Python3 BP神经网络
转自麦子学院
"""
network.py
~~~~~~~~~~ A module to implement the stochastic gradient descent learning
algorithm for a feedforward neural network. Gradients are calculated
using backpropagation. Note that I have focused on making the code
simple, easily readable, and easily modifiable. It is not optimized,
and omits many desirable features.
""" #### Libraries
# Standard library
import random # Third-party libraries
import numpy as np class Network(object): def __init__(self, sizes):
"""The list ``sizes`` contains the number of neurons in the
respective layers of the network. For example, if the list
was [2, 3, 1] then it would be a three-layer network, with the
first layer containing 2 neurons, the second layer 3 neurons,
and the third layer 1 neuron. The biases and weights for the
network are initialized randomly, using a Gaussian
distribution with mean 0, and variance 1. Note that the first
layer is assumed to be an input layer, and by convention we
won't set any biases for those neurons, since biases are only
ever used in computing the outputs from later layers."""
self.num_layers = len(sizes)
self.sizes = sizes
self.biases = [np.random.randn(y, 1) for y in sizes[1:]]
self.weights = [np.random.randn(y, x)
for x, y in zip(sizes[:-1], sizes[1:])] def feedforward(self, a):
"""Return the output of the network if ``a`` is input."""
for b, w in zip(self.biases, self.weights):
a = sigmoid(np.dot(w, a)+b)
return a def SGD(self, training_data, epochs, mini_batch_size, eta,
test_data=None):
"""Train the neural network using mini-batch stochastic
gradient descent. The ``training_data`` is a list of tuples
``(x, y)`` representing the training inputs and the desired
outputs. The other non-optional parameters are
self-explanatory. If ``test_data`` is provided then the
network will be evaluated against the test data after each
epoch, and partial progress printed out. This is useful for
tracking progress, but slows things down substantially."""
if test_data: n_test = len(test_data)
n = len(training_data)
for j in range(epochs):
random.shuffle(training_data)
mini_batches = [
training_data[k:k+mini_batch_size]
for k in range(0, n, mini_batch_size)]
for mini_batch in mini_batches:
self.update_mini_batch(mini_batch, eta)
if test_data:
print ("Epoch {0}: {1} / {2}".format(
j, self.evaluate(test_data), n_test))
else:
print ("Epoch {0} complete".format(j)) def update_mini_batch(self, mini_batch, eta):
"""Update the network's weights and biases by applying
gradient descent using backpropagation to a single mini batch.
The ``mini_batch`` is a list of tuples ``(x, y)``, and ``eta``
is the learning rate."""
nabla_b = [np.zeros(b.shape) for b in self.biases]
nabla_w = [np.zeros(w.shape) for w in self.weights]
#一个一个的进行训练 跟吴恩达的Mini-Batch 不一样
for x, y in mini_batch:
delta_nabla_b, delta_nabla_w = self.backprop(x, y)
nabla_b = [nb+dnb for nb, dnb in zip(nabla_b, delta_nabla_b)]
nabla_w = [nw+dnw for nw, dnw in zip(nabla_w, delta_nabla_w)]
self.weights = [w-(eta/len(mini_batch))*nw
for w, nw in zip(self.weights, nabla_w)]
self.biases = [b-(eta/len(mini_batch))*nb
for b, nb in zip(self.biases, nabla_b)] def backprop(self, x, y):
"""Return a tuple ``(nabla_b, nabla_w)`` representing the
gradient for the cost function C_x. ``nabla_b`` and
``nabla_w`` are layer-by-layer lists of numpy arrays, similar
to ``self.biases`` and ``self.weights``."""
nabla_b = [np.zeros(b.shape) for b in self.biases]
nabla_w = [np.zeros(w.shape) for w in self.weights]
# feedforward
activation = x
activations = [x] # list to store all the activations, layer by layer
zs = [] # list to store all the z vectors, layer by layer
for b, w in zip(self.biases, self.weights):
z = np.dot(w, activation)+b
zs.append(z)
activation = sigmoid(z)
activations.append(activation)
# backward pass
delta = self.cost_derivative(activations[-1], y) * \
sigmoid_prime(zs[-1])
nabla_b[-1] = delta
nabla_w[-1] = np.dot(delta, activations[-2].transpose())
# Note that the variable l in the loop below is used a little
# differently to the notation in Chapter 2 of the book. Here,
# l = 1 means the last layer of neurons, l = 2 is the
# second-last layer, and so on. It's a renumbering of the
# scheme in the book, used here to take advantage of the fact
# that Python can use negative indices in lists.
for l in range(2, self.num_layers):
z = zs[-l]
sp = sigmoid_prime(z)
delta = np.dot(self.weights[-l+1].transpose(), delta) * sp
nabla_b[-l] = delta
nabla_w[-l] = np.dot(delta, activations[-l-1].transpose())
return (nabla_b, nabla_w) def evaluate(self, test_data):
"""Return the number of test inputs for which the neural
network outputs the correct result. Note that the neural
network's output is assumed to be the index of whichever
neuron in the final layer has the highest activation."""
test_results = [(np.argmax(self.feedforward(x)), y)
for (x, y) in test_data]
return sum(int(x == y) for (x, y) in test_results) def cost_derivative(self, output_activations, y):
"""Return the vector of partial derivatives \partial C_x /
\partial a for the output activations."""
return (output_activations-y) #### Miscellaneous functions
def sigmoid(z):
"""The sigmoid function."""
return 1.0/(1.0+np.exp(-z)) def sigmoid_prime(z):
"""Derivative of the sigmoid function."""
return sigmoid(z)*(1-sigmoid(z))
该算法比我之前写的神经网络算法准确率高,但是在测试过程中发现有错误,各个地方的注释我是没看明白,与理论结合不是很好。本人在他的基础上进行了改进,提高了算法的扩展程度,自己也亲测了改进后的代码,效果杠杠的。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Jan 18 15:27:24 2018 @author: markli
""" import numpy as np;
import random; def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x); def tanh_derivative(x):
return 1.0 - np.tanh(x)*np.tanh(x); def logistic(x):
return 1/(1 + np.exp(-x)); def logistic_derivative(x):
return logistic(x)*(1-logistic(x)); def ReLU(x,a=1):
return max(0,a * x); def ReLU_derivative(x,a=1):
return 0 if x < 0 else a; class NeuralNetwork:
'''
Z = W * x + b
A = sigmod(Z)
Z 净输入
x 样本集合 n * m n 个特征 m 个样本数量
b 偏移量
W 权重
A 净输出
'''
def __init__(self,layers,active_function=[logistic],active_function_der=[logistic_derivative],learn_rate=0.9):
"""
初始化神经网络
layer中存放每层的神经元数量,layer的长度即为网络的层数
active_function 为每一层指定一个激活函数,若长度为1则表示所有层使用同一个激活函数
active_function_der 激活函数的导数
learn_rate 学习速率
"""
self.weights = [np.random.randn(x,y) for x,y in zip(layers[1:],layers[:-1])];
self.biases = [np.random.randn(x,1) for x in layers[1:]];
self.size = len(layers);
self.rate = learn_rate;
self.sigmoids = [];
self.sigmoids_der = [];
for i in range(len(layers)-1):
if(len(active_function) == self.size-1):
self.sigmoids = active_function;
else:
self.sigmoids.append(active_function[0]);
if(len(active_function_der)== self.size-1):
self.sigmoids_der = active_function_der;
else:
self.sigmoids_der.append(active_function_der[0]); def fit(self,TrainData,epochs=1000,mini_batch_size=32):
"""
运用后向传播算法学习神经网络模型
TrainData 是(X,Y)值对
X 输入特征矩阵 m*n 维 n 个特征,m个样本
Y 输入实际值 t*m 维 t个类别标签,m个样本
epochs 迭代次数
mini_batch_size mini_batch 一次的大小,不使用则mini_batch_size = 1
"""
n = len(TrainData);
for i in range(epochs):
random.shuffle(TrainData)
mini_batches = [
TrainData[k:k+mini_batch_size]
for k in range(0, n, mini_batch_size)];
for mini_batch in mini_batches:
self.BP(mini_batch, self.rate); def predict(self, x):
"""前向传播"""
i = 0;
for b, w in zip(self.biases, self.weights):
x = self.sigmoids[i](np.dot(w, x)+b);
i = i + 1;
return x def BP(self,mini_batch,rate):
"""
BP 神经网络算法
"""
size = len(mini_batch); nabla_b = [np.zeros(b.shape) for b in self.biases]; #存放每次训练b的变化量
nabla_w = [np.zeros(w.shape) for w in self.weights]; #存放每次训练w的变化量
#一个一个的进行训练
for x, y in mini_batch:
delta_nabla_b, delta_nabla_w = self.backprop(x, y);
nabla_b = [nb+dnb for nb, dnb in zip(nabla_b, delta_nabla_b)]; #累加每次训练b的变化量
nabla_w = [nw+dnw for nw, dnw in zip(nabla_w, delta_nabla_w)]; #累加每次训练w的变化量
self.weights = [w-(rate/size)*nw
for w, nw in zip(self.weights, nabla_w)];
self.biases = [b-(rate/size)*nb
for b, nb in zip(self.biases, nabla_b)]; def backprop(self, x, y):
"""
x 是一维 的行向量
y 是一维行向量
"""
nabla_b = [np.zeros(b.shape) for b in self.biases];
nabla_w = [np.zeros(w.shape) for w in self.weights];
# feedforward
activation = np.atleast_2d(x).reshape((len(x),1)); #转换为列向量
activations = [activation]; # 存放每层a
zs = []; # 存放每z值
i = 0;
for b, w in zip(self.biases, self.weights):
z = np.dot(w, activation)+b;
zs.append(z);
activation = self.sigmoids[i](z);
activations.append(activation);
i = i + 1;
# backward pass
y = np.atleast_2d(y).reshape((len(y),1)); #将y转化为列向量
#delta cost对z的偏导数
delta = self.cost_der(activations[-1], y) * \
self.sigmoids_der[-1](zs[-1]);
nabla_b[-1] = delta;
nabla_w[-1] = np.dot(delta, np.transpose(activations[-2]));
#从后往前遍历每一层,从倒数第2层开始
for l in range(2, self.size):
z = zs[-l]; #当前层的z
sp = self.sigmoids_der[-l](z); #对z的偏导数值
delta = np.multiply(np.dot(np.transpose(self.weights[-l+1]), delta), sp); #求出当前层的误差
nabla_b[-l] = delta;
nabla_w[-l] = np.dot(delta, np.transpose(activations[-l-1]));
return (nabla_b, nabla_w) """
损失函数
cost_der 差的平方损失函数对a 的导数
cost_cross_entropy_der 交叉熵损失函数对a的导数
"""
def cost_der(self,a,y):
return a - y; def cost_cross_entropy_der(self,a,y):
return (a-y)/(a * (1-a));
以上是BP神经网络算法源码,下面给出一个数字识别程序,用来测试上述代码的正确性。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from network_mark import NeuralNetwork
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split digits = load_digits();
X = digits.data;
y = digits.target;
X -= X.min(); # normalize the values to bring them into the range 0-1
X /= X.max(); nn = NeuralNetwork([64,100,10]);
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y);
labels_train = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_train);
labels_test = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_test); # X_train.shape (1347,64)
#y_train.shape(1347)
#labels_train.shape (1347,10)
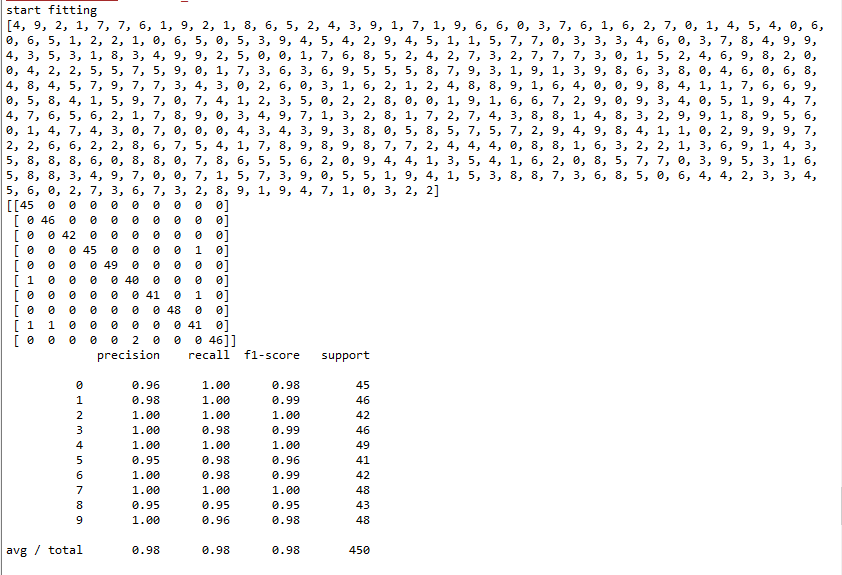
#labels_test.shape(450,10) print ("start fitting");
Data = [(x,y) for x,y in zip(X_train,labels_train)];
#print(Data);
nn.fit(Data,epochs=500,mini_batch_size=32);
result = nn.predict(X_test.T);
predictions = [np.argmax(result[:,y]) for y in range(result.shape[1])]; print(predictions);
#for i in range(result.shape[1]):
# y = result[:,i];
# predictions.append(np.argmax(y));
##print(np.atleast_2d(predictions).shape);
print (confusion_matrix(y_test,predictions));
print (classification_report(y_test,predictions));
最后是测试结果,效果很客观。
Python3 BP神经网络的更多相关文章
- Python实现bp神经网络识别MNIST数据集
title: "Python实现bp神经网络识别MNIST数据集" date: 2018-06-18T14:01:49+08:00 tags: [""] cat ...
- python手写bp神经网络实现人脸性别识别1.0
写在前面:本实验用到的图片均来自google图片,侵删! 实验介绍 用python手写一个简单bp神经网络,实现人脸的性别识别.由于本人的机器配置比较差,所以无法使用网上很红的人脸大数据数据集(如lf ...
- BP神经网络反向传播之计算过程分解(详细版)
摘要:本文先从梯度下降法的理论推导开始,说明梯度下降法为什么能够求得函数的局部极小值.通过两个小例子,说明梯度下降法求解极限值实现过程.在通过分解BP神经网络,详细说明梯度下降法在神经网络的运算过程, ...
- BP神经网络原理及python实现
[废话外传]:终于要讲神经网络了,这个让我踏进机器学习大门,让我读研,改变我人生命运的四个字!话说那么一天,我在乱点百度,看到了这样的内容: 看到这么高大上,这么牛逼的定义,怎么能不让我这个技术宅男心 ...
- BP神经网络
秋招刚结束,这俩月没事就学习下斯坦福大学公开课,想学习一下深度学习(这年头不会DL,都不敢说自己懂机器学习),目前学到了神经网络部分,学习起来有点吃力,把之前学的BP(back-progagation ...
- 数据挖掘系列(9)——BP神经网络算法与实践
神经网络曾经很火,有过一段低迷期,现在因为深度学习的原因继续火起来了.神经网络有很多种:前向传输网络.反向传输网络.递归神经网络.卷积神经网络等.本文介绍基本的反向传输神经网络(Backpropaga ...
- BP神经网络推导过程详解
BP算法是一种最有效的多层神经网络学习方法,其主要特点是信号前向传递,而误差后向传播,通过不断调节网络权重值,使得网络的最终输出与期望输出尽可能接近,以达到训练的目的. 一.多层神经网络结构及其描述 ...
- 极简反传(BP)神经网络
一.两层神经网络(感知机) import numpy as np '''极简两层反传(BP)神经网络''' # 样本 X = np.array([[0,0,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1],[1, ...
- BP神经网络
BP神经网络基本原理 BP神经网络是一种单向传播的多层前向网络,具有三层或多层以上的神经网络结构,其中包含输入层.隐含层和输出层的三层网络应用最为普遍. 网络中的上下层之间实现全连接,而每层神经元之 ...
随机推荐
- docker maven 出错:Failed to execute goal com.spotify:docker-maven-plugin:...: Request error: POST https://192.168.99.100:2376/build?t=
Spring Boot项目构建docker镜像,出错Failed to execute goal com.spotify:docker-maven-plugin:0.4.13:build (defau ...
- NO.6: 若不想编译器提供自动生成的函数,就应该明确拒绝
1.为驳回编译器自动生成函数的技能,可把这些函数的声明放入private,如果是继承类型可把base class的这些函数声明private,可在编译期间得到警告
- Python3:if __name__ == '__main__' 详解
一般在风格比较好的代码中会有一行if __name__ == '__main__' :代码,这里说明一下这句代码的用处,先上两个代码test1.py和test2.py: # test1.py prin ...
- HTML5 文件API
filelist 表示文件对象的列表. <form name="upload"> <input type="file" name=" ...
- python实现windows Service服务程序
python实现windows Service服务程序 win32serviceutil.ServiceFramework是封装得很好的Windows服务框架,本文通过继承它来实现. 通过SvcDoR ...
- POJ - 2240 Arbitrage(Bellman-Ford)
https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-2240 题意 已知n种货币,以及m种货币汇率及方式,问能否通过货币转换,使得财富增加. 分析 Bellman-Ford判断正环,注意初始 ...
- Codeforces 666 B. World Tour
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/666/B 题意: 给定一张边权均为1的有向图,求四个不同的点A,B,C,D,使得dis[A][B]+dis[B][C ...
- 《高性能MySQL》——第五章创建高性能索引
1.创建索引基本语法格 在MySQL中,在已经存在的表上,可以通过ALTER TABLE语句直接为表上的一个或几个字段创建索引.基本语法格式如下: ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD [UNIQUE ...
- 一组数字,从1到n,从中减少了3个数,顺序打乱,放在n-3的数组里,找出丢失数字
曾经看到有这样一个JS题:有一组数字,从1到n,从中减少了3个数,顺序也被打乱,放在一个n-3的数组里请找出丢失的数字,最好能有程序,最好算法比较快假设n=10000 下面我也来贴一个算法. func ...
- google浏览器测试时清理缓存、强制不用缓存刷新快捷键(常用、效率)
Ctrl+Shift+Del 清除Google浏览器缓存的快捷键 Ctrl+Shift+R 重新加载当前网页而不使用缓存内容
