《STL系列》之map原理及实现
上一篇文章《STL系列》之vector原理及实现,介绍了vector的原理及实现,这篇文章介绍map的原理及实现。STL实现源码下载。
STL中map的实现是基于RBTree的,我在实现的时候没有采用RBTree,觉得这东西有点复杂,我的map采用的是排序数组(CSortVector)。map中的Key存在排序数据中,通过二分查找判断某个Key是否在map中,时间复杂度为O(logN)。在用一个CVector存Key和Value,为了方便拿到Key和Value,这里有点冗余,Key被存了两次。
现在先介绍我的CSortVector,先贴出完整的代码,如下:
#ifndef _CSORTVECTOR_H_
#define _CSORTVECTOR_H_ namespace cth
{
template<typename T>
class csortvector:public NoCopy
{
public:
typedef const T* const_iterator;
typedef T* iterator;
csortvector()
{
initData();
} csortvector(int capa,const T& val=T())
{
initData(capa);
newCapacity(capacity_);
for (int i=;i<size_;i++)
buf[i]=val;
} ~csortvector()
{
if (buf)
{
delete[] buf;
buf=NULL;
}
size_=capacity_=;
} int add(const T& t )
{
int index=-;
if (size_==)
{
newCapacity(calculateCapacity());
buf[size_++]=t;
index=;
}else{
int start=;
int end=size_-;
while(start<=end)
{
index=(start+end)/;
if(buf[index]==t)
{
goto SORTVECTOR_INSERT;
}
else if(buf[index]>t)
{
end=index-;
}
else
{
start=index+;
}
} if(buf[index]<t)
{
index++;
}
SORTVECTOR_INSERT:
insert(index,t);
}
return index;
} void insert(int index,const T& t)
{
assert(index>= && index<=size_);
if (size_==capacity_)
{
newCapacity(calculateCapacity());
}
memmove(buf+index+,buf+index,(size_-index)*sizeof(T));
buf[index]=t;
size_++;
} int indexOf(const T& t)
{
int begin=;
int end=size_-;
int index=-;
while (begin<=end)
{
index=begin+(end-begin)/;
if (buf[index]==t)
{
return index;
}else if (buf[index]<t)
{
begin=index+;
}else{
end=index-;
}
}
return -;
} int remove(const T& t)
{
int index=indexOf(t);
if (index>=)
{
memmove(buf+index ,buf+index+,(size_-index)*sizeof(T));
buf[--size_]=T();
}
return index;
} void erase(const_iterator iter)
{
remove(*iter);
} const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(&buf[]);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(&buf[size_]);
} const T& operator[](int index) const
{
assert(size_> && index>= && index<size_);
return buf[index];
} void clear()
{
if (buf)
{
for (int i=;i<size_;i++)
{
buf[i]=T();
}
}
size_=capacity_=;
} bool empty() const
{
return size_==;
} int size() const
{
return size_;
} int capacity() const
{
return capacity_;
}
private:
void newCapacity(int capa)
{
assert (capa>size_) ;
capacity_=capa;
T* newBuf=new T[capacity_];
if (buf)
{
memcpy(newBuf,buf,size_*sizeof(T) );
delete [] buf;
}
buf=newBuf;
} inline void initData(int capa)
{
buf=NULL;
size_=capacity_=capa>?capa:;
} inline int calculateCapacity()
{
return capacity_*/+;
}
int size_;
int capacity_ ;
T* buf;
}; } #endif
CSortVector和CVector有点类似,只不过CSortVector中的数据在插入的时候需要排序,其他的接口比较相识。CSortVector的关键实现就是二分查找。新增和删除的时候都是通过二分查找,定位到指定的位置,在进行相关操作。这里有必要特意列出二分查找的实现,如下:
int indexOf(const T& t)
{
int begin=;
int end=size_-;
int index=-;
while (begin<=end)
{
index=begin+(end-begin)/;
if (buf[index]==t)
{
return index;
}else if (buf[index]<t)
{
begin=index+;
}else{
end=index-;
}
}
return -;
}
CSortVector测试代码如下:
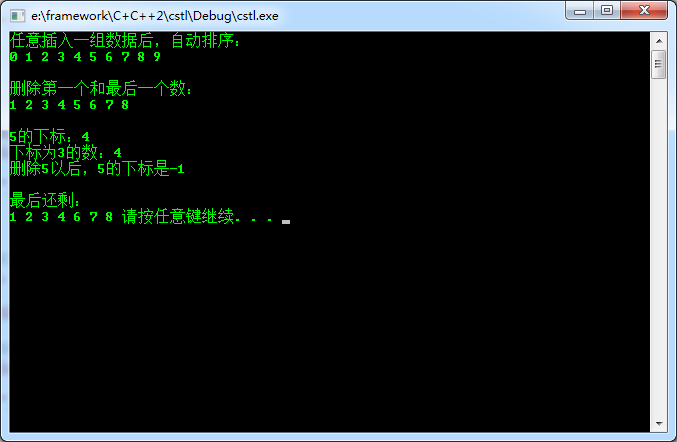
void csortvectorTest()
{
csortvector<int> l;
l.add();
l.add();
l.add();
l.add();
l.add();
l.add();
l.add();
l.add();
l.add();
l.add();
cout<<"任意插入一组数据后,自动排序:"<<endl;
for (int i=;i<l.size();i++)
{
cout<<l[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl<<endl; l.erase(l.begin());
l.erase(l.end()-);
cout<<"删除第一个和最后一个数:"<<endl;
for (int i=;i<l.size();i++)
{
cout<<l[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl<<endl; cout<<"5的下标:"<<l.indexOf()<<endl;
cout<<"下标为3的数:"<<l[]<<endl;
l.remove();
cout<<"删除5以后,5的下标是"<<l.indexOf()<<endl<<endl; cout<<"最后还剩:"<<endl;
for (int i=;i<l.size();i++)
{
cout<<l[i]<<" ";
}
}
运行结果如下:
注意:由于CSortVector中的元素要排序,所以其中的元素要实现运算符”<”。
介绍完CSortVector,接下来说说CMap。其实CSortVector已经解决CMap的大部分功能了,后者只需要在前者的基础之上简单的封装即可完事。CMap源码如下:
#ifndef _CMAP_H_
#define _CMAP_H_
#include "csortvector.h"
namespace cth
{
template<typename Key,typename Value>
struct pair
{
typedef Key first_type;
typedef Value second_type;
pair(){}
pair(const Key& key,const Value& val):first(key),second(val){}
pair(const pair& other):first(other.first),second(other.second){}
Key first;
Value second;
}; class NoCopy
{
public:
inline NoCopy(){}
NoCopy(const NoCopy&);
NoCopy& operator=(const NoCopy&);
}; template<typename Key,typename Value>
class cmap:public NoCopy
{
public:
typedef pair<Key,Value>* iterator;
typedef const pair<Key,Value>* const_iterator;
cmap(){}
int insert(const pair<Key,Value>& item)
{
iterator iter=find(item.first);
if (iter!=end())
{
return iter-begin();
}
int index=Keys.add(item.first);
if (index>=)
{
index=Values.insert(Values.begin() + index,item);
}
return index;
} int insert(const Key& key,const Value& val)
{
pair<Key,Value> item;
item.first=key;
item.second=val;
return insert(item);
} Value& operator[](const Key& key)
{
int index=Keys.indexOf(key);
if (index<)
{
index=insert(key,Value());
}
return Values[index].second;
} iterator begin()
{
return iterator(&*Values.begin());
} iterator end()
{
return iterator(&*Values.end());
} iterator find(const Key& key)
{
int index=Keys.indexOf(key);
if (index<)
{
return end();
}else
{
return iterator(&Values[index]);
}
} void erase(const Key& key)
{
int index=Keys.remove(key) ;
if (index>=)
{
cvector<pair<Key,Value>>::iterator iter=Values.begin()+index;
Values.erase(iter);
}
} void erase(const_iterator iter)
{
int index=Keys.remove(iter->first) ;
if (index>=)
{
cvector<pair<Key,Value>>::iterator iter=Values.begin()+index;
Values.erase(iter);
}
} int size()
{
return Keys.size();
} bool empty()
{
return Keys.size()==;
} void clear()
{
Keys.clear();
Values.clear();
} private:
csortvector<Key> Keys;
cvector<pair<Key,Value>> Values;
}; }
#endif
插入操作,CMap的插入操作分两种,一种是通过insert方法;另一种是通过操作符[]。
Insert方法是先找到Key在Keys中的位置,如果已经存在就返回,CMap不允许重复,如果不存在就通过二分查找找到对应的位置,插入Key,并在Values中对应的地方插入Value。
通过操作符[]插入:如m[1]=1;刚开始我也不知道这个是怎么实现的,后来突然明白,操作符[]返回的是一个引用,其实就是给我m[1]的返回值赋值,调用的也是返回值的operator=,CMap只用实现operator[]就行。
其他的方法都是一些简单的封装,这里就不在累赘,最后概述一下CMap的实现:
CMap是基于一个排序数组CSortVector实现的,将Key存入排序数据中,Value和Key通过Pair<Key,Value>存在CVector中,通过二分查找确定某个Key是否存在,不存在就将这个Key插入排序数据中,返回Key在数组中的索引,并将Pair<Key,Value>存在CVector中对应的位置。删除还是通过二分查找寻找,找到就将两个数组中对应的元素删除。
CMap测试代码运行如下:

《STL系列》之map原理及实现的更多相关文章
- STL 中的map 与 hash_map的理解
可以参考侯捷编著的<STL源码剖析> STL 中的map 与 hash_map的理解 1.STL的map底层是用红黑树存储的,查找时间复杂度是log(n)级别: 2.STL的hash_ma ...
- Java 集合系列 15 Map总结
java 集合系列目录: Java 集合系列 01 总体框架 Java 集合系列 02 Collection架构 Java 集合系列 03 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例 Java ...
- java基础解析系列(七)---ThreadLocal原理分析
java基础解析系列(七)---ThreadLocal原理分析 目录 java基础解析系列(一)---String.StringBuffer.StringBuilder java基础解析系列(二)-- ...
- STL中的map、unordered_map、hash_map
转自https://blog.csdn.net/liumou111/article/details/49252645 在之前使用STL时,经常混淆的几个数据结构,特别是做Leetcode的题目时,对于 ...
- STL中的map和unordered_map
STL中的map和unordered_map map 头文件:#include 原理:std::map的内部实现了一颗红黑树,有对其键值进行排序的功能,所以map是一个有序的容器,map中的每一个元素 ...
- [STL] STL各容器实现原理
STL共有六大组件1.容器 2.算法 3.迭代器 4.仿函数 6.适配器 STL容器的实现原理 STL来管理数据十分方便,省去了我们自己构建数据结构的时间.其实,STL的实现也是基于我们常见的数据结构 ...
- UVa 11991:Easy Problem from Rujia Liu?(STL练习,map+vector)
Easy Problem from Rujia Liu? Though Rujia Liu usually sets hard problems for contests (for example, ...
- Java 集合系列 08 Map架构
java 集合系列目录: Java 集合系列 01 总体框架 Java 集合系列 02 Collection架构 Java 集合系列 03 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例 Java ...
- java基础解析系列(六)---注解原理及使用
java基础解析系列(六)---注解原理及使用 java基础解析系列(一)---String.StringBuffer.StringBuilder java基础解析系列(二)---Integer缓存及 ...
随机推荐
- [转载]PHP 5.6 on CentOS/RHEL 7.0 and 6.6 via Yum
https://webtatic.com/packages/php56/ PHP 5.6.5 has been released on PHP.net on 22nd January 2014, an ...
- jsp-avaBean
package javaBean; public class pagecount { private long count=0; public long getcount() { return cou ...
- shell语法快速入门(1)
#得到绝对路径 DIR=$(cd `dirname $0`;pwd) $DIR/file.txt #去掉#注释 egrep -v "(#|^$)" /etc/zabbix/zabb ...
- wordnet的一些入门性介绍
关于wordnet的介绍很多,中英文都有,我这里主要是参考了别人的.自己组织了一下. 1.简介 1.1关于词典 Wordnet是一个由普林斯顿大学认识科学实验室在心理学教授乔治·A·米勒的指导下建立和 ...
- MySQL prepare 原理
Prepare的好处 Prepare SQL产生的原因.首先从mysql服务器执行sql的过程开始讲起,SQL执行过程包括以下阶段 词法分析->语法分析->语义分析->执行计划优化 ...
- Spring Mobile 1.1.0.RC1 和 1.0.2 发布
Spring Mobile 1.1.0.RC1 发布了,该版本包含: 支持 Firefox OS 设备的检测 修复了使用 LiteDeviceDelegatingViewResolver 处理重定向和 ...
- sqlhelper sqlparameter 实现增删改查
这是sqlHelper.cs类,类内里封装了方法 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Sy ...
- Javascript开发之工具归纳
写在前面 由于JS开发对我来说是全新的技术栈,开发过程中遇到了各种各样的框架.工具,同时也感叹一下相对于.Net的框架(工具框架以及测试框架等)JS框架真的是太丰富了.社区的力量果然强大---也是由此 ...
- 在Android中进行单元测试遇到的问题
问题1.Cannot connect to VM socket closed 在使用JUnit进行测试的时候,遇到这个问题.网上的解释是:使用Eclipse对Java代码进行调试,无论是远程JVM还 ...
- Html5 学习系列(五)Canvas绘图API快速入门(1)
引言:Canvas绘图API快速入门 在接触HTML5的初学者包括我都在很多地方见到非常炫的一些页面,甚至好多学习HTML5的开发者都是冲着Web端的页游去的,那么HTML5那么绚丽的页面效果以及游戏 ...
