数如下:
protected RpcEndpoint(final RpcService rpcService, final String endpointId) {
// 保存rpcService和endpointId
this.rpcService = checkNotNull(rpcService, "rpcService");
this.endpointId = checkNotNull(endpointId, "endpointId");
// 通过RpcService启动RpcServer
this.rpcServer = rpcService.startServer(this);
// 主线程执行器,所有调用在主线程中串行执行
this.mainThreadExecutor = new MainThreadExecutor(rpcServer, this::validateRunsInMainThread);
}
在RpcEndpoint中还定义了一些方法如runAsync(Runnable)、callAsync(Callable, Time)方法来执行Rpc调用,值得注意的是在Flink的设计中,对于同一个Endpoint,所有的调用都运行在主线程,因此不会有并发问题,当启动RpcEndpoint/进行Rpc调用时,其会委托RcpServer进行处理。
3.3. RpcService
Rpc服务的接口,其主要作用如下:
- 根据提供的RpcEndpoint来启动RpcServer(Actor);
- 根据提供的地址连接到RpcServer,并返回一个RpcGateway;
- 延迟/立刻调度Runnable、Callable;
- 停止RpcServer(Actor)或自身服务;
在Flink中其实现类为AkkaRpcService。
3.3.1. AkkaRpcService
AkkaRpcService中封装了ActorSystem,并保存了ActorRef到RpcEndpoint的映射关系,在构造RpcEndpoint时会启动指定rpcEndpoint上的RpcServer,其会根据Endpoint类型(FencedRpcEndpoint或其他)来创建不同的Actor(FencedAkkaRpcActor或AkkaRpcActor),并将RpcEndpoint和Actor对应的ActorRef保存起来,然后使用动态代理创建RpcServer,具体代码如下:
public <C extends RpcEndpoint & RpcGateway> RpcServer startServer(C rpcEndpoint) {
checkNotNull(rpcEndpoint, "rpc endpoint");
CompletableFuture<Void> terminationFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
final Props akkaRpcActorProps;
// 根据RpcEndpoint类型创建不同类型的Props
if (rpcEndpoint instanceof FencedRpcEndpoint) {
akkaRpcActorProps = Props.create(
FencedAkkaRpcActor.class,
rpcEndpoint,
terminationFuture,
getVersion(),
configuration.getMaximumFramesize());
} else {
akkaRpcActorProps = Props.create(
AkkaRpcActor.class,
rpcEndpoint,
terminationFuture,
getVersion(),
configuration.getMaximumFramesize());
}
ActorRef actorRef;
// 同步块,创建Actor,并获取对应的ActorRef
synchronized (lock) {
checkState(!stopped, "RpcService is stopped");
actorRef = actorSystem.actorOf(akkaRpcActorProps, rpcEndpoint.getEndpointId());
actors.put(actorRef, rpcEndpoint);
}
LOG.info("Starting RPC endpoint for {} at {} .", rpcEndpoint.getClass().getName(), actorRef.path());
// 获取Actor的路径
final String akkaAddress = AkkaUtils.getAkkaURL(actorSystem, actorRef);
final String hostname;
Option<String> host = actorRef.path().address().host();
if (host.isEmpty()) {
hostname = "localhost";
} else {
hostname = host.get();
}
// 解析该RpcEndpoint实现的所有RpcGateway接口
Set<Class<?>> implementedRpcGateways = new HashSet<>(RpcUtils.extractImplementedRpcGateways(rpcEndpoint.getClass()));
// 额外添加RpcServer和AkkaBasedEnpoint类
implementedRpcGateways.add(RpcServer.class);
implementedRpcGateways.add(AkkaBasedEndpoint.class);
final InvocationHandler akkaInvocationHandler;
// 根据不同类型动态创建代理对象
if (rpcEndpoint instanceof FencedRpcEndpoint) {
// a FencedRpcEndpoint needs a FencedAkkaInvocationHandler
akkaInvocationHandler = new FencedAkkaInvocationHandler<>(
akkaAddress,
hostname,
actorRef,
configuration.getTimeout(),
configuration.getMaximumFramesize(),
terminationFuture,
((FencedRpcEndpoint<?>) rpcEndpoint)::getFencingToken);
implementedRpcGateways.add(FencedMainThreadExecutable.class);
} else {
akkaInvocationHandler = new AkkaInvocationHandler(
akkaAddress,
hostname,
actorRef,
configuration.getTimeout(),
configuration.getMaximumFramesize(),
terminationFuture);
}
// Rather than using the System ClassLoader directly, we derive the ClassLoader
// from this class . That works better in cases where Flink runs embedded and all Flink
// code is loaded dynamically (for example from an OSGI bundle) through a custom ClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();
// 生成RpcServer对象,而后对该server的调用都会进入Handler的invoke方法处理,handler实现了多个接口的方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
RpcServer server = (RpcServer) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
classLoader,
implementedRpcGateways.toArray(new Class<?>[implementedRpcGateways.size()]),
akkaInvocationHandler);
return server;
}
当启动RpcServer后,即创建了相应的Actor(注意此时Actor的处于停止状态)和动态代理对象,需要调用RpcEndpoint#start启动启动Actor,此时启动RpcEndpoint流程如下(以非FencedRpcEndpoint为例):
调用RpcEndpoint#start;
委托给RpcServer#start;
调用动态代理的AkkaInvocationHandler#invoke;发现调用的是StartStoppable#start方法,则直接进行本地方法调用;invoke方法的代码如下:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); Object result;
// 先匹配指定类型(handler已实现接口的方法),若匹配成功则直接进行本地方法调用;若匹配为FencedRpcGateway类型,则抛出异常(应该在FencedAkkaInvocationHandler中处理);其他则进行Rpc调用
if (declaringClass.equals(AkkaBasedEndpoint.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(Object.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(RpcGateway.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(StartStoppable.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(MainThreadExecutable.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(RpcServer.class)) {
result = method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (declaringClass.equals(FencedRpcGateway.class)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("AkkaInvocationHandler does not support the call FencedRpcGateway#" +
method.getName() + ". This indicates that you retrieved a FencedRpcGateway without specifying a " +
"fencing token. Please use RpcService#connect(RpcService, F, Time) with F being the fencing token to " +
"retrieve a properly FencedRpcGateway.");
} else {
result = invokeRpc(method, args);
} return result;
}调用AkkaInvocationHandler#start;
通过ActorRef#tell给对应的Actor发送消息
rpcEndpoint.tell(ControlMessages.START, ActorRef.noSender());;调用AkkaRpcActor#handleControlMessage处理控制类型消息;
在主线程中将自身状态变更为Started状态;
经过上述步骤就完成了Actor的启动过程,Actor启动后便可与Acto通信让其执行代码(如runSync/callSync等)和处理Rpc请求了。下面分别介绍处理执行代码和处理Rpc请求;
3.3.1.1. 执行代码
与Actor通信,通过调用runSync/callSync等方法其直接执行代码。
下面以scheduleRunAsync方法为例分析请求Actor执行代码流程,方法代码如下:
public void scheduleRunAsync(Runnable runnable, long delayMillis) {
checkNotNull(runnable, "runnable");
checkArgument(delayMillis >= 0, "delay must be zero or greater");
// 判断是否为本地Actor
if (isLocal) {
long atTimeNanos = delayMillis == 0 ? 0 : System.nanoTime() + (delayMillis * 1_000_000);
// 向Actor发送消息runnable
tell(new RunAsync(runnable, atTimeNanos));
} else {
// 抛出异常,不支持远程发送Runnable消息
throw new RuntimeException("Trying to send a Runnable to a remote actor at " +
rpcEndpoint.path() + ". This is not supported.");
}
}
AkkaInvocationHandler#invoke -> AkkaInvocation#scheduleRunAsync;
AkkaRpcActor#handleMessage -> AkkaRpcActor#handleRpcMessage,其中handleRpcMessage方法如下:
protected void handleRpcMessage(Object message) {
// 根据消息类型不同进行不同的处理
if (message instanceof RunAsync) {
handleRunAsync((RunAsync) message);
} else if (message instanceof CallAsync) {
handleCallAsync((CallAsync) message);
} else if (message instanceof RpcInvocation) {
handleRpcInvocation((RpcInvocation) message);
} else {
log.warn(
"Received message of unknown type {} with value {}. Dropping this message!",
message.getClass().getName(),
message); sendErrorIfSender(new AkkaUnknownMessageException("Received unknown message " + message +
" of type " + message.getClass().getSimpleName() + '.'));
}
}AkkaRpcActor#handleRunAsync,其代码如下:
private void handleRunAsync(RunAsync runAsync) {
// 获取延迟调度时间
final long timeToRun = runAsync.getTimeNanos();
final long delayNanos; // 若为0或已经到了调度时间,则立刻进行调度
if (timeToRun == 0 || (delayNanos = timeToRun - System.nanoTime()) <= 0) {
// run immediately
try {
runAsync.getRunnable().run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("Caught exception while executing runnable in main thread.", t);
ExceptionUtils.rethrowIfFatalErrorOrOOM(t);
}
}
else {
// schedule for later. send a new message after the delay, which will then be immediately executed
// 计算出延迟时间
FiniteDuration delay = new FiniteDuration(delayNanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS); // 重新封装消息
RunAsync message = new RunAsync(runAsync.getRunnable(), timeToRun); final Object envelopedSelfMessage = envelopeSelfMessage(message); // 等待指定延迟时间后给自己再发送一个消息
getContext().system().scheduler().scheduleOnce(delay, getSelf(), envelopedSelfMessage,
getContext().dispatcher(), ActorRef.noSender());
}
}注意:当还未到调度时间时,该Actor会延迟一段时间后再次给自己发送消息;
3.3.1.2. 处理Rpc请求
当调用非AkkaInvocationHandler实现的方法时,则进行Rpc请求。
下面分析处理Rpc调用的流程。
AkkaInvocationHandler#invokeRpc,其方法如下:
private Object invokeRpc(Method method, Object[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取方法相应的信息
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
Time futureTimeout = extractRpcTimeout(parameterAnnotations, args, timeout); // 创建RpcInvocationMessage(可分为LocalRpcInvocation/RemoteRpcInvocation)
final RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = createRpcInvocationMessage(methodName, parameterTypes, args); Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); final Object result; // 无返回,则使用tell方法
if (Objects.equals(returnType, Void.TYPE)) {
tell(rpcInvocation); result = null;
} else {
// execute an asynchronous call
// 有返回,则使用ask方法
CompletableFuture<?> resultFuture = ask(rpcInvocation, futureTimeout); CompletableFuture<?> completableFuture = resultFuture.thenApply((Object o) -> {
// 调用返回后进行反序列化
if (o instanceof SerializedValue) {
try {
return ((SerializedValue<?>) o).deserializeValue(getClass().getClassLoader());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new CompletionException(
new RpcException("Could not deserialize the serialized payload of RPC method : "
+ methodName, e));
}
} else {
// 直接返回
return o;
}
}); // 若返回类型为CompletableFuture则直接赋值
if (Objects.equals(returnType, CompletableFuture.class)) {
result = completableFuture;
} else {
try {
// 从CompletableFuture获取
result = completableFuture.get(futureTimeout.getSize(), futureTimeout.getUnit());
} catch (ExecutionException ee) {
throw new RpcException("Failure while obtaining synchronous RPC result.", ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(ee));
}
}
} return result;
}AkkaRpcActor#handleRpcInvocation,其代码如下:
private void handleRpcInvocation(RpcInvocation rpcInvocation) {
Method rpcMethod = null; try {
// 获取方法的信息
String methodName = rpcInvocation.getMethodName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = rpcInvocation.getParameterTypes(); // 在RpcEndpoint中找指定方法
rpcMethod = lookupRpcMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error("Could not load method arguments.", e); // 异常处理
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not load method arguments.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Could not deserialize rpc invocation message.", e);
// 异常处理
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not deserialize rpc invocation message.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
} catch (final NoSuchMethodException e) {
log.error("Could not find rpc method for rpc invocation.", e);
// 异常处理
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not find rpc method for rpc invocation.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
} if (rpcMethod != null) {
try {
// this supports declaration of anonymous classes
rpcMethod.setAccessible(true); // 返回类型为空则直接进行invoke
if (rpcMethod.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE)) {
// No return value to send back
rpcMethod.invoke(rpcEndpoint, rpcInvocation.getArgs());
}
else {
final Object result;
try {
result = rpcMethod.invoke(rpcEndpoint, rpcInvocation.getArgs());
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
log.debug("Reporting back error thrown in remote procedure {}", rpcMethod, e); // tell the sender about the failure
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(e.getTargetException()), getSelf());
return;
} final String methodName = rpcMethod.getName(); // 方法返回类型为CompletableFuture
if (result instanceof CompletableFuture) {
final CompletableFuture<?> responseFuture = (CompletableFuture<?>) result;
// 发送结果(使用Patterns发送结果给调用者,并会进行序列化并验证结果大小)
sendAsyncResponse(responseFuture, methodName);
} else {
// 类型非CompletableFuture,发送结果(使用Patterns发送结果给调用者,并会进行序列化并验证结果大小)
sendSyncResponse(result, methodName);
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error while executing remote procedure call {}.", rpcMethod, e);
// tell the sender about the failure
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(e), getSelf());
}
}
}将结果返回给调用者AkkaInvocationHandler#ask;
经过上述步骤就完成Rpc(本地/远程)调用,可以看到底层也是通过Akka提供的tell/ask方法进行通信;
4. 总结
RPC框架是Flink任务运行的基础,Flink整个RPC框架基于Akka实现,并对Akka中的ActorSystem、Actor进行了封装和使用,文章主要分析了Flink底层RPC通信框架的实现和相关流程,Flink整个通信框架的组件主要由RpcEndpoint、RpcService、RpcServer、AkkaInvocationHandler、AkkaRpcActor等构成。RpcEndpoint定义了一个Actor的路径;RpcService提供了启动RpcServer、执行代码体等方法;RpcServer/AkkaInvocationHandler提供了与Actor通信的接口;AkkaRpcActor为Flink封装的Actor。
【Flink】Flink 底层RPC框架分析的更多相关文章
- RPC框架分析
RPC框架分析 常用的框架 .net(WCF) .net中分布式框架集大成者,提供多种通信方式,多种安全策略的调用(配置繁琐). java 1.RMI JDK原生(严格的说来算不上框架). 2.Du ...
- 浅谈RPC框架
RPC(Remote Promote Call) RPC(Remote Promote Call):一种进程间通信方式.允许像调用本地服务一样调用远程服务. RPC框架的主要目标就是让远程服务调用更简 ...
- Flink及主流流框架spark,storm比较
干货 | Flink及主流流框架比较 IT刊 百家号17-05-2220:16 引言 随着大数据时代的来临,大数据产品层出不穷.我们最近也对一款业内非常火的大数据产品 - Apache Flink做了 ...
- 如何利用Flink实现超大规模用户行为分析
如何利用Flink实现超大规模用户行为分析 各位晚上好,首先感谢大家参与我的这次主题分享,同时也感谢 InfoQ AI 前线组织这次瀚思科技主题月! 瀚思科技成立于 2014 年,按行业划分我们是 ...
- 大数据框架对比:Hadoop、Storm、Samza、Spark和Flink——flink支持SQL,待看
简介 大数据是收集.整理.处理大容量数据集,并从中获得见解所需的非传统战略和技术的总称.虽然处理数据所需的计算能力或存储容量早已超过一台计算机的上限,但这种计算类型的普遍性.规模,以及价值在最近几年才 ...
- 数据框架对比:Hadoop、Storm、Samza、Spark和Flink——flink支持SQL,待看
简介 大数据是收集.整理.处理大容量数据集,并从中获得见解所需的非传统战略和技术的总称.虽然处理数据所需的计算能力或存储容量早已超过一台计算机的上限,但这种计算类型的普遍性.规模,以及价值在最近几年才 ...
- Spark RPC框架源码分析(一)简述
Spark RPC系列: Spark RPC框架源码分析(一)运行时序 Spark RPC框架源码分析(二)运行时序 Spark RPC框架源码分析(三)运行时序 一. Spark rpc框架概述 S ...
- Spark RPC框架源码分析(二)RPC运行时序
前情提要: Spark RPC框架源码分析(一)简述 一. Spark RPC概述 上一篇我们已经说明了Spark RPC框架的一个简单例子,Spark RPC相关的两个编程模型,Actor模型和Re ...
- Spark RPC框架源码分析(三)Spark心跳机制分析
一.Spark心跳概述 前面两节中介绍了Spark RPC的基本知识,以及深入剖析了Spark RPC中一些源码的实现流程. 具体可以看这里: Spark RPC框架源码分析(二)运行时序 Spark ...
随机推荐
- Parallel file system processing
A treewalk for splitting a file directory is disclosed for parallel execution of work items over a f ...
- 关于ExpandableListView的一个小例子
喜欢显示好友QQ那样的列表,可以展开,可以收起,在android中,以往用的比较多的是listview,虽然可以实现列表的展示,但在某些情况下,我们还是希望用到可以分组并实现收缩的列表,那就要用到an ...
- freemarker写select包(四)
freemarker写select包 1.宏定义 <#macro select id datas value="" key="" text="& ...
- Poco logger 日志使用小析
Poco logger 日志使用小析 Poco logger 日志使用小析 日志 logger 库选择 Pocologger 架构简析 步骤一 生成消息 步骤二 写入logger 步骤三 导入chan ...
- poj1548Robots dfs实践
//搜索每一行 //该生产线的整点已被清除 //然后位置,然后转移到下一个步走的最后一点 //然后,所有点的下面一行清晰 //然后重复上面的操作 #include<iostream> #i ...
- DataTemplate
DataTemplate作用是布局+数据绑定 使用DataTemplate 同时完成样式布局和数据绑定 <Window.Resources> <DataTemplate x:Key= ...
- XF 按钮控件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ContentPage xmlns="http:/ ...
- 如何在wpf程序中使用DependencyProperty
作为例子,我决定定义一个MyBorderEx,在WPF常用的"Border"控件中创建一个名为Transparency的属性,来指示它的透明度,这个属性值在0-255间变化,255 ...
- Microsoft Enterprise Library 5.0 系列(四)
企业库日志应用程序模块工作原理图: 从上图我们可以看清楚企业库日志应用程序模块的工作原理,其中LogFilter,Trace Source,Trace Listener,Log Formatter的信 ...
- IE的BHO通过IHTMLDocument2接口获得网页源代码
参考了凤之焚的专栏:http://blog.csdn.net/lion_wing/article/details/769742 但是他的源码有些问题,即IHTMLElementCollection接口 ...
