【C】——幻方算法
一、幻方按照阶数可分成了三类,即奇数阶幻方、双偶阶幻方、单偶阶幻方。
二、奇数阶幻方(劳伯法)
奇数阶幻方最经典的填法是罗伯法。填写的方法是:
把1(或最小的数)放在第一行正中;按以下规律排列剩下的(n×n-1)个数:
(1)每一个数放在前一个数的右上一格;
(2)如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了顶行那么就把它放在底行,仍然要放在右一列;
(3)如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了最右列那么就把它放在最左列,仍然要放在上一行;
(4)如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了顶行且超出了最右列,那么就把它放在底行且最左列;
(5)如果这个数所要放的格已经有数填入,那么就把它放在前一个数的下一行同一列的格内。
例,用该填法获得的5阶幻方:
|
17 |
24 |
1 |
8 |
15 |
|
23 |
5 |
7 |
14 |
16 |
|
4 |
6 |
13 |
20 |
22 |
|
10 |
12 |
19 |
21 |
3 |
|
11 |
18 |
25 |
2 |
9 |
二、双偶数阶幻方(海尔法)
所谓双偶阶幻方就是当n可以被4整除时的偶阶幻方,即4K阶幻方。在说解法之前我们先说明一个“互补数”定义:就是在n阶幻方中,如果两个数的和等于幻方中最大的数与1的和(即n×n+1),我们称它们为一对互补数。如在三阶幻方中,每一对和为10的数,是一对互补数 ;在四阶幻方中,每一对和为17的数,是一对互补数。
双偶数阶幻方最经典的填法是海尔法。填写的方法是:
以8阶幻方为例:
(1)先把数字按顺序填。然后,按4×4把它分割成4块(如图)
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
|
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
|
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
|
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
|
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 |
48 |
|
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 |
55 |
56 |
|
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 |
61 |
62 |
63 |
64 |
(2)每个小方阵对角线上的数字(如左上角小方阵部分),换成和它互补的数。
|
64 |
2 |
3 |
61 |
60 |
6 |
7 |
57 |
|
9 |
55 |
54 |
12 |
13 |
51 |
50 |
16 |
|
17 |
47 |
46 |
20 |
21 |
43 |
42 |
24 |
|
40 |
26 |
27 |
37 |
36 |
30 |
31 |
33 |
|
32 |
34 |
35 |
29 |
28 |
38 |
39 |
25 |
|
41 |
23 |
22 |
44 |
45 |
19 |
18 |
48 |
|
49 |
15 |
14 |
52 |
53 |
11 |
10 |
56 |
|
8 |
58 |
59 |
5 |
4 |
62 |
63 |
1 |
三、单偶数阶幻方(斯特拉兹法)
所谓单偶阶幻方就是当n不可以被4整除时的偶阶幻方,即4K+2阶幻方。如(n=6,10,14……)的幻方。
单偶数阶幻方最经典的填法是斯特拉兹法。填写的方法是:
以10阶幻方为例。这时,k=2。
(1)把魔方阵分为A,B,C,D四个象限,这样每一个象限肯定是奇数阶。用罗伯法,依次在A象限,D象限,B象限,C象限按奇数阶幻方的填法填数。
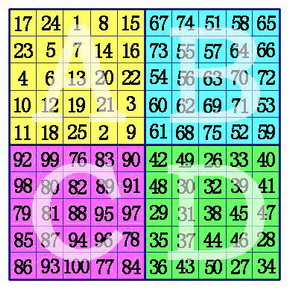
(2)在A象限的中间行、中间格开始,按自左向右的方向,标出k格。A象限的其它行则标出最左边的k格。将这些格,和C象限相对位置上的数互换位置。
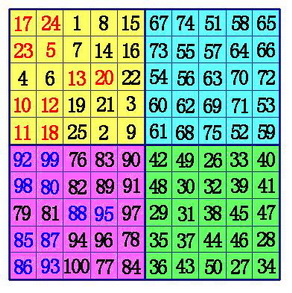
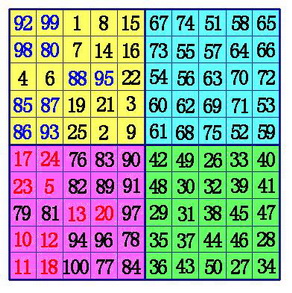
(3)在B象限所有行的中间格,自右向左,标出k-1格。(注:6阶幻方由于k-1=0,所以不用再作B、D象限的数据交换),将这些格,和D象限相对位置上的数互换位置。
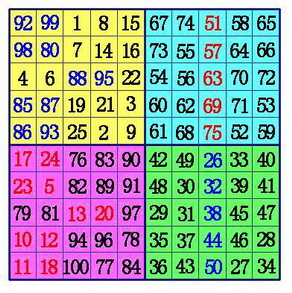
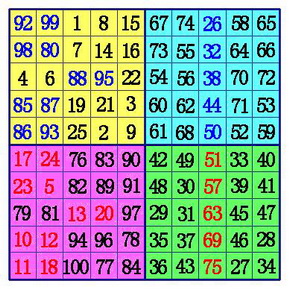
以上内容来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/panlijiao/archive/2012/05/11/2496757.html
实现代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #define COL 20
#define ROW 20 void deal_argv(int argc, char **argv, int *degree) {
if (argc != ) {
printf("cmd: ./a.out degree\n");
exit(-);
} else {
*degree = atoi(argv[]);
if (*degree <= || *degree > ) {
printf("the degree is between 3 and 20\n");
exit(-);
}
}
} void show_array(int (*array)[ROW], int degree) {
int row, col;
for (row = ; row < degree; row++){
for (col = ; col < degree; col++)
printf("%5d", array[row][col]);
printf("\n");
}
} void init_array(int (*array)[ROW], int size) {
memset(array, , size);
} void odd_num_magic_square(int degree, int (*array)[ROW], int x, int y, int num) {
int element = ;
int col = ;
int row = degree / ; for (element = num; element <= degree * degree + num - ; element++) {
array[col + x][row + y] = element;
if (array[(col - + degree) % degree + x][(row + ) % degree + y] != ) {
col = (col + + degree) % degree;
} else {
row = (row + ) % degree;
col = (col - + degree) % degree;
}
}
} void fill_array(int (*array)[ROW], int degree) {
int row, col;
int num = ; for (col = ; col < degree; col++)
for (row = ; row < degree; row++)
array[col][row] = num++;
} void double_magic_square(int degree, int (*array)[ROW]) {
int complement = ;
int deg = degree / ;
int row, col; fill_array(array, degree);
complement = degree * degree + ; for (col = ; col < deg; col++) {
for (row = ; row < deg; row++) {
array[col * ][row * ] = complement - array[col * ][row * ];
array[col * + ][row * + ] = complement - array[col * + ][row * + ];
array[col * + ][row * + ] = complement - array[col * + ][row * + ];
array[col * + ][row * + ] = complement - array[col * + ][row * + ]; array[col * + ][row * ] = complement - array[col * + ][row * ];
array[col * + ][row * + ] = complement - array[col * + ][row * + ];
array[col * + ][row * + ] = complement - array[col * + ][row * + ];
array[col * ][row * + ] = complement - array[col * ][row * + ];
}
}
} void change_value(int *value_a, int *value_b) {
int tmp;
tmp = *value_a;
*value_a = *value_b;
*value_b = tmp;
} void single_magic_square(int degree, int (*array)[ROW]) {
int deg = degree / ;
int k = ;
int row, col;
int tmp_row = ; odd_num_magic_square(deg, array, , , );
odd_num_magic_square(deg, array, deg, deg, deg * deg + );
odd_num_magic_square(deg, array, , deg, deg * deg * + );
odd_num_magic_square(deg, array, deg, , deg * deg * + ); k = (degree - ) / ;
for (row = ; row < k; row++) {
for (col = ; col < deg; col++) {
if (col == deg / ) {
change_value(&array[col][deg / + row], &array[col + deg][deg / + row]);
} else {
change_value(&array[col][row], &array[col + deg][row]);
}
}
} for (row = ; row < k - ; row++) {
for (col = ; col < deg; col++) {
tmp_row = row + deg + deg / + - k + ;
change_value(&array[col][tmp_row], &array[col + deg][tmp_row]);
}
} } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int array[COL][ROW];
int degree = ; deal_argv(argc, argv, °ree); init_array(array, sizeof(array));
if ((degree % ) != ) {
odd_num_magic_square(degree, array, , , );
show_array(array, degree);
} else if (degree % == ) {
double_magic_square(degree, array);
show_array(array, degree);
} else {
single_magic_square(degree, array);
show_array(array, degree);
} return ;
}
【C】——幻方算法的更多相关文章
- 任意N阶幻方算法实现
算法原理请参考:https://www.zhihu.com/question/23531676 先定义一些通用的函数,比如创建空幻方,删除幻方,打印幻方. 创建幻方 int **NewMagicS(i ...
- 任意阶魔方阵(幻方)的算法及C语言实现
写于2012.10: 本来这是谭浩强那本<C程序设计(第四版)>的一道课后习题,刚开始做得时候去网上找最优的算法,结果发现奇数和双偶数(4的倍数)的情况下算法都比较简单,但是单偶数(2的倍 ...
- 任意阶幻方(魔方矩阵)C语言实现
魔方又称幻方.纵横图.九宫图,最早记录于我国古代的洛书.据说夏禹治水时,河南洛阳附近的大河里浮出了一只乌龟,背上有一个很奇怪的图形,古人认为是一种祥瑞,预示着洪水将被夏禹王彻底制服.后人称之为&quo ...
- acm算法模板(1)
1. 几何 4 1.1 注意 4 1.2 几何公式 4 1.3 多边形 6 1.4 多边形切割 9 1.5 浮点函数 10 1.6 面积 15 1.7 球面 16 1.8 三角形 17 1.9 三维几 ...
- Java 实现奇数阶幻方的构造
一.设计的流程图如下所示 二.Java 语言的代码实现 package MagicSquare; //奇数幻方的实现 public class Magic_Odd { //n 为幻方的阶数 publi ...
- 魔方阵算法及C语言实现
1 魔方阵概念 填充的,每一行.每一列.对角线之和均相等的方阵,阶数n = 3,4,5….魔方阵也称为幻方阵. 例如三阶魔方阵为: 魔方阵有什么的规律呢? 魔方阵分为奇幻方和偶幻方.而偶幻方又分为是4 ...
- 【算法】C语言趣味程序设计编程百例精解
C语言趣味程序设计编程百例精解 C/C++语言经典.实用.趣味程序设计编程百例精解(1) https://wenku.baidu.com/view/b9f683c08bd63186bcebbc3c. ...
- ACM主要算法
ACM主要算法ACM主要算法介绍 初期篇 一.基本算法(1)枚举(poj1753, poj2965)(2)贪心(poj1328, poj2109, poj2586)(3)递归和分治法(4)递推(5)构 ...
- ACM常用算法
数据结构 栈,队列,链表 哈希表,哈希数组 堆,优先队列 双端队列 可并堆 左偏堆 二叉查找树 Treap 伸展树 并查集 集合计数问题 二分图的识别 平衡二叉树 二叉排序树 线段树 一维线段树 二维 ...
随机推荐
- EDMA3随笔
最近查DM814x上两个M3莫名其妙挂掉的问题查了将近两周,最后发现居然是各个模块的dma乱用引起的. A8上的音频mcasp用了两个dma通道…… TI给的simcop里面imx实现的swosd又用 ...
- SQL Server 利用锁提示优化Row_number()-程序员需知
网站中一些老页面仍采用Row_number类似的开窗函数进行分页处理,此时如果遭遇挖坟帖的情形可能就需要漫长的等待且消耗巨大.这里给大家介绍根据Row_number()特性采用特定锁Hint提升查询速 ...
- 配置ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS odoo 10.0开发环境
使用VMware Fusion 8.5.0创建ubuntu 64bit虚拟机:使用ubuntu-16.04.1-desktop-amd64.iso镜像缺省安装ubuntu,用户名odoo,密码1234 ...
- Dynamic CRM 2013学习笔记(十五)报表设计:报表入门、开发工具及注意事项
本文是关于CRM 2013报表开发入门介绍,包括开发工具的使用,以及不同于普通Reporting service的相关注意事项. 一.CRM报表简介 报表有两种,SQL-based报表和Fetch-b ...
- Dynamic CRM 2013学习笔记(三十二)自定义审批流3 - 节点及实体配置
上次介绍了<Dynamic CRM 2013学习笔记(十九)自定义审批流1 - 效果演示> 以及如何配置自定义审批流的按钮:<Dynamic CRM 2013学习笔记(二十一)自定义 ...
- 360浏览器下jquery.validate.unobtrusive的日期验证问题
今天在招聘频道(job.cnblogs.com)遭遇这样一个问题——在360浏览器下,在一个表单验证中,虽然输入了有效的日期,却总是提示日期格式错误,见下图: 而在Chrome/Safari/Fire ...
- ibatis + log4net 配置注意事项
一 在web.config或app.config中配置 <configuration> <configSections> <sectionGroup name=" ...
- [ACM_其他] Square Ice (poj1099 规律)
Description Square Ice is a two-dimensional arrangement of water molecules H2O, with oxygen at the v ...
- [游戏模版3] Win32 画笔 画刷 图形
>_<:introduce the functions of define\create\use pen and brush to draw all kinds of line and s ...
- 升级ruby版本那"不堪回首的经历"
前段时间在玩Chef-一个IT基础设施自动化工具.由于Chef是由Ruby写的一个gem,那么就需要安装Ruby.当然Ruby我早就安装了,并且使用rvm来管理Ruby及Gem.本来一切看似正常,但是 ...
